 Tìm kiếm
Tìm kiếm
PHỤ LỤC II Nghị định số 136/2020/NĐ-CP: DANH MỤC CƠ SỞ CÓ NGUY HIỂM VỀ CHÁY, NỔ
| Số hiệu: | 136/2020/NĐ-CP | Loại văn bản: | Nghị định |
| Nơi ban hành: | Chính phủ | Người ký: | Nguyễn Xuân Phúc |
| Ngày ban hành: | 24/11/2020 | Ngày hiệu lực: | 10/01/2021 |
| Ngày công báo: | 07/12/2020 | Số công báo: | Từ số 1125 đến số 1126 |
| Lĩnh vực: | Tài nguyên - Môi trường | Tình trạng: | Còn hiệu lực |
TÓM TẮT VĂN BẢN
Bỏ một số điều kiện an toàn về PCCC đối với khu dân cư
Ngày 24/11/2020, Chính phủ ban hành Nghị định 136/2020/NĐ-CP hướng dẫn Luật Phòng cháy và chữa cháy, Luật Phòng cháy và chữa cháy sửa đổi.
Theo đó, khu dân cư phải bảo đảm các điều kiện an toàn về phòng cháy, chữa cháy (PCCC) sau đây:
- Có phương án chữa cháy được cấp có thẩm quyền phê duyệt.
- Có lực lượng dân phòng được huấn luyện nghiệp vụ PCCC và tổ chức sẵn sàng chữa cháy đáp ứng yêu cầu chữa cháy tại chỗ.
- Có nội quy về PCCC, về sử dụng điện, sử dụng lửa và các chất dễ cháy, nổ phù hợp với quy chuẩn, tiêu chuẩn kỹ thuật về PCCC hoặc theo quy định của Bộ Công an.
- Có hệ thống giao thông, nguồn nước phục vụ chữa cháy, giải pháp chống cháy lan, phương tiện PCCC bảo đảm số lượng và chất lượng phù hợp với quy chuẩn, tiêu chuẩn kỹ thuật về PCCC hoặc theo quy định của Bộ Công an.
Điều kiện an toàn về PCCC quy định như trên phải được Chủ tịch UBND cấp xã tổ chức thực hiện và duy trì trong suốt quá trình hoạt động.
Như vậy, so với quy định hiện hành tại Điều 8 Nghị định 79/2014/NĐ-CP thì không còn quy định một số nội dung như:
- Hệ thống điện phải bảo đảm tiêu chuẩn an toàn về PCCC.
- Có thiết kế và phải được thẩm duyệt thiết kế về PCCC đối với khu dân cư xây dựng mới.
Nghị định 136/2020/NĐ-CP có hiệu lực từ ngày 10/01/2021 và thay thế Nghị định 79/2014/NĐ-CP ngày 31/7/2014.
Văn bản tiếng việt
Văn bản tiếng anh
PHỤ LỤC II
DANH MỤC CƠ SỞ CÓ NGUY HIỂM VỀ CHÁY, NỔ
(Kèm theo Nghị định số: 136/2020/NĐ-CP ngày 24 tháng 11 năm 2020 của Chính phủ)
1. Trụ sở cơ quan nhà nước các cấp cao từ 10 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích của các khối nhà làm việc từ 25.000 m3 trở lên.
2. Nhà chung cư, nhà tập thể, nhà ở ký túc xá cao từ 7 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích từ 10.000 m3 trở lên; nhà hỗn hợp cao từ 5 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
3. Nhà trẻ, trường mẫu giáo, mầm non có từ 350 cháu trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích các khối nhà học tập, phục vụ học tập từ 5.000 m3 trở lên; trường tiểu học, trung học cơ sở, trung học phổ thông, trường phổ thông có nhiều cấp học có tổng khối tích các khối nhà học tập, phục vụ học tập từ 5.000 m3 trở lên; trường cao đẳng, đại học, học viện, trường trung cấp chuyên nghiệp, trường dạy nghề, cơ sở giáo dục thường xuyên cao từ 7 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích các khối nhà học tập, phục vụ học tập từ 10.000 m3 trở lên; cơ sở giáo dục khác được thành lập theo Luật Giáo dục có tổng khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
4. Bệnh viện có từ 250 giường bệnh trở lên; phòng khám đa khoa, khám chuyên khoa, nhà điều dưỡng, phục hồi chức năng, chỉnh hình, nhà dưỡng lão, cơ sở phòng chống dịch bệnh, trung tâm y tế, cơ sở y tế khác được thành lập theo Luật Khám bệnh, chữa bệnh cao từ 5 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
5. Nhà hát, rạp chiếu phim, rạp xiếc có từ 600 chỗ ngồi trở lên; trung tâm hội nghị, tổ chức sự kiện cao từ 5 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích của các nhà tổ chức hội nghị, sự kiện từ 10.000 m3 trở lên; nhà văn hóa, cơ sở kinh doanh dịch vụ karaoke, vũ trường, quán bar, câu lạc bộ, thẩm mỹ viện, kinh doanh dịch vụ xoa bóp, công viên giải trí, vườn thú, thủy cung có khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
6. Chợ hạng 1, chợ hạng 2; trung tâm thương mại, điện máy, siêu thị, cửa hàng bách hóa, cửa hàng tiện ích, nhà hàng, cửa hàng ăn uống có tổng diện tích kinh doanh từ 500 m2 trở lên hoặc có khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
7. Khách sạn, nhà khách, nhà nghỉ, nhà trọ, cơ sở lưu trú khác được thành lập theo Luật Du lịch cao từ 7 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích của các khối nhà phục vụ lưu trú từ 10.000 m3 trở lên.
8. Nhà làm việc của doanh nghiệp, tổ chức chính trị, xã hội cao từ 7 tầng trở lên hoặc có tổng khối tích của các khối nhà làm việc từ 10.000 m3 trở lên.
9. Bảo tàng, thư viện, triển lãm, nhà trưng bày, nhà lưu trữ, nhà sách, nhà hội chợ có khối tích từ 10.000 m3 trở lên.
10. Bưu điện, cơ sở truyền thanh, truyền hình, viễn thông cao từ 5 tầng trở lên hoặc có khối tích của khối nhà chính từ 10.000 m3 trở lên; nhà lắp đặt thiết bị thông tin, trung tâm lưu trữ, quản lý dữ liệu có khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
11. Sân vận động có sức chứa từ 40.000 chỗ ngồi trở lên; nhà thi đấu thể thao; cung thể thao trong nhà có sức chứa từ 500 chỗ ngồi trở lên; trung tâm thể dục thể thao, trường đua, trường bắn có tổng khối tích của các nhà thể thao từ 10.000 m3 trở lên hoặc có sức chứa từ 5.000 chỗ trở lên; cơ sở thể thao khác được thành lập theo Luật Thể dục, thể thao có khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
12. Cảng hàng không; đài kiểm soát không lưu; bến cảng biển; cảng cạn; cảng thủy nội địa loại I, loại II; bến xe khách loại 1, loại 2; trạm dừng nghỉ loại 1; nhà ga đường sắt, nhà chờ cáp treo vận chuyển người có khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên; công trình tàu điện ngầm; cơ sở đăng kiểm phương tiện giao thông cơ giới; cửa hàng kinh doanh, sửa chữa, bảo dưỡng ô tô, mô tô, xe gắn máy có diện tích kinh doanh từ 500 m2 trở lên hoặc có khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên.
13. Gara để xe có sức chứa từ 10 xe ô tô trở lên.
14. Cơ sở hạt nhân; cơ sở sản xuất, kinh doanh, bảo quản, sử dụng vật liệu nổ công nghiệp và tiền chất thuốc nổ; kho vật liệu nổ công nghiệp, tiền chất thuốc nổ; cảng xuất, nhập vật liệu nổ công nghiệp, tiền chất thuốc nổ; kho vũ khí, công cụ hỗ trợ.
15. Cơ sở khai thác, chế biến, sản xuất, vận chuyển, kinh doanh, bảo quản dầu mỏ và sản phẩm dầu mỏ, khí đốt trên đất liền; kho dầu mỏ và sản phẩm dầu mỏ, kho khí đốt; cảng xuất, nhập dầu mỏ và sản phẩm dầu mỏ, khí đốt; cửa hàng kinh doanh xăng dầu; cửa hàng kinh doanh chất lỏng dễ cháy, cửa hàng kinh doanh khí đốt có tổng lượng khí tồn chứa từ 200 kg trở lên.
16. Cơ sở công nghiệp có hạng nguy hiểm cháy, nổ A, B có tổng khối tích của các khối nhà có dây chuyền công nghệ sản xuất chính từ 5.000 m3 trở lên; hạng nguy hiểm cháy, nổ C có tổng khối tích của các khối nhà có dây chuyền công nghệ sản xuất chính từ 10.000 m3 trở lên; hạng nguy hiểm cháy, nổ D, E có tổng khối tích của các khối nhà có dây chuyền công nghệ sản xuất chính từ 15.000 m3 trở lên.
17. Nhà máy điện; trạm biến áp có điện áp từ 110 kV trở lên.
18. Hầm có hoạt động sản xuất, bảo quản, sử dụng chất cháy, nổ có tổng khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên; kho hàng hóa, vật tư cháy được hoặc hàng hóa vật tư không cháy đựng trong các bao bì cháy được có tổng khối tích từ 5.000 m3 trở lên./.
|
THE GOVERNMENT |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No. 136/2020/ND-CP |
Hanoi, November 24, 2020 |
PROVIDING GUIDELINES FOR A NUMBER OF ARTICLES OF LAW ON FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHTING AND LAW ON AMENDMENTS TO LAW ON FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHITNG
Pursuant to the Law on Government Organization dated June 19, 2015 and Law on Amendments to Law on Government Organization and Law on Local Government Organization dated November 22, 2019;
Pursuant to the Law on People’s Public Security Force dated November 20, 2018;
Pursuant to the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting dated June 29, 2001 and Law on Amendments to Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting dated November 22, 2013;
At the request of the Minister of Public Security;
The Government hereby promulgates a Decree providing guidelines for a number of Articles of Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting and Law on Amendments to Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting.
This Decree provides for fire prevention and fighting, organization of fire prevention and fighting forces and equipment, fire prevention and fighting service business, funding for fire prevention and fighting, responsibilities of ministries, ministerial-level agencies, Governmental agencies and People’s Committees at all levels for fire prevention and fighting.
This Decree is applicable to regulatory bodies, organizations, households and individuals operating and/or living in the territory of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Promulgated together with this Decree are the following appendixes:
1. Appendix I: List of facilities requiring fire management
2. Appendix II: List of facilities at risk of fire or explosion
3. Appendix III: List of facilities under police management
4. Appendix IV: List of facilities under management of commune-level People’s Committees
5. Appendix V: List of projects, works and motor vehicles requiring appraisal of fire safety design
6. Appendix VI: List of fire prevention and firefighting equipment
7. Appendix VII: List of fire prevention and firefighting equipment requiring inspection
8. Appendix VIII: Specifications of signal flags, signage, armband and tape used in firefighting operations
9. Appendix IX: Forms used in firefighting operations
Article 4. Facilities requiring fire management
1. The facilities the definition of which is provided for in Clause 3 Article 3 of the 2001 Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting, which is amended according to Clause 1 Article 1 of the 2013 Law on Amendments to Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting (hereinafter collectively referred to as “Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting”), are subject to fire management.
A regulatory body or an organization may have one or more than one facility; multiple regulatory bodies and/or organizations may be located on the premises of one facility.
2. List of facilities requiring fire management is provided for in Appendix I enclosed therewith.
Article 5. Fire safety requirements applicable to facilities
1. Any facility mentioned in the list in Appendix III enclosed therewith must satisfy the following fire safety requirements:
a) Regulations, prohibition signs, signage, plans or instruction signs concerning fire prevention, fighting and escape are provided in accordance with fire prevention and fighting regulations and standards or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
b) There are internal and specialized firefighting forces suitable for the facility’s characteristics and having received training in fire prevention and fighting operation, and on-site combat-ready firefighters according to regulations, excluding the case provided for in Point g Clause 2 Article 31 herein;
c) There is a firefighting plan approved by the competent authority.
d) Power system, lightning protection system, antistatic system, electrical equipment, spark-generating equipment, heat-generating equipment, and the use of fire sources and heat sources must ensure fire safety in accordance with regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
dd) There are sufficient and quality traffic system, water supply system and communication system supporting fire fighting, system for management of database on fire prevention and fighting, incident notification system, fire alarm system, firefighting system, fire blocking system, smoke blocking system, fire escape system, other fire prevention and fighting equipment, and rescue equipment in accordance with regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
e) The fire safety and firefighting authority (hereinafter referred to as “firefighting authority”) has issued a certificate of design appraisal and design appraisal document (if any) and written approval of fire safety commissioning results for projects and works included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith, excluding national defense facilities operating for military purpose and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements manufactured or converted for military purpose by national defense facilities.
2. Any facility mentioned in the list in Appendix IV enclosed therewith must satisfy the following fire safety requirements:
a) The requirements in Points a, c and d Clause 1 herein; a certificate of design appraisal and design appraisal document (if any) and written approval of fire safety commissioning results are required for the facilities included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith;
b) There are sufficient and quality traffic system, water supply system and communication system supporting fire fighting, fire alarm system, firefighting system, fire blocking system, smoke blocking system, fire escape system, other fire prevention and fighting equipment, and rescue equipment in accordance with technical regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
c) There are fire prevention and fighting regulations and task assignment. Persons in charge of fire prevention and fighting must join training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operation according to regulations in Article 33 of this Decree.
3. Any regulatory body or organization located on the premises of a facility having satisfied the fire safety requirements in Clauses 1 and 2 herein shall perform the following tasks intra vires:
a) Ensure compliance with the requirements in Point a Clause 1 herein;
b) Use electrical equipment, spark-generating equipment, heat-generating equipment, fire sources and heat sources in accordance with fire safety requirements;
c) Assign persons to the facility’s internal firefighting force;
d) Cooperate with the facility head in complying with fire safety requirements intra vires.
4. Heads of the facility and the regulatory body/ies and/or organization(s) located on the premises thereof must ensure that the fire safety requirements in Clauses 1, 2 and 3 herein are satisfied before putting the facility to operation and throughout the facility's operation.
In case multiple regulatory bodies and/or organizations are located on the premises of one facility, the facility head shall take charge in managing and maintaining compliance with fire safety requirements in the whole facility.
5. There are documents supporting management and monitoring of fire prevention and fighting of the facilities included in the lists in Appendix III and Appendix IV enclosed therewith, which are formulated and retained by facility heads. The components of these documents are provided for by the Ministry of Public Security.
Article 6. Fire safety requirements applicable to residential areas
1. A residential area is a place where individuals and households live as parts of a village, hamlet, mountain village, neighborhood and equivalent residential unit (hereinafter collectively referred to as “village”). A village is a residential area subject to fire management.
2. Residential areas must satisfy the following fire safety requirements:
a) Regulations on fire prevention and fighting and use of electricity, fire, flammable materials and explosives are provided in accordance with technical regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
b) There are sufficient and quality traffic system, water supply for firefighting, fire spread preventing solutions and, fire prevention and fighting equipment in accordance with technical regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
c) There is a firefighting plan approved by the competent authority.
d) There are a neighborhood having received training in fire prevention and fighting operation and on-site combat-ready firefighters.
3. Chairpersons of commune-level People’s Committees must organize and maintain compliance with the fire safety requirements in Clause 2 throughout the existence of the residential areas.
Article 7. Fire safety requirements applicable to households
1. Households must satisfy the fire safety requirements in Clause 1 Article 17 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting.
2. Households engaging in business operations must satisfy the following fire safety requirements:
a) The requirements in Clause 1 herein;
b) Regulations on fire prevention and fighting and use of electricity, fire, flammable materials and explosives are provided in accordance with technical regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
c) There are solutions for fire escape, fire spread prevention and smoke blocking between the living quarters and the business area.
3. Household heads must organize and maintain compliance with the fire safety requirements in Clauses 1 and 2 herein throughout the existence of the households.
4. The households mentioned in Clause 2 herein and issued with the enterprise registration certificate must satisfy the fire safety requirements corresponding to the type of enterprise that they are according to regulations in Article 5 of this Decree.
Article 8. Fire safety requirements applicable to motor vehicles
1. Road motor vehicles with at least 04 seats must meet conditions for inspected operation; and materials and goods on the vehicles must be arranged in compliance with fire safety requirements.
Road motor vehicles with more than 09 seats, inland watercrafts and railway vehicles must satisfy the following requirements:
a) Regulations, prohibition signs, signage and instruction signs are provided in accordance with fire prevention and fighting regulations and standards or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
b) The power system, fuel, materials and goods on these vehicles must be arranged in compliance with fire safety requirements;
c) There are sufficient and quality firefighting equipment appropriate to the characteristics and operations of the vehicles in accordance with regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting or regulations of the Ministry of Public Security;
d) There are fire prevention and fighting regulations and task assignment and on-site combat-ready firefighters.
2. The motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements mentioned in section 21 in Appendix V enclosed therewith must comply with the following fire safety requirements and maintain such compliance:
a) The requirements in Clause 1 herein;
b) The firefighting authority has issued a certificate of design appraisal and design appraisal document (if any) and written approval of fire safety commissioning results, excluding motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements manufactured or converted for military purpose by national defense facilities;
c) There is a firefighting plan approved by the vehicle owner.
3. A motor vehicle may transport goods posing fire or explosion hazard on the road, inland waterway or railway when it has obtained the permit for transport of goods posing fire or explosion hazard issued by the police authority according to regulations of laws on road, inland waterway and railway transport of dangerous goods (excluding cases within the competence of the Ministry of National Defense) and must comply with the following fire safety requirements and maintain such compliance:
a) The requirements in Clause 1 herein;
b) The vehicle’s motor must be separated from the cargo compartment by fire-resistant materials or buffer chamber as per regulations;
c) The motor’s exhaust pipe must be covered and ensure fire and explosion safety;
d) The floor and structure of the cargo compartment and other areas of the vehicle at fire and explosion risk must be made of fire-resistant materials;
dd) Technical safety and environmental protection requirements per regulations;
e) Road vehicles transporting liquids posing fire or explosion hazard must be grounded;
g) Road motor vehicles must bear signage of goods posing fire and explosion hazards (Form No. PC01) on the windshield; railway vehicles must bear signage of goods posing fire and explosion hazards (Form No. PC01) on both of their sides throughout the transport process;
h) Inland watercrafts must fly the letter B signal flag in the day and set up red signal light at night throughout the transport process. Specifications and standards of the signal flag and light are provided for by the Ministry of Transport.
4. Drivers and crewmembers of vehicles transporting passengers and goods posing fire and explosion hazards shall comply with the following requirements:
a) Drivers must have a driving license according to regulations of laws on road, inland waterway and railway transport;
b) Drivers and crewmembers of motor passengers vehicles with more than 29 seats and motor vehicles transporting goods posing fire and explosion hazards shall participate in training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting according to regulations in Article 33 herein.
Article 9. Issuance of licenses to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards and transport of goods posing fire and explosion hazards
1. Applications and procedures for issuance of licenses to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards of classes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 9 by road motor vehicles and by inland waterways are provided for in the Government’s Decree No. 42/2020/ND-CP dated April 08, 2020 on list of dangerous goods, transport of dangerous goods by land motor vehicles and transport of dangerous goods by inland waterways (hereinafter referred to as “Decree No. 42/2020/ND-CP”).
2. An application for the license to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards by railway includes:
a) An application for the license to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards (Form No. PC02);
b) Certified true copy (or copy together with the authentic copy for comparison) of the enterprise registration certificate of the applicant, which proves that the applicant is permitted to trade or transport dangerous goods;
c) List of goods posing fire and explosion hazards and weight and transport route thereof (route start and end); list of escorts;
d) Copy certified by the enterprise of the transport contract or written agreement on transport of goods posing fire and explosion hazards by railway between the consignor and the rail transport enterprise;
dd) Plan for incident prevention and response during transport of goods posing fire and explosion hazards bearing the signature and seal of the applicant;
e) Plan for vehicle cleaning and assurance of environmental protection requirements post-transport according to existing regulations on environmental protection.
3. The applicant shall submit 01 application prepared per Clause 2 herein to the competent authority in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
4. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations in Clause 2 herein, receive it and fill out the acknowledgement of receipt of application for administrative procedure concerning fire prevention and fighting (using Form No. PC03) (hereinafter referred to as “acknowledgement of application receipt”);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations in Clause 2 herein, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application as per regulations and fill out the written instruction on revision of application for administrative procedure concerning fire prevention and fighting (using Form No. PC04) (hereinafter referred to as “application revision instruction”).
5. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
6. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
7. Within 05 working days starting from the date of receipt of a valid application, the competent authority shall inspect the vehicle’s fire safety based on the requirements stated in Clause 3 Article 8 herein, consider and issue the license to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards (using Form No. PC05) and signage of goods posing fire and explosion hazards (using Form No. PC01). If the application is rejected, the competent authority must provide an explanation in writing.
8. Competence in issuance of licenses to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards by road, inland waterway or railway:
a) Fire safety, firefighting, and rescue authorities affiliated to provincial police authorities (hereinafter referred to as “fire departments”) have the power to issue the license to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards to vehicles of applicants whose business premises are located in and vehicles operating in areas under their management;
b) District-level police authorities have the power to issue the license to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards to vehicles of applicants whose business premises are located in and vehicles operating in areas under their management and beyond the competence of fire departments and to cases authorized by fire departments.
9. Licenses to transport goods posing fire and explosion hazards may be used across the country and shall be used once for vehicles operating under a charter agreement; shall remain valid for no more than 24 months for vehicles transporting goods posing fire and explosion hazards per a transport plan or agreement within the effective period of the inspection certificate for compliance with technical safety and environmental protection requirements (for road motor vehicles), certificate for compliance with technical safety and environmental protection requirements (for inland watercrafts) or certificate for compliance with quality, technical safety and environmental protection requirements (for railway vehicles).
10. Transport of goods posing fire and explosion hazards by road motor vehicles, inland watercrafts and railway vehicles shall adhere to regulations of Decree No. 42/2020/ND-CP and the Government’s Decree No. 65/2018/ND-CP dated May 12, 2018 elaborating some Articles of Law on Railway Transport.
Article 10. Fire safety requirements applicable to formulation of or amendment to planning for construction of cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones, hi-tech parks and other functional zones according to Law on Planning
Requirements for formulation of or amendment to planning for construction of cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones, hi-tech parks and other functional zones according to the Law on Planning:
1. Building sites of works and work clusters, land areas and land lots must be located in a manner that prevents fire from spreading and minimizes the effects of heat, smoke, dust and noxious gases produced by fire on surrounding residential areas and works.
2. Size and load capacity of transport systems and spaces must enable firefighting operations of motor firefighting equipment.
3. Firefighting water supply; communication systems and power supply must be available for firefighting activities and fire incident reporting.
4. Building sites of premises of firefighting authorities must be located according to regulations of technical regulations and standards on construction planning.
5. All projects must make a cost estimate for fire prevention and fighting items.
Article 11. Fire safety requirements applicable to development of projects on and designs for construction or renovation or repurposing of works
Development of projects on and designs for construction or renovation or repurposing of works and work items (hereinafter collectively referred to as “works”) must be compliant with fire safety regulations and standards. To be specific:
1. Building sites of works must ensure adequate fire safety separation distance from surrounding works.
2. Every work must have a fire resistance level appropriate to its size and purpose; and have solutions for fire safety and preventing fire from spreading to other items of the work and between the work and another work.
3. Production technology, power system, lightning protection system, antistatic system and explosion protection system of works and locations of technical systems and equipment must adhere to fire safety requirements.
4. Fire escape routes, lighting and instructions and fire alarm signals; smoke exhaust ventilation systems; and rescue equipment must ensure fast and safe escape.
5. Size and load capacity of transport systems and parking lots must enable firefighting operations of motor firefighting equipment; firefighting water supply must enable firefighting activities.
6. Quantities, locations and technical specifications of fire alarm and firefighting systems and other firefighting equipment of every work must be appropriate to the characteristics and purpose of the work.
Article 12. Funding for fire safety in investment and construction
1. Funding for fire safety in investment and construction includes funding for the fire safety items mentioned in Articles 10 and 11 of this Decree and other amounts of funding for development of fire safety design projects and appraisal, testing, inspection, construction and commissioning in relation to fire safety.
2. Funding for fire safety in investment and construction must be allocated during the stage of work design and investment project development.
Article 13. Development and appraisal of fire safety design
1. Construction, renovation or repurposing of projects and works and manufacturing or conversion of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements must comply with fire prevention and fighting regulations and standards. Planning schemes and construction design dossiers of projects, works and motor vehicles mentioned in Appendix V enclosed therewith shall be formulated by units eligible according to regulations and are subject to fire safety design appraisal.
2. Fire safety design appraisal refers to inspection and comparison of design content and solutions of projects, works and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements with standards and regulations of Vietnamese law related to fire prevention and fighting or foreign and international standards on fire prevention and fighting applicable in Vietnam carried out by competent authorities following the procedure stipulated by law.
Fire safety design appraisal results shall provide a basis for consideration and planning approval, project approval, construction design appraisal and construction permit granting.
3. Fire safety designs of the following subjects require appraisal:
a) Schemes for or amendments to planning for construction of cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones, hi-tech parks and other functional zones according to the Law on Planning;
b) Projects and works which are mentioned in Appendix V enclosed therewith and the construction, renovation or repurposing of which affects one of the fire safety conditions provided for in Point b Clause 5 herein;
c) Motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements which are mentioned in Section 21 of Appendix V enclosed therewith and the manufacturing or conversion of which affects one of the fire safety conditions provided for in Point c Clause 5 herein.
4. Components of applications for fire safety design appraisal:
a) For application for feedback on construction planning scheme: application for consideration of and feedback on fire safety solution of entity formulating the planning (made using Form No. PC06); documents and detailed planning drawings at a scale of 1/2000 (for industrial parks of more than 20ha) or 1/500 (for the remaining cases) showing requirements for fire safety solutions mentioned in Clauses 1, 2, 3 and 4 Article 10 herein;
b) For application for building site approval prior to design of independent works posing fire or explosion hazard and mentioned in Sections 15 and 16 of Appendix V enclosed therewith (excluding internal filling stations and gas using facilities): application for building site approval by investor (made using Form No.06), and letter of authorization per the law if the investor authorizes another unit to carry out this task; certificate of land use rights or written proof of lawful land use rights for land of the project/work; drawings and documents showing current topographic conditions of the land relevant to fire safety such as fire resistance level of the work, distance between the work and surrounding works, wind direction and height of the work;
c) For application for feedback on fundamental design of project/work: application for consideration of and feedback on fire safety solution of investor (made using Form No. PC06), and letter of authorization per the law if the investor authorizes another unit to carry out this task; decision to approve construction investment guidelines (for state-funded projects); written approval of construction investment guidelines (if any) or investment registration certificate (if any) or certificate of land use rights or written proof of lawful land use rights (for the remaining cases); certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business of fire safety design consultancy unit; fundamental design description and drawings showing requirements for fire safety solutions mentioned in Article 11 herein;
d) For application for appraisal of technical design or construction drawing design: application for appraisal of fire safety design of investor (made using Form No. PC06), and letter of authorization per the law if the investor authorizes another unit to carry out this task; written feedback on fundamental fire safety design from the firefighting authority (if any); decision to approve construction investment guidelines (for state-funded projects); written approval of construction investment guidelines (if any) or investment registration certificate (if any) or certificate of land use rights or written proof of lawful land use rights (for the remaining cases); certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business of fire safety design consultancy unit; cost estimate for construction of work; drawings and description of technical design or construction drawing design showing fire safety requirements mentioned in Article 11 herein; copies of design appraisal certificate, design appraisal document, drawing bearing seal of fire safety appraisal (for renovation/amended design dossiers); document on construction design appraisal by construction authority (if any);
dd) For application for appraisal of technical design of motor vehicle subject to special fire safety requirements: application for appraisal of fire safety design of investor/vehicle owner (made using Form No. PC06), and letter of authorization per the law if the investor/vehicle owner authorizes another unit to carry out this task; certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business of fire safety design consultancy unit; estimated investment in vehicle; technical design description and drawings showing fire safety requirements mentioned in Points b and c Clause 1 and Points b, c, d and e Clause 3 Article 8 herein;
e) Documents included in these applications shall be the authentic copy or certified or notarized true copy or copy/photocopy submitted together with its authentic copy for comparison. The design description and drawing must be certified by the applicant. For applications in a foreign language, a Vietnamese translation must be provided and the applicant shall take responsibility for the content of the translation.
5. Appraised items:
a) For planning schemes: compliance of planning schemes with regulations in Clauses 1, 2, 3 and 4 Article 10 herein;
b) For projects and works: compliance of their designs with existing regulations on the following matters: list of regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting, technical documents, technical instructions and technologies applicable to work design; roads for fire trucks, fire safety separation distance from surrounding works; water supply for fire fighting; fire resistance levels, fire and explosion hazard classes and purpose-based space division related to fire prevention and fighting; solutions for fire and fire spread prevention; smoke dispersion solutions; escape solutions; solutions for rescue and rescue support; plans for lightning and static prevention; solutions for supply of power to fire prevention and fighting system and other technical systems relevant to fire prevention and fighting; fire alarm and firefighting systems and firefighting equipment of works;
c) For motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements: fire safety solutions suitable for characteristics of operations and fire and explosion hazards of vehicles; conditions for fire prevention, fire spread prevention, escape and human rescue during fire; fire safety solutions applicable to power system, fuel system and engine; fire alarm and firefighting systems and other firefighting equipment; systems and equipment for detection and handling of leakage of gases and liquids posing fire and explosion hazards;
d) For construction or renovation of fire prevention and fighting systems or equipment of works having undergone commissioning and been put into use according to regulations: fire safety design of the constructed or renovated parts of the fire prevention and fighting systems or equipment.
6. The applicant shall submit 01 application prepared according to Clause 4 herein to the competent authority mentioned in Clause 12 herein in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
7. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations in Clause 4 herein, receive it and fill out the acknowledgement of application receipt (using Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations in Clause 4 herein, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application as per regulations and fill out the application revision instruction (using Form No. PC04).
8. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
d) If an application is invalid (the applying project or work does not require fire safety design appraisal according to regulations in Appendix V enclosed therewith or the receiving authority is not competence in appraising fire safety design of the applying project or work according to regulations in Clause 12 herein), the receiving authority shall notify the applicant that the application is rejected within the time limit prescribed in Clause 10 herein in writing and in the way in which the applicant sent their application.
9. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
10. Time limit for fire safety design appraisal:
Time limit for fire safety design appraisal starting from the date of receipt of a valid and adequate application:
a) For construction planning schemes: no later than 05 working days;
b) Building site approval: no later than 05 working days;
c) Fundamental designs: no later than 10 working days for projects of national importance and group A projects; no later than 05 working days for the remaining projects;
d) Technical designs or construction drawing designs: no later than 15 working days for projects and works of national importance and group A projects and works; no later than 10 working days for the remaining projects and works;
dd) Technical designs of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements: no later than 10 working days.
11. Results of fire safety design appraisal:
a) For planning schemes: firefighting authorities shall give their feedback on fire safety solutions in writing;
b) For building site approval: firefighting authorities shall approve of the building sites in writing;
c) For fundamental designs: firefighting authorities shall give their feedback on fire safety solutions in writing;
d) For technical designs or construction drawing designs and technical designs of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements: firefighting authorities shall issue the certificate of fire safety design appraisal (made using Form No. PC07) and stamp the seal of fire safety design appraisal (made using Form No. PC08) on appraised descriptions and drawings and return these documents to applicants. Every applicant shall submit a file containing the photocopy or copy of the application bearing the seal of appraisal to the firefighting authority carrying out the appraisal for retention purpose according to regulations before receiving the certificate of fire safety design appraisal;
For technical designs or construction drawing designs of renovation or repurposing of works or conversion of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements: firefighting authorities shall approve of the fire safety design (using Form No.08) in writing and stamp the seal of fire safety design appraisal (made using Form No. PC08) on appraised descriptions and drawings and return these documents to applicants. Every applicant shall submit a file containing the photocopy or copy of the application bearing the seal of appraisal to the firefighting authority carrying out the appraisal for retention purpose according to regulations before receiving the written approval of fire safety design appraisal;
dd) If firefighting authorities do not announce the results provided for in Points a, b, c and d herein, they shall provide a written explanation and return the applications to applicants within the time limit prescribed in Clause 10 herein.
12. Competence in fire safety design appraisal:
a) Police Department of Fire Prevention and Firefighting and Rescue has the power to appraise fire safety designs of projects and works meeting criteria for projects and works of national importance and group A projects and works as per the law on public investment (excluding state-funded projects and works whose investors are provincial governments); works of more than 100 m in height; works located in 02 or more central-affiliated cities and provinces; watercrafts of 50 m or more in length carrying passengers or flammable liquids, flammable gases, explosives and chemicals posing fire and explosion hazards; and work investment projects proposed by fire departments (excluding national defense facilities operating for military purpose and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements manufactured or converted for military operations by national defense facilities);
b) Fire departments have the power to appraise fire safety designs of planning schemes for cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones, hi-tech parks and other functional zones according to the Law on Planning located in localities under their management; projects and works fire safety designs of which are not appraised by Police Department of Fire Prevention and Firefighting and Rescue and which are located in localities under their management, and cases authorized by Police Department of Fire Prevention and Firefighting and Rescue; motor vehicles which are subject to special fire safety requirements and located in localities under their management and fire safety designs of which are not appraised by Police Department of Fire Prevention and Firefighting and Rescue, and cases authorized by Police Department of Fire Prevention and Firefighting and Rescue, excluding national defense facilities operating for military purpose and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements manufactured or converted for military operations by national defense facilities.
13. Construction, renovation or repurposing of projects and works not included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith must satisfy fire safety requirements stipulated by fire prevention and fighting regulations and standards.
14. Fees of fire safety design appraisal shall be included in the total investment of each project, work and motor vehicle.
Article 14. Responsibilities of investors, motor vehicle owners, project consultancy and construction supervision units, design consultancy units, construction units, authorities competent in approving planning, authorities competent in approving construction investment projects, authorities competent in granting construction permits and firefighting authorities in investment and construction
1. Responsibilities of the investor/motor vehicle owner:
a) Develop the design project according to regulations in Article 11 herein and approved planning. If the work/motor vehicle is subject to special fire safety requirements according to the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith, construction shall start when its design dossier has been appraised by the firefighting authority competent in appraising fire safety design;
b) Organize construction and construction inspection and supervision according to the appraised fire safety design. In case there is any change to the fire safety design or a piece of fire safety equipment during the construction process that affects one or more than one of the contents provided for in Point b or c Clause 5 Article 13 herein, an additional design shall be prepared to ensure compliance with fire safety regulations and standards, and the change must be appraised before construction;
c) Organize fire safety commissioning if the project, work or motor vehicle is subject to special fire safety requirements according to the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith and take responsibility for the commissioning results;
d) Ensure fire safety of their work from construction to commissioning, handover and putting into operation;
dd) Provide dossiers on appraisal of fire safety design and commissioning of their work/motor vehicle for the manager/user when putting the work/motor vehicle into use, which will be presented at the request of the competent authority;
e) Present dossiers on appraisal of fire safety design and commissioning of their work/motor vehicle at the request of the competent authority.
2. Responsibilities of the project consultancy and construction supervision unit:
a) Take responsibility before the law and the investor for performance of fire safety tasks in compliance with regulations of law on project consultancy and supervision consultancy under the agreement between the investor and the consultancy unit;
b) Participate in the commissioning process.
3. Responsibilities of the design consultancy unit:
a) Make a design in compliance with fire safety requirements; take responsibility for the quality of the design product;
b) Exercise designer's supervision during the construction process.
4. Responsibilities of the construction unit:
a) Build the work in accordance with the appraised fire safety design;
b) Ensure fire safety of areas under its management from construction to handover;
c) Formulate the as-built dossier; prepare documents and conditions necessary for commissioning and participate in commissioning.
5. Responsibilities of authorities competent in approving planning, authorities competent in approving construction investment projects and authorities competent in granting construction permits:
a) Authorities competent in approving planning and authorities competent in approving construction investment projects for projects and works included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith shall approve these projects and works after the reply to the fire safety design appraisal results provided for in Clause 11 Article 13 herein;
b) For projects and works included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith, authorities competent in granting construction permits shall request the investor to present the fire safety design appraisal certificate and document (if any) and the drawing bearing the seal of fire safety design appraisal of the firefighting authority before granting the construction permit.
6. Responsibilities of firefighting authorities:
a) Consider and decide whether to approve the building sites of the works mentioned in Sections 15 and 16 of Appendix V enclosed therewith (excluding internal filling stations and gas using facilities) and fire safety solutions for construction planning projects and design dossiers of the facilities mentioned in Appendix V enclosed therewith;
b) Appraise the fire safety design in the technical design dossier or construction drawing design of projects, works and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements according to the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith;
c) Inspect fire safety commissioning results of projects, works, work items and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements according to the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith;
d) Inspect fire safety during construction of works included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith.
Article 15. Fire safety commissioning and inspection of results thereof
1. The investor or owner of a project, work or motor vehicle which is subject to special fire safety requirements and the fire safety design of which has been appraised must organize fire safety commissioning for the project, work or motor vehicle. The investor or owner shall request the firefighting authority appraising the fire safety design to inspect the commissioning results and issue a written approval of fire safety commissioning results before putting the work or motor vehicle into use.
Fire safety commissioning comprises commissioning of each part, stage, work item and system and commissioning for handover; for parts of a project, work or motor vehicle which is subject to special fire safety requirements that are hidden from view during the construction process, they must be commissioned before starting other tasks. The investor has the power to decide commissioning of an individual part of the work if the area to undergo commissioning could operate independently and meet fire safety requirements; the firefighting authority must inspect the commissioning results and issue a written approval of the results before that part of the work could be put into use.
2. Application for fire safety commissioning includes:
a) Copy of fire safety design appraisal certificate and document submitted together with the dossier bearing the appraisal seal the firefighting authority;
b) Copy of certificate of fire prevention and fighting equipment inspection (hereinafter referred to as “equipment inspection certificate");
c) Records of testing, commissioning of each part and comprehensive commissioning of the fire prevention and fighting system;
d) As-built drawings of the fire prevention and fighting system and items related to fire prevention and fighting in accordance with the appraised design dossier;
dd) Written guidelines for operation and maintenance of fire prevention and fighting equipment and system and systems related to fire prevention and fighting of the work or motor vehicle;
e) Records of commissioning of work items and systems related to fire prevention and fighting;
g) Copies of certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business of the supervision consultancy unit (if any) and fire prevention and fighting system construction unit.
Documents in the application must be certified by the investor or vehicle owner, supervision consultancy unit and construction unit. The application must be translated into Vietnamese if it is in a foreign language.
3. Content of inspection of fire safety commissioning results from investors and vehicle owners by firefighting authorities:
a) Inspect content and validity of the application for fire safety commissioning prepared by the investor or vehicle owner according to regulations in Clause 2 herein;
b) Inspect consistency between the commissioning results from the investor or vehicle owner and the appraised design;
c) Organize inspection and testing of actual operation probability of fire prevention and fighting equipment and systems related to fire prevention and fighting of the work or motor vehicle to compare with the commissioning results from the investor or vehicle owner. The inspection must be recorded in writing (using Form No. PC10).
4. The applicant shall submit 01 application containing the documents mentioned in Clause 2 herein together with the report on results of construction, inspection, testing and commissioning of fire prevention and fighting system, equipment and solutions and an application for inspection of fire safety commissioning results (using Form No. PC11) to the firefighting authority appraising the fire safety design in any of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
The application must be submitted at least 10 working days (for projects and works of national importance and group A projects and works) or at least 07 working days (for the remaining works and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements) prior to the date upon which the inspection takes place.
5. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations, receive it and fill out 02 copies of the acknowledgement of application receipt (Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application and fill out 02 copies of the application revision instruction (Form No. PC04).
6. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
7. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
8. Within 10 working days (for projects and works of national importance and group A projects and works) or 07 working days (for the remaining works and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements) from the date of receipt of an application adequate per regulations in Clause 4 herein, the firefighting authority shall inspect the commissioning results and draw up an inspection record (using Form No. PC10). Within 7 working days from the date of approval of the inspection record, the firefighting authority shall consider and decide to issue a written approval of fire safety commissioning results (using Form No. PC12) and return the commissioning dossier received to the applicant. If the commissioning results are rejected, the firefighting authority must provide a written explanation for the applicant.
9. The written approval of fire safety commissioning results shall provide a basis for the authority competent in granting permits to put works and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements into use.
Article 16. Fire safety inspection
1. Entities subject to inspection:
a) Facilities requiring fire management;
b) Residential areas, households, forests, motor vehicles and technical infrastructures related to fire prevention and fighting of cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones and hi-tech parks;
c) Works included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith in their construction stage, excluding national defense facilities operating for military purpose;
d) Fire prevention and fighting service businesses.
2. Inspected items:
a) Fire safety requirements applicable to facilities, residential areas, households and motor vehicles provided for in Articles 5, 6, 7 and 8 herein;
b) Forest fire safety requirements according to regulations of the Government’s Decree No. 156/2018/ND-CP dated November 16, 2018 elaborating a number of Articles of Law on Forestry;
c) Fire safety requirements applicable to construction works in their construction stages: fire safety design appraisal certificate or document for works included in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith; regulations on fire prevention and fighting and fire escape signage; regulations on fire safety task assignment by the investor and construction unit intra vires; duties of personnel in charge of fire safety; use of power system, electrical equipment, spark-generating equipment, heat-generating equipment, fire sources and heat sources; and provision of emergency firefighting equipment appropriate to the characteristics of the work;
d) Performance of fire prevention and fighting duty of heads of regulatory bodies and organizations, investors, contractors, motor vehicle owners, household heads and forest owners per the law;
dd) Requirements applicable to fire prevention and fighting service businesses per regulations in Article 41 of this Decree.
3. Fire safety inspection shall be carried out on a regular, periodic and ad hoc basis. To be specific:
a) Heads of facilities and owners of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements, household heads and forest owners shall organize fire safety inspection on a regular basis intra vires;
b) Heads of facilities included in the list in Appendix III enclosed therewith shall inspect fire safety of their facilities on a regular basis; send biannual reports on the inspection results to the supervisory police authority and take responsibility before the law for these results;
c) Chairpersons of commune-level People’s Committees shall direct and organize fire safety inspection on an annual basis; and ad hoc inspection upon detection of any of the cases provided for in Points a and b Clause 1 Article 17 herein or a violation against fire safety regulations that can lead to fire or explosion or for the purpose of security and order preservation as per instructional documents of the competent authority for facilities included in the list in Appendix IV enclosed therewith, and residential areas under their management;
d) Chairpersons of People’s Committees at district level and higher shall direct and organize ad hoc inspection for the purpose of security and order preservation as per instructional documents of the competent authority for the entities mentioned in Points and b Clause 1 herein intra vires;
dd) Police authorities shall inspect fire safety on a biannual basis for facilities included in the list in Appendix II enclosed therewith; on an annual basis for technical infrastructures related to fire prevention and fighting of cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones and hi-tech parks, and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements and the remaining facilities included in the list in Appendix III enclosed therewith; and on an ad hoc basis upon detection of any of the cases provided for in Points a and b Clause 1 Article 17 herein or a violation against fire safety regulations that can lead to fire or explosion or for the purpose of security and order preservation as per instructional documents of the competent authority intra vires; and on an annual basis during the construction process for construction works included in the list in Appendix IV enclosed therewith.
4. Fire prevention and fighting service businesses shall be subject to inspection on a periodic and ad hoc basis. To be specific:
After a fire prevention and fighting service business is granted a certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business, the competent police authority mentioned in Clause 12 Article 45 herein shall inspect the business on an annual basis to determine the business’s compliance with conditions for fire prevention and fighting service business and maintenance of such compliance; and on an ad hoc basis upon detection of sign of breaching of a condition for fire prevention and fighting service business provided for in Article 41 herein or misuse of fire prevention and fighting operations to compromise security or disturb order, which requires handling at the request of the competent authority. Upon detection of such violation, draw up a record (using Form No. PC10) and propose a revocation decision (made using Form PC35) to the competent authority for signing.
5. Inspection procedure;
a) For fire safety inspection
The bodies and individuals with competence in inspection mentioned in Points c and dd Clause 3 herein shall notify the inspected entity of the inspection time, inspected items and inspection team members 03 working days prior to the date of a periodic inspection. When inspecting the fire safety of a facility managed by a subordinate body, notify the subordinate body of the inspection. Where necessary, request the subordinate body to join the inspection team and provide documents and update situation related to fire prevention and fighting of the inspected facility. Notify the inspection results to the subordinate body;
The bodies and individuals with competence in inspection mentioned in Points c, d and dd Clause 3 herein shall notify the specific reason for an ad hoc inspection to the inspected entity. When carrying out an ad hoc inspection, police officers must present a letter of introduction from their supervisory body;
Inspected entities must prepare for all notified inspected items and assign the competent or responsible person(s) to work with the bodies and individuals competent in carrying out the inspection;
b) For inspection of fire prevention and fighting service businesses per regulations in Clause 4 herein:
The police authority having granted the certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business must notify the inspected entity of the inspection time, inspected items and inspection team members 03 working days prior to the date of a periodic inspection;
The competent bodies and individuals shall notify the specific reason for an ad hoc inspection to the inspected entity. When carrying out an ad hoc inspection, police officers must present a letter of introduction from their supervisory body;
Inspected entities must prepare for all notified inspected items and assign the competent or responsible person(s) to work with the bodies and individuals competent in carrying out the inspection;
c) The competent bodies and individuals mentioned in Points c, d and dd Clauses 3 and 4 herein shall record their periodic and ad hoc inspections in writing (using Form No. PC10). In case the inspected entity fails to sign the inspection record, the record must be certified by two witnesses or the local government.
Article 17. Temporary suspension and suspension of operations of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals not meeting fire safety requirements
1. Cases subject to temporary suspension of operations:
a) Presence of a fire or heat source in an environment at risk of fire or explosion or appearance of an environment at risk of fire or explosion in the presence of a fire or heat source (hereinafter referred to as “direct fire or explosion risk”);
b) Failure to remedy a serious violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations after the competent authority has requested remedy in writing, including illegal storage and use of goods posing fire or explosion hazard; production, trade, division and filling of goods posing fire or explosion hazard without permit or at unauthorized location; and obstruction of fire escape and buffer chamber during fire or explosion that can lead to serious damage to human lives and property;
c) Extremely serious violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations:
Renovation or repurposing of a facility or an item of a facility or conversion of a motor vehicle subject to special fire safety requirements according to the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith that affects one of the fire safety conditions provided for in Points b and c Clause 5 Article 13 herein without a fire safety design appraisal document from the competent police authority;
Putting a work, work item or motor vehicle subject to special fire safety requirements according to the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith into use without a written approval of fire safety commissioning results from the competent police authority.
2. Temporary suspension of operations shall be limited to the operations that pose a risk of fire or explosion or violate fire prevention and fighting regulations.
3. The temporary suspension duration shall be determined based on the ability to eliminate the direct fire or explosion risk or remedy the violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations and shall not exceed 30 days.
4. If facilities and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements and households and individuals whose operations are temporarily suspended according to regulations in Clause 1 herein fail to remedy their violations by the end of the temporary suspension period, their operations will be suspended. This suspension may apply to a part or the whole operations of the facilities and motor vehicles, households and individuals.
5. The temporary suspension or suspension decision shall be made in writing; a verbal temporary suspension decision may be made for the case provided for in Point a Clause 1 herein but a written decision must be issued afterwards.
6. Procedure for temporary suspension of operations:
a) Upon detection of a case subject to temporary suspension of operations as per regulations in Clause 1 herein, the present official shall request the organization or individual to stop its/their operations or violation according to the following procedure:
Draw up a record of the extent of direct fire or explosion risk or violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations.
Issue the temporary suspension decision or report to the competent person for issuance of the temporary suspension decision;
b) The temporary suspension decision shall be made in writing (using Form No. PC13). In an emergency, a verbal temporary suspension decision may be made and a written decision shall be issued afterwards. A verbal temporary suspension decision must include full name, post, workplace of the present official, extent of the risk or violation and temporarily suspended operations;
The issuer of the temporary suspension decision shall organize supervision of elimination of the direct fire or explosion risk.
7. Procedure for suspension of operations:
a) Upon end of the temporary suspension period, the temporary suspension decision issuer shall organize an inspection of the facility, motor vehicle, household or individual whose operation is imposed the temporary suspension decision to consider its/their ability to eliminate the direct fire or explosion risk or remedy the violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations. The inspection must be recorded in writing (using Form No. PC10);
b) Upon end of the inspection, if deeming the direct fire or explosion risk not eliminated or the violation not remedied or irremediable, the temporary suspension decision issuer shall consider and issue a decision to suspend operations of the facility, motor vehicle, household or individual (using Form No. PC14).
8. Competence in temporary suspension and suspension of operations:
a) The Minister of Public Security has the power to issue decisions to temporarily suspend or suspend a part or the whole operations of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals across the country, excluding national defense facilities operating for military purpose and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements manufactured or converted for military purpose by national defense facilities;
b) Chairpersons of commune-level People’s Committees have the power to issue decisions to temporarily suspend or suspend a part or the whole operations of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals under their management. Chairpersons of district-level People’s Committees have the power to temporarily suspend or suspend a part of the whole operations of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals subject to the inspections provided for in Point d Clause 3 Article 16 herein;
c) Heads of Central Departments of Fire Safety, Firefighting and Rescue, heads of provincial police authorities, heads of fire departments, heads of district-level police authorities and heads of commune-level police authorities have the power to issue decision to temporarily suspend or suspend a part or the whole operations of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals under their management intra vires, excluding national defense facilities operating for military purpose and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements manufactured or converted for military purpose by national defense facilities;
d) Police officers have the power to temporarily suspend operations in the cases provided for in Point a Clause 1 herein and must report to their superiors, who have the power to issue the temporary suspension decision according to regulations in Point c herein, as soon as possible.
9. The temporary suspension decision or suspension decision must be delivered to the entity whose operation is imposed such temporary suspension or suspension, supervisory body thereof (if any), the People's Committee of the commune or district where the premises or place of residence of the temporarily suspended or suspended entity are/is located; in case the temporarily suspended or suspended operations concern multiple entities, each entity shall receive one decision.
10. Measures to ensure execution of temporary suspension and suspension decisions:
a) Upon receipt of a temporary suspension or suspension decision, heads of facilities, regulatory bodies and organizations, motor vehicle operators or owners, household heads and individuals must comply with the decision immediately and eliminate the direct fire or explosion risk or remedy the violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations as soon as possible;
b) Authorities competent in issuing temporary suspension or suspension decisions shall announce temporary suspension and suspension of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals not meeting fire safety requirements on websites and via the media until these entities are permitted to resume their operations. An announcement shall include name of the offender, the violation and imposed penalty.
Article 18. Resumption of operations of facilities, motor vehicles, households and individuals
1. The person competent in issuing the temporary suspension or suspension decision has the power to resume the temporarily suspended or suspended operation. If the competent person has decided to suspend an operation verbally and yet to issue a decision, but the direct fire or explosion risk or violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations is eliminated or remedied immediately, they may decide to resume the operation verbally.
2. During the temporary suspension period or upon end of the temporary suspension period, if the direct fire or explosion risk has been eliminated or violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations has been remedied, the facility head, motor vehicle owner, household head or individual must submit an application for operation resumption (using Form No. PC15) to the competent person who issued the temporary suspension decision for consideration and decision to resume the operation.
3. If a facility, motor vehicle, household or individual whose operation is suspended meets all fire safety requirements and wishes to resume its/their operation, the facility head, motor vehicle owner, household head or individual shall submit an application for operation resumption (using Form No. PC15) to the competent person who issued the suspension decision for consideration and decision to resume the operation.
4. The applicant shall submit 01 application to the workplace of the competent person mentioned in Clause 8 Article 17 herein in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
5. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt (made using Form No. PC03) to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
6. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
7. Within 07 working days starting from the date of receipt of the application for operation resumption, the person having issued the temporary suspension decision or suspension decision must inspect elimination of the direct fire or explosion risk or remedy of the violation against fire prevention and fighting regulations or fire safety requirements, record the inspection in writing (using Form No. PC10), consider and decide to issue the operation resumption decision (using Form No. PC16). If the operation resumption decision is not issued, a written explanation must be provided for the applicant in the way in which the applicant sent their application.
8. The operation resumption decision must be delivered to the entity whose operation is imposed temporary suspension or suspension, supervisory body thereof (if any), and the People's Committee of the commune or district where the premises or place of residence of the temporarily suspended or suspended entity are/is located; and posted on websites and via the media.
Article 19. Firefighting plans
1. a) Types of firefighting plans:
a) Facility firefighting plan (Form No. PC17);
b) Police authority firefighting plan (Form No. PC18).
2. Requirements for and basic content of a firefighting plan:
a) The plan includes the dangers posed by fire, explosion and toxic hazards and firefighting-related conditions;
b) The plan provides the most complicated fire scenario and some other possible typical fire scenarios, different levels of fire spread possibility;
c) The plan elaborates mobilization and use of forces and equipment, direction organization, technical measures, tactics and support activities concerning firefighting for each stage of each fire scenario;
d) The plan must be revised in a timely manner and reapproved by the competent authority upon large change in size, dangers posed by fire, explosion and toxic hazards and firefighting-related conditions.
3. Responsibility for firefighting plan formulation and cooperation in firefighting plan formulation:
a) Chairpersons of commune-level People’s Committees, heads of facilities requiring fire management and owners of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements shall organize formulation of facility firefighting plans for residential areas, facilities and vehicles employing on-site forces and equipment under their management (using Form No. PC17);
b) Heads of district-level police authorities shall organize formulation of police authority firefighting plans for facilities mentioned in the list in Appendix II enclosed therewith and residential areas facing high fire and explosion risk in localities under their fire management (using Form No. PC18);
c) Heads of fire departments shall organize formulation of police authority firefighting plans for the remaining facilities mentioned in the list in Appendix II enclosed therewith as well as firefighting plans requiring mobilization of local organizations, regulatory bodies, military and police and police forces of multiple central-affiliated cities and provinces (using Form No. PC18).
When formulating firefighting plans, police authorities must notify heads of facilities and Chairpersons of People’s Committees of communes where residential areas facing high fire and explosion risk are located of the plan formulation time and requirements for the formulation at least 03 working days before the formulation begins.
Chairpersons of People’s Committees of communes where residential areas facing high fire and explosion risk are located and heads of facilities mentioned in Appendix II enclosed therewith shall provide necessary documents and information related to firefighting plan formulation at the request of police authorities, assign personnel to join the formulation and satisfy conditions supporting the formulation.
4. Application for approval of facility firefighting plan for facilities mentioned in Appendix III enclosed therewith:
a) Application for approval of facility firefighting plan (made using Form No. PC19);
b) 02 copies of facility firefighting plan bearing the signature and seal of the person in charge of formulation (if any).
5. The applicant shall submit 01 application prepared according to Clause 4 herein to the competent authority in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
6. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations in Clause 4 herein, receive it and fill out the acknowledgement of application receipt (using Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations in Clause 4 herein, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application as per regulations and fill out the application revision instruction (using Form No. PC04).
7. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
8. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
9. Firefighting plan management:
a) Facility firefighting plans shall be retained in facilities, in residential areas and on motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements;
b) Every police authority firefighting plan shall be retained at the premises of the formulating police authority. Regulatory bodies and organizations whose forces and equipment are involved in the plan may copy and disseminate content related to their tasks.
10. Responsibility for organization of firefighting plan drills:
a) Chairpersons of commune-level People’s Committees, heads of facilities and owners of motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements shall ensure all necessary conditions and organize firefighting plan drills for facilities, residential areas and vehicles under their management;
b) Police authorities shall organize drills of their firefighting plans at the request of persons competent in approval;
c) Forces and equipment involved in a firefighting plan must participate in a satisfactory manner when mobilized for drills;
d) The person in charge of organizing facility firefighting plan drills shall send the plan and a report on results of the drills to the supervisory police authority and take responsibility before the law for the results.
11. Police authorities shall provide guidelines for and inspect firefighting plan formulation, drills, management and employment.
Article 20. Responsibility for fire incident reporting, fire fighting and firefighting participation
1. Anyone detecting a fire must inform people around them about it and notify one or all of the following units:
a) The neighborhood watch or internal/specialized firefighting force of the locality where the fire occurs;
b) The nearest police authority or firefighting authority;
c) The government of the locality where the fire occurs.
2. Upon receipt of report on a fire in a locality under their management, the regulatory bodies and units mentioned in Clause 1 herein shall promptly arrive at the scene to suppress the fire and, concurrently, notify other essential regulatory bodies and units for reinforcement.
3. Upon receipt of report on a fire outside of the locality under its management, the regulatory body/unit mentioned in Point b Clause 1 herein shall promptly notify the regulatory bodies and units managing the locality where the fire occurs to have the fire suppressed; and, concurrently, report to the supervisory unit for consideration and decision to mobilize forces and equipment for reinforcement upon request.
4. Persons present at the fire scene must take all suitable measures to save human lives, prevent the fire from spreading and suppress the fire; firefighting participants must obey all orders from the incident commander.
5. Police forces, military forces, militia and self-defense forces, health, power, water, urban environment and transport authorities as well as other relevant regulatory bodies shall suppress the fire and participate in the firefighting operation according to regulations in Clauses 2, 3 and 4 Article 33 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting.
Article 21. Incident commanders
1. The incident commander in a people’s police force shall be the highest-ranking leader of the firefighting authority present at the fire scene.
2. In case where the fire spreads from one facility to another or from one facility to a residential area or vice versa before the firefighting authority arrive at the fire scene, the incident commanders of the facility and the residential area must cooperate with each other in directing firefighting operation.
3. In case where the firefighting authority has yet to reach a motor vehicle caught on fire on the premises of a facility or in a village or forest, the incident commander in charge of the motor vehicle on fire shall cooperate with the person in charge of local firefighting operation in directing firefighting operation.
4. When the highest-ranking person of the people's police force arrives at the fire scene, the incident commander mentioned in Clause 2 Article 37 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting shall join the firefighting command team and take orders from the incident commander of the people’s police force.
Article 22. Firefighting commanding and directing tasks
1. Firefighting commanding tasks:
a) Mobilize forces, equipment, property, water supply and firefighting substances and materials for firefighting operations;
b) Identify the fire area, provide firefighting tactics and technical measures and organize adoption thereof;
c) Set requirements for assurance of public and traffic order;
d) Organize logistics activities, support and healthcare for firefighting operations;
dd) Establish communication for firefighting operations;
e) Organize political education in fire fighting;
g) Organize notification of the fire incident;
h) Decide to end firefighting operations;
i) Cooperate in organizing protection of the fire scene;
k) Organize experience-learning meetings;
l) Propose other requests in support of firefighting operations.
2. Firefighting operations direction shall be carried out in the cases provided for in Article 39 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting. Persons in charge of firefighting operations direction shall organize and direct safe and effective firefighting activities and recovery from fire damage.
3. Before the firefighting authority arrives at the fire scene, a regulatory body or organization head or Chairperson of the People's Committee at commune level or higher shall perform the tasks mentioned in Clauses 1 and 2 herein. When the firefighting authority arrives at the fire scene, its leader shall perform the tasks mentioned in Clause 1 herein; and the regulatory body or organization head or Chairperson of the People's Committee at commune level or higher shall command firefighting operations and perform the directing tasks mentioned in Clause 2 herein.
Article 23. Competence in and procedures for mobilization of forces, equipment and property for firefighting purpose
1. Competence in mobilization of forces, equipment and property for firefighting purpose:
a) Regulatory body or organization heads and Chairpersons of commune-level People’s Committees have the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of regulatory bodies, organizations, households and individuals under their management; and must propose mobilization of forces, equipment and property not under their management to the person competent in mobilization of these forces, equipment and property for decision;
b) Fire department heads and heads of provincial police authorities have the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of firefighting forces under their management, shall notify managers of the mobilized forces, equipment and property, and must propose mobilization of forces, equipment and property not under their management to the person competent in mobilization of these forces, equipment and property for decision;
c) Chairpersons of district-level People’s Committees have the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of regulatory bodies and organizations under their management; and must propose mobilization of forces, equipment and property not under their management to the person competent in mobilization of these forces, equipment and property for decision;
d) Heads of provincial police authorities have the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of police forces under their management; and must propose mobilization of forces, equipment and property not under their management to the person competent in mobilization of these forces, equipment and property for decision;
dd) Head of the Central Department of Fire safety, Firefighting, and Rescue has the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of firefighting authorities throughout the country. They must propose mobilization of forces, equipment and property not under their management to the person competent in mobilization of these forces, equipment and property for decision, and notify managers of the mobilized forces, equipment and property;
e) Chairpersons of provincial People’s Committees have the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of regulatory bodies, organizations, households and individuals under their management and military forces stationed in their provinces, and must notify managers of the mobilized forces, equipment and property;
g) The Minister of Public Security has the power to mobilize forces, equipment and property of regulatory bodies, organizations, households and individuals throughout the country, and must notify managers of the mobilized forces, equipment and property.
2. Procedures for mobilization of forces, equipment and property for firefighting purpose:
a) Mobilization of forces, equipment and property for firefighting purpose must be documented in an order for mobilization of forces, equipment and property for firefighting purpose (made using Form No. PC20); in case of emergency, the mobilization order may be given verbally and shall be documented within the 03 following working days. The person giving a verbal mobilization order must provide their full name, post and workplace as well as the grounds for mobilization, requirements for mobilized persons, equipment and property, and assembly time and point;
b) In case of mobilization of forces, equipment and property of a regulatory body, organization or individual not under their management, the incident commander may mobilize these forces, equipment and property for firefighting purpose with the verbal permission of the competent person, and shall advise this competent person on issuance of a written mobilization decision.
Article 24. Mobilization of prioritized vehicles, personnel and equipment of military forces, international organizations and foreign organizations and individuals in Vietnam for firefighting purpose
1. Military personnel and equipment not on emergency duty may be mobilized for firefighting and firefighting support purposes. Upon receipt of an order for mobilization of forces and equipment for firefighting and firefighting support purposes, military leaders must execute the order immediately or report to the competent authority for execution.
2. The following vehicles shall not be mobilized for firefighting and firefighting support purposes:
a) Military vehicles and police vehicles on emergency duty;
b) Ambulances on duty;
c) Dike protection vehicles, vehicles on natural disaster recovery or emergency duty per the law;
d) Motorcades led by the police;
dd) Vehicles in funeral processions;
e) Other prioritized vehicles per the law.
3. Personnel and vehicles of international organizations and foreign organizations and individuals in Vietnam may be mobilized for firefighting and firefighting support purposes, excluding international organizations and foreign organizations and individuals entitled to privileges and immunities as prescribed by law and conventions to which Vietnam is a signatory.
Article 25. Priority for personnel and equipment mobilized for firefighting purpose and exercise of priority rights
1. When operating for firefighting and firefighting support purposes, road vehicles, watercrafts, aircrafts and other vehicles of firefighting authorities may use priority signals and exercise traffic priority right and other priority rights as per the law.
Road motor vehicles and inland watercrafts of regulatory bodies, organizations and individuals mobilized for firefighting purpose are entitled to the priority rights mentioned in Point b Clause 2 Article 36 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting, and given priority when crossing bridges and using ferries, and exempt from road tolls.
2. When a person mobilized for firefighting purpose presents a mobilization order or notification of mobilization request from the competent person (in case the mobilization order is issued verbally), the vehicle owner or vehicle operator or persons with relevant responsibility shall permit the mobilized person to leave as soon as practicable.
Article 26. Urgent situations where right to demolish houses, works and obstacles and move property during firefighting operations may be exercised
The incident commander of a firefighting authority may exercise the right to demolish houses, works and obstacles and move property provided for in Point d Clause 1 Article 38 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting in the following urgent situations:
1. A person is trapped by the fire or the fire is directly threatening the lives of multiple persons.
2. The fire poses a direct risk of explosion or toxic hazard; a risk to the environment; a major threat to human lives and property; or a threat to political situation or foreign affairs unless preventive measures are promptly taken.
3. The houses, works and obstacles obstruct firefighting operations and there is no other more effective firefighting option.
Article 27. Return of and compensation for equipment and property mobilized for firefighting purpose
Equipment and property of regulatory bodies, organizations, households and individuals mobilized for firefighting or firefighting support purpose must be returned immediately after firefighting operations end. Mobilized equipment and property that are damaged, and houses and works that are demolished according to regulations in Points c and d Clause 1 Article 38 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting shall be compensated as per the law.
Article 28. Suppression of fire on premises of diplomatic missions, consular missions, representatives of international organizations and houses of members thereof
1. Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter the premises of the following bodies for firefighting purpose at the request or with the permission of the head or authorized person of these bodies:
a) Diplomatic missions;
b) Consular missions of countries with which Vietnam has signed a consular agreement stipulating that Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter the premises of these missions for firefighting purpose at the request or with the permission of the heads or authorized persons of these missions;
c) Representatives of international organizations affiliated to the United Nations;
d) Representatives of intergovernmental international organizations not affiliated to the United Nations, and mass organizations of international organizations with which Vietnam has signed an agreement stipulating that Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter the premises of these bodies for firefighting purpose at the request or with the permission of the heads or authorized persons of these bodies.
2. Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter the premises of consular missions and representatives of international organizations besides those mentioned in Clause 1 herein for firefighting purpose without a request or permission from the heads or authorized persons of these bodies.
3. Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter the houses of the following persons for firefighting purpose at the request or with the permission of these persons:
a) Members of diplomatic missions, and family members of members of diplomatic missions who do not hold Vietnamese nationality; administrative and technical staff and their family members who do not hold Vietnamese nationality or reside permanently in Vietnam;
b) Members of consular posts who do not hold Vietnamese nationality or reside permanently in Vietnam; if the consular agreements between Vietnam and the home countries of these persons stipulate that Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter their houses for firefighting purpose at their request or with their permission.
4. Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter the houses of members of consular missions and representatives of international organizations besides those mentioned in Clause 3 herein for firefighting purpose without a request or permission from these members.
Article 29. Signal flags, signage, armband and tape used in firefighting operations
1. Signal flags, signage, armband and tape used in firefighting operations include:
a) Firefighting signal flag; signal flag of firefighting command team;
b) Incident commander armband;
c) Fire area signboard, fire area barricade tape;
d) Fire area no entry sign.
2. Specifications of signal flags, signage, armband and tape used in firefighting operations are provided for in Appendix VIII enclosed therewith.
Article 30. Establishment and management of neighborhood watch and assurance of operating conditions thereof
1. The commune-level police authority shall advise the Chairperson of the People’s Committee at the same level on establishment of the neighborhood watch at the request of the village head and directly direct operations of the neighborhood watch. The Chairperson of the commune-level People’s Committee shall decide establishment, promulgate operating regulations, ensure funding, workplace, equipment and necessary conditions and maintain operation of the neighborhood watch.
2. Neighborhood watch composition:
a) The neighborhood watch shall have from 10 to 20 members on payroll, including 01 leader and 01 vice leader; one more person shall be appointed vice leader if the payroll has from 20 to 30 members. The neighborhood watch may be divided into smaller teams consisting of from 05 to 09 members on payroll, including 01 leader and 01 vice leader;
b) The Chairperson of the commune-level People’s Committee has the power to appoint the leader and vice leader(s) of the neighborhood watch and leaders and vice leaders of neighborhood watch teams.
3. The neighborhood watch shall comprise of persons regularly present at their places of residence.
4. The police authority shall direct, inspect and provide guidance on fire prevention and fighting operations for the neighborhood watch.
Article 31. Establishment and management of internal and specialized firefighting forces and assurance of operating conditions thereof
1. Heads of facilities and owners of businesses of infrastructures for industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones and hi-tech parks shall establish an internal firefighting force and directly maintain its operation on a full-time or part-time basis. Heads of the regulatory bodies and organizations mentioned in Clause 3 Article 44 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting shall establish and maintain a specialized firefighting force and directly maintain its operation on a full-time or part-time basis.
2. Heads of regulatory bodies and organizations directly managing a facility shall decide establishment, promulgate operating regulations, ensure funding, equipment and necessary conditions and maintain operation of the internal firefighting force and specialized firefighting force.
3. Composition of internal and specialized firefighting forces:
a) For facilities with less than 10 regular workers, all workers shall participate in the internal and/or specialized firefighting force, which shall be led by the facility head;
b) For facilities with from 10 to 50 regular workers, the internal and/or specialized firefighting force shall have at least 10 members on payroll, including 01 leader;
c) For facilities with from 50 to 100 regular workers, the internal and/or specialized firefighting force shall have at least 15 members on payroll, including 01 leader and 01 vice leader;
d) For facilities with more than 100 regular workers, the internal and/or specialized firefighting force shall have at least 25 members on payroll, including 01 leader and 02 vice leaders;
dd) For facilities with multiple independent business units and factories and more than 100 regular workers, each unit or factory shall have 01 internal and/or specialized firefighting team with at least 05 members on payroll, including 01 leader;
e) For facilities provided with motor firefighting equipment, the standing members of the internal or specialized firefighting force on payroll must correspond to the number of equipment;
g) For automated electrical substations the automated fire safety systems of which are connected with and display and report fire incidents to the supervisory authorities, and which have systems for management of databases on fire prevention, fire fighting and fire reporting to firefighting authorities, they are not require to establish and maintain an internal firefighting force. Regulatory bodies and organizations directly operating and managing electrical substations shall satisfy fire safety conditions applicable to their electrical substation and maintain such satisfaction.
4. Police authorities shall direct, inspect and provide guidance on fire prevention and fighting operations for internal and specialized firefighting forces.
Article 32. Volunteer fire prevention and fighting
1. Individuals volunteering for fire prevention and fighting must register with the People’s Committees of the communes where they reside or their workplaces or commune-level People's Committees, regulatory bodies and organizations responsible for receiving their registration and drawing up and sending a list of volunteers to the supervisory police authority.
Organizations volunteering for fire prevention and fighting must register with the supervisory police authority.
2. Organizations and individuals having registered for volunteer fire prevention and fighting must fulfill their duties and follow the direction of the leader and vice leaders of the neighborhood watch and internal firefighting forces or other competent persons according to regulations.
3. Fire prevention and fighting volunteers are entitled to benefits offered to members of the neighborhood watch and internal firefighting forces.
Article 33. Training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operations
1. Persons required to participate in training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operations include:
a) The persons holding the incident commander title provided for in Clause 2 Article 37 of the Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting;
b) Members of the neighborhood watch and internal firefighting forces;
c) Members of specialized firefighting forces:
d) Persons working in an environment containing fire or explosion hazard or regularly coming into contact with goods posing fire or explosion hazard;
dd) Drivers and crewmembers of motor passengers vehicles with more than 29 seats and motor vehicles transporting goods posing fire or explosion hazard;
e) Persons in charge of fire prevention and fighting in facilities included in the list in Appendix IV enclosed therewith;
g) Members of forest fire fighting forces.
2. Content of training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operations comprises:
a) Legal knowledge and knowledge about fire prevention and fighting suitable for each type of trainees;
b) Methods for communication and establishment of the all people’s fire prevention and fighting movement;
c) Fire prevention measures; firefighting techniques, tactics and measures;
d) Methods for firefighting plan formulation and drills;
dd) Methods for preservation and use of fire prevention and fighting equipment;
e) Methods for fire safety inspection.
3. Duration of training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operations
a) Duration of first training and refresher courses: from 16 to 24 hours for the persons mentioned in Points a, b, d, dd, e and g Clause 1 herein and from 32 to 48 hours for the persons mentioned in Point c Clause 1 herein;
b) Duration of retraining for reissuance of an expired certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations: at least 16 hours for the persons mentioned in Points a, b, d, dd, e and g Clause 1 herein and 32 hours for the persons mentioned in Point c Clause 1 herein;
c) Duration of annual refresher courses: at least 08 hours for the persons mentioned in Points a, b, d, dd, e and g Clause 1 herein and at least 16 hours for the persons mentioned in Point c Clause 1 herein.
4. Responsibility for organization of training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operations:
a) Chairpersons of People’s Committees at all levels and heads of regulatory bodies, organizations and facilities shall organize training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting operations for persons under their management;
b) Any regulatory body, organization, facility or individual wishing to participate in a training or refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations may request the police authority or a provider of training in fire prevention and fighting operations certified as eligible for fire prevention and fighting service business to provide the course. The regulatory body, organization, facility or individual participating in the course shall incur the training cost.
5. Application for certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations includes:
a) For providers of training in fire prevention and fighting operations: an application for examination and issuance of the training certificate (made using Form No. PC21); training plan, program and content; and list of trainee’s resume;
b) For regulatory bodies, organizations and facilities requesting the police authority or a provider of training in fire prevention and fighting operations to provide training: an application for training, examination and issuance of the training certificate (made using Form No. PC22); and list of trainee’s resume;
c) For individuals wishing to receive training and apply for the certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations: an application for training, examination and issuance of the training certificate (made using Form No. PC23).
6. Application for reissuance of a damaged certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations includes an application for reissuance of the training certificate (made using Form No. PC24) and issued training certificate.
7. Application for reissuance of a lost certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations includes an application for reissuance of the training certificate (made using Form No. PC24).
8. The applicant shall submit 01 application prepared according to Clause 13 herein to the competent authority in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
9. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations, receive it and fill out 02 copies of the acknowledgement of application receipt (using Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations in Clause 4 herein, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application as per regulations and fill out the application revision instruction (using Form No. PC04).
10. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
11. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
12. Time limit for handling of procedures for training, examination, issuance and reissuance of the certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations:
a) For providers of training in fire prevention and fighting operations: within 05 working days starting from the date of receipt of a valid application, the police authority shall assess training results of trainees;
b) For regulatory bodies, organizations, facilities and individuals requesting the police authority to provide training:
If there are 20 trainees or more, within 05 working days starting from the date of receipt of a valid application, the police authority shall provide the training and assess training results of the trainees;
If there are less than 20 trainees, the police authority shall gather trainees; and, when there are sufficient trainees, notify the training time and location and assess training results;
c) Within 05 working days starting from the date upon which a pass result is available, the competent police authority shall issue the certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations (made using Form No. 02 promulgated together with the Government’s Decree No. 83/2017/ND-CP dated July 18, 2017) to trainees having completed the training course. A written explanation must be provided for trainees not granted a certificate.
d) The certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations shall be reissued within 05 working days starting from the date of receipt of a valid application. A written explanation must be provided for rejected applications.
13. Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue, fire departments and district-level police authorities have the power to issue the certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations, which is valid throughout the country for 5 years starting from the date of issuance. When the certificate expires, the holder must undergo training in order to be issued with a new certificate.
Article 34. Benefits offered to firefighting participants and members of the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces
1. Persons mobilized to participate in and support firefighting operations directly per a mobilization order by the competent person are entitled to the following benefits:
a) Receive an amount equal to 30% of the region-based daily minimum wage if they are mobilized for less than 02 hours;
b) Receive an amount equal to 45% of the region-based daily minimum wage if they are mobilized for from 02 to less than 04 hours;
c) If they are mobilized for 04 hours or more or for multiple days, they are entitled to an amount equal to 60% of the region-based daily minimum wage every 04 hours. If they are mobilized from 10:00 PM to 6:00 AM, they are entitled to twice the abovementioned amount;
d) If they are involved in an accident or sustain an injury, their medical bills will be covered; if they sustain an injury that reduces their work capacity according to the conclusion of the medical examination council, they are entitled to a benefit corresponding to the level of work capacity reduction; if they are deceased, they are entitled to death benefits and funeral payment. The abovementioned benefits shall be provided by social insurance and health insurance according to regulations; if a recipient of any of these benefits is an eligible social/health insurance participant, their benefit shall be provided by local government budget or the body managing them;
dd) If they sustain an injury in a manner mentioned in the Ordinance on Benefits for People with Meritorious Services to Revolutions, they may be considered for receipt of benefits offered to war invalids or similar benefits;
e) If they are deceased in a manner mentioned in the Ordinance on Benefits for People with Meritorious Services to Revolutions, they may be considered for recognition as martyrs.
2. Chairpersons of the People’s Committees of provinces and central-affiliated cities shall propose decision on monthly benefit rates for leaders and vice leaders the neighborhood watch, which are set based on actual situation of each province/city but no lower than 15% of the region-based minimum wage, to the People's Council of the same level.
3. Leaders and vice leaders of internal and specialized firefighting forces operating on a part-time basis are entitled to full wages and other allowances (if any) and regular remuneration from their managing bodies. Based on actual situation, heads of their managing bodies shall decide the benefit rate for each title, which shall be no lower than 20% of the region-based minimum wage.
4. When participating in a training or refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations, members of the neighborhood watch are entitled to an amount equal to 60% of the region-based daily minimum wage on a daily basis; members of internal and specialized firefighting forces may be exempt from their duties and receive full wages and other allowances (if any), and are entitled to an amount equal to 30% of the region-based daily minimum wage on a daily basis.
5. When the persons mentioned in Clause 4 herein participate in a training or refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations and got involved in an accident, suffer from bodily harm or are deceased, they are entitled to social insurance benefits, death benefits and funeral payment; if they are eligible social insurance participants, these amounts shall be provided by local government budget or their managing bodies.
Article 35. Mobilization of neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces for fire prevention and fighting operations
1. Competence in mobilization of the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces for fire prevention and fighting operations:
a) Chairpersons of the People’s Committees at all levels and heads of regulatory bodies and organizations have the power to mobilize the neighborhood watch, internal firefighting forces and specialized firefighting forces under their management;
b) Heads of provincial police authorities, heads of fire departments and heads of district-level police authorities have the power to mobilize the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces in the localities under their management;
c) Head of the Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue has the power to mobilize the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces across the country,
2. Upon receipt of a mobilization order, managers of the mobilized neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces must follow the order.
3. Procedure for mobilization of the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces for fire prevention and fighting operations:
a) When mobilized for communication activities, meetings, marches and maneuvers concerning fire prevention and fighting, firefighting plan drills; elimination of fire and explosion risks; recovery from fire damage and other fire prevention and fighting operations, the neighborhood watch, internal firefighting forces and specialized firefighting forces shall comply with requests from competent persons;
b) The neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces must be mobilized for fire prevention and fighting operations by a mobilization order (made using Form No. PC20); in case of emergency, they may be mobilized verbally and a written mobilization order shall be issued no later than 03 working days afterwards. A verbal mobilization order must include full name, post, workplace, address and phone number of the person giving the order, the exact number of people to mobilize, assembly time and point, and information on the operation;
c) Mobilization orders shall be sent to the mobilized entities and archived.
Article 36. Benefits offered to officers, non-commissioned officers and soldiers of firefighting authorities
Besides benefits offered to officers, non-commissioned officers and soldiers of the police force according to regulations, officers, non-commissioned officers and soldiers of firefighting authorities are entitled to special diet after training or working; and benefits offered according to the list of extremely arduous, hazardous and dangerous occupations prescribed by law.
FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHTING EQUIPMENT
Article 37. Fire prevention and fighting equipment
1. Fire prevention and fighting equipment includes motor equipment, equipment, machines, tools, chemicals and support tools used for fire prevention and fighting as well as human and property rescue and mentioned in Appendix VI enclosed therewith.
2. Motor firefighting equipment of firefighting authorities are mentioned in Section 1 of Appendix VI enclosed therewith.
3. Requirements for domestically manufactured or imported fire prevention and fighting equipment:
a) They must meet technical specifications laid down for fire prevention and fighting purposes;
b) They are compliant with Vietnamese regulations and standards or foreign or international standards applicable in Vietnam.
Article 38. Inspection of fire prevention and fighting equipment
1. Inspection of fire prevention and fighting equipment is a procedural activity carried out by competent authorities and organizations to inspect, assess and certify the compliance of fire prevention and fighting equipment with requirements and regulations stated in technical regulations and standards or fire safety requirements according to guidelines from the Ministry of Public Security.
2. The fire prevention and fighting equipment included in the list in Appendix VII enclosed therewith and domestically manufactured, assembled or converted or imported must undergo an inspection and be issued with a equipment inspection certificate before they are put into use.
3. Inspected items:
a) Type and design of the equipment;
b) Technical specifications related to the quality of the equipment.
4. Inspection methods:
a) Inspect quantity, origin, manufacturing date, serial number and technical specifications of the equipment;
b) Inspect type and design of the equipment;
c) Inspect, test and assess quality of sample equipment.
The sample equipment used for inspection shall be randomly selected using the sampling method stipulated in the corresponding technical regulation or standard. In case there is no technical regulation or standard providing for inspection, testing and assessment of quality of sample of a type of fire prevention and fighting equipment, foreign or international regulations and standards applicable in Vietnam shall apply. Results of inspections performed by foreign authorities and organizations permitted to consider issuance of the inspection certificate by competent authorities of their home countries are acceptable;
d) Assess results and draw up a record of fire prevention and fighting equipment inspection (using Form No. PC25).
5. Components of applications for inspection and/or issuance of the equipment inspection certificate:
a) Application for inspection and issuance of the equipment inspection certificate includes an application for inspection and issuance of the equipment inspection certificate (made using Form No. PC26) by the unit directly and domestically manufacturing, assembling or converting or importing the equipment; certificate of origin or factory release certificate; equipment quality certificate (if any); and technical documents of the inspected equipment;
b) Application for inspection of fire prevention and fighting equipment includes an application for fire prevention and fighting equipment inspection (made using Form No. PC26) by the unit directly and domestically manufacturing, assembling or converting or importing the equipment; certificate of origin or factory release certificate; equipment quality certificate (if any); and technical documents of the inspected equipment;
c) Application for issuance of the equipment inspection certificate includes an application for issuance of the equipment inspection certificate (made using Form No. PC27); inspection record by provider of technical fire prevention and fighting inspection consultancy (hereinafter referred to as “inspection consultancy provider”); record of inspected equipment sampling (made using Form No. PC28); certificate of origin or factory release certificate; equipment quality certificate (if any); and technical documents of the inspected equipment;
d) Documents included in these applications shall be the authentic copy or notarized or certified true copy or copy/photocopy submitted together with its authentic copy for comparison. For applications in a foreign language, a Vietnamese translation must be provided and the applicant shall take responsibility for the content of the translation.
6. The applicant shall submit 01 application prepared according to Clause 5 herein to the competent police authority mentioned in Clause 11 herein in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
7. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations in Clause 5 herein, receive it and fill out the acknowledgement of application receipt (using Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations in Clause 5 herein, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application as per regulations and fill out the application revision instruction (using Form No. PC04).
8. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
9. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
10. Time limit for application processing:
a) In case of application for inspection by the police authority and issuance of the equipment inspection certificate:
Within 02 working days starting from the date of receipt of an application valid according to regulations in Point a Clause 5 herein, the receiving police authority shall notify the applicant that the sample will be selected by probability sampling, and draw up a sampling record after finishing sampling (using Form No. PC28). Within 03 working days starting from the date upon which the inspection results and inspection record are available, the police authority shall notify the inspection results and issue the equipment inspection certificate to the applicant; and provide a written explanation for the applicant if not issuing the certificate.
b) In case of application for issuance of the equipment inspection certificate to equipment inspected by inspection consultancy provider:
Within 05 working days starting from the date of receipt of an application valid according to regulations in Point c Clause 5 herein, the competent police authority shall consider and assess the inspection results and issue the equipment inspection certificate; and provide a written explanation for the applicant if not issuing the certificate;
c) Each piece of fire prevention and fighting equipment shall undergo inspection once before it is issued with the equipment inspection certificate (made using Form No. PC29) and affixed with an inspection stamp. Within 03 working days starting from the date of issuance of the equipment inspection certificate, the inspecting unit shall cooperate with the issuing authority in affixing the inspection stamp to the equipment according to the issued equipment inspection certificate.
11. Competence in inspection and issuance of the equipment inspection certificate:
a) Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue has the power to inspect and issue the equipment inspection certificate to the fire prevention and fighting equipment included in the list in Appendix VII enclosed therewith;
b) Fire departments have the power to issue the equipment inspection certificate to the fire prevention and fighting equipment mentioned in Sections 2, 3, 6, 7 and 8 of Appendix VII enclosed therewith and owned by regulatory bodies and organizations whose premises are located in the localities under their management, and to cases authorized by the Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue;
c) Police-affiliated units eligible and permitted to perform inspection by the Ministry of Public Security; and inspection consultancy providers certified as eligible to engage in fire prevention and fighting service business may receive inspection applications, sample, perform inspection and make inspection records (using Form No. PC25) for the types of fire prevention and fighting equipment which are mentioned in the list in Appendix VII enclosed therewith and of which they are permitted to perform inspection. After the inspection results are available, they must send a written notification together with the inspection record to the applicant applying for the inspection, who will then complete their application for issuance of the equipment inspection certificate according to regulations in Point c Clause 5 herein and submit the application to the competent police authority for consideration and issuance of the certificate.
Article 39. Provision of equipment to firefighting authorities
Firefighting authorities shall be provided with modern fire prevention and fighting equipment and other equipment in adequate and consistent quantity and quality, meeting fire prevention, firefighting and rescue requirements in all cases and within capacity of state budget.
Article 40. Management and use of fire prevention and fighting equipment
1. Fire prevention and fighting equipment must be managed, maintained and repaired according to regulations and be ready for firefighting operations. Motor firefighting equipment may also be used for the following purposes:
a) Political security preservation;
b) Protection of public order and social safety;
c) Human rescue; emergency intervention;
d) Natural disaster control and recovery.
2. The Minister of Public Security or an authorized person and Chairpersons of provincial People’s Committees have the right to mobilize motor firefighting equipment for the purposes mentioned in Clause 1 herein.
3. Head of Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue, heads of provincial police authorities, heads of fire departments and heads of district-level police authorities have the right to mobilize motor firefighting equipment for the purposes mentioned in Points b, c and d Clause 1 herein intra vires.
4. Heads of regulatory bodies and organizations have the right to mobilize motor firefighting equipment for the purposes mentioned in Points c and d Clause 1 herein intra vires.
FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHTING SERVICE BUSINESS
Article 41. Conditions for fire prevention and fighting service business
1. Fire prevention and fighting service businesses (hereinafter referred to as “service businesses”) include enterprises; cooperatives; cooperative unions; branches and facilities affiliated to enterprises, cooperatives and cooperative unions; service providers of regulatory bodies and organizations; and household businesses.
2. Heads and legal representatives of the service businesses mentioned in Clause 1 herein must have a degree or certificate concerning completion of a refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations and undersign any of the following documents: enterprise registration certificate; investment registration certificate; branch/affiliate operation registration certificate; cooperative/cooperative union registration certificate; certificate of registration of branch/business location of cooperative/cooperative union; operation license issued by the competent authority; household business registration certificate; or establishment document or operation license and tax identification number notification (for service providers).
In case the head or legal representative of a service business is a foreigner who has a degree or certificate concerning completion of a refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations or practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting issued by a foreign authority or organization, the degree or certificate must undergo consular legalization.
3. Requirements for facilities and equipment of fire prevention and fighting service business:
a) For service businesses providing fire safety design consultancy, appraisal consultancy or supervision consultancy, they shall have business premises; and equipment enabling fire safety design consultancy, appraisal consultancy or supervision consultancy;
b) For service businesses providing technical fire prevention and fighting inspection consultancy, they shall have laboratories and inspection equipment whose quality is certified by competent authorities;
c) For service businesses providing consultancy concerning transfer of fire prevention and fighting technology; or training in fire prevention and fighting operations, they shall have equipment enabling technology transfer consultancy; or equipment and location for training in fire prevention and fighting operations;
d) For service businesses engaging in fire prevention and fighting system construction, they shall have equipment enabling fire prevention and fighting system construction;
dd) For service businesses engaging in production and assembling of fire prevention and fighting equipment, they shall have business premises; and factories and equipment for production, assembling and testing of fire prevention and fighting equipment.
4. For service businesses providing fire safety design consultancy, appraisal consultancy and supervision consultancy, besides the conditions in Clauses 2 and 3 herein, each of these businesses must have at least 02 individuals who hold a practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy suitable for the consultancy area in compliance with regulations in Points and d Clause 3 Article 43 herein; in which, at least 01 individual takes charge of fire safety design, appraisal and supervision.
5. For service businesses providing technical fire prevention and fighting inspection consultancy, besides the conditions in Clauses 2 and 3 herein, each of these businesses must have at least 02 individuals who hold a practitioner certificate in compliance with regulations in Point c Clause 3 Article 43 herein.
6. For service businesses providing consultancy concerning transfer of fire prevention and fighting technology; or training in fire prevention and fighting operations, besides the conditions in Clauses 2 and 3 herein, each of these businesses shall have at least 01 person holding a bachelor’s degree or higher in fire prevention and fighting or another major suitable for the business’s scope of service and a certificate of completion of refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations.
7. For service businesses engaging in fire prevention and fighting system construction, besides the conditions in Clauses 2 and 3 herein, each of these businesses must have at least 01 construction manager who has a practitioner certificate in managing fire prevention and fighting construction in compliance with regulations in Point dd Clause 3 Article 43 herein.
8. For service businesses engaging in production and assembling of fire prevention and fighting equipment, besides the conditions in Clauses 2 and 3 herein, each of these businesses shall have at least 01 person holding a bachelor’s degree or higher in fire prevention and fighting or another major suitable for the business’s scope of service and a certificate of completion of refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations.
9. Service businesses engaging in trade of fire prevention and fighting equipment shall adhere to regulations in Clauses 2 and 3 herein.
10. The persons mentioned in Clauses 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 herein must directly participate in service business operations of their businesses.
A person who has used a degree or certificate to enable operation of a service business may not use this degree or certificate to enable operation of another service business.
Article 42. Conditions for individual providers of fire prevention and fighting services
An individual may provide fire prevention and fighting services under the following conditions:
1. The individual has a practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting suitable for their business operations.
2. The individual works for a service business.
Article 43. Degrees and certificates concerning fire prevention and fighting and conditions for issuance of certificates concerning fire prevention and fighting
1. Degrees concerning fire prevention and fighting:
a) Doctor’s degree in fire prevention and fighting;
b) Master’s degree and equivalent degrees in fire prevention and fighting;
c) Bachelor’s degree and equivalent degrees in fire prevention and fighting;
d) College’s degree in fire prevention and fighting;
dd) Intermediate professional education diploma in fire prevention and fighting.
2. Certificates concerning fire prevention and fighting:
a) Certificate of completion of refresher course on fire prevention and fighting;
b) Practitioner certificates in fire prevention and fighting consultancy: practitioner certificate in fire safety consultancy; practitioner certificate in fire safety appraisal consultancy; practitioner certificate in fire safety supervision consultancy; practitioner certificate in technical fire prevention and fighting inspection consultancy; and practitioner certificate in managing fire prevention and fighting construction.
3. Conditions for granting of certificates concerning fire prevention and fighting:
a) Those who have completed a refresher course on fire prevention and fighting will be granted a certificate of completion of refresher course on fire prevention and fighting.
The certificate of completion of refresher course on fire prevention and fighting shall be granted by educational institutions providing training in fire prevention and fighting operations and is valid throughout the country;
b) Conditions for granting of practitioner certificates in fire safety design consultancy and fire safety appraisal consultancy:
The applicant holds a college's degree or higher in fire prevention and fighting or bachelor’s degree or higher in a major suitable for their scope of consultancy and a certificate of completion of refresher course in fire prevention and fighting operations;
The applicant has provided fire safety design or appraisal consultancy for at least 03 projects and/or works issued with the certificate of fire safety design appraisal by firefighting authorities.
c) Conditions for granting of practitioner certificate in technical fire prevention and fighting inspection:
The applicant holds a college's degree or higher in fire prevention and fighting or bachelor’s degree or higher in a major suitable for their scope of consultancy and a certificate of completion of refresher course in fire prevention and fighting operations;
d) Conditions for granting of practitioner certificate in fire safety supervision consultancy:
The applicant holds a intermediate professional education diploma or higher in fire prevention and fighting or intermediate professional education diploma or higher in a major suitable for their scope of consultancy and a certificate of completion of refresher course in fire prevention and fighting operations;
The applicant has supervised the construction of at least 03 projects and/or works issued with the written approval of fire safety commissioning results by firefighting authorities;
The applicant has a certificate of completion of refresher course in construction supervision operations.
dd) Conditions for granting of practitioner certificate in managing fire prevention and fighting construction:
The applicant holds a intermediate professional education diploma or higher in fire prevention and fighting or intermediate professional education diploma or higher in a major suitable for their work and a certificate of completion of refresher course in fire prevention and fighting operations;
The applicant has supervised the construction of the fire prevention and fighting system of at least 03 projects and/or works issued with the written approval of fire safety commissioning results by firefighting authorities.
4. Conditions for persons in charge of fire safety design, appraisal and supervision:
a) They have a practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy mentioned in Point b Clause 2 herein appropriate to their titles;
b) They have at least 03 years of experience relevant to their work and have provided fire safety design, appraisal or supervision consultancy for at least 03 projects and/or works issued with the certificate of fire safety design appraisal and written approval of fire safety commissioning results by firefighting authorities.
5. The suitable majors mentioned in Article 41 and this Article include the following academic disciplines: architecture and planning; construction; construction management (excluding construction economics); construction and architectural engineering technology; mechanical engineering technology; electrical, electronic and telecommunications engineering technology; oil and gas technology and extraction; mechanical engineering and engineering mechanics (excluding printing engineering); and electrical, electronic and telecommunications engineering (excluding biomedical engineering) according to regulations of the Ministry of Education and Training.
Article 44. Practitioner certificates in fire prevention and fighting consultancy
1. Application for issuance of a practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy includes:
a) An application for issuance of practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy (made using Form No. PC30);
b) Declaration of professional experience in fire prevention and fighting operations (made using Form No. PC31);
c) Degrees and certificates related to application for issuance of the certificate;
d) 02 3x4 cm color photos of the applicant.
2. Application for reissuance of a practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy upon addition to the applicant’s scope of consultancy includes the documents mentioned in Clause 1 herein and the issued practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy.
3. Application for reissuance of an expired or damaged practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy includes the documents mentioned in Points a and d Clause 1 herein and the issued practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy.
4. Application for reissuance of a lost practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy includes the documents mentioned in Points a and d Clause 1 herein and a declaration of loss of the certificate with confirmation of the police authority of the locality where the certificate is lost.
5. Documents included in applications for issuance or reissuance of practitioner certificates in fire prevention and fighting consultancy submitted to police authorities shall be the authentic copy or notarized or certified true copy or copy/photocopy submitted together with its authentic copy for comparison.
6. The applicant shall submit 01 application to the competent authority specified in Clause 11 in any of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
7. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations, receive it and fill out 02 copies of the acknowledgement of application receipt (using Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application and fill out the application revision instruction (using Form No. PC04).
8. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
9. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
10. Within 07 working days from the date of receipt of a valid application, the competent authority shall consider and issue or reissue the practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy (using Form No. PC32). If the application is rejected, the competent authority must send a written explanation to the applicant.
11. Competence in issuance and reissuance of practitioner certificates in fire prevention and fighting consultancy:
Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue has the power to issue and reissue practitioner certificates in fire prevention and fighting consultancy nationwide.
12. Practitioner certificates in fire prevention and fighting consultancy are valid nationwide.
Article 45. Certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business
1. Application for issuance of a certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business includes:
a) An application for issuance of certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business (made using Form No. PC33);
b) Degree or certificate concerning completion of a refresher course in fire prevention and fighting of the head or legal representative of the service business;
c) List of holders of a practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy suitable for the service business’s scope of service; and practitioner certificate in fire prevention and fighting consultancy and decision on employment or labor contract of each holder;
d) Written proof of availability of facilities and equipment necessary for business operations: certificate of ownership or agreement on lease of business location; list of equipment for business operations; certificate of laboratory quality and assessment of calibration of inspection equipment by the competent authority (for application for issuance of certificate of eligibility for technical fire prevention and fighting inspection consultancy).
2. Application for reissuance of a certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business upon change of head or legal representative includes the documents mentioned in Points a and b Clause 1 herein and the issued certificate of eligibility of fire prevention and fighting service business.
3. Application for reissuance of a certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business upon change of business location or change or addition to fire prevention and fighting service business lines includes the documents mentioned in Points a, c and d Clause 1 herein and the issued certificate of eligibility of fire prevention and fighting service business.
4. Application for reissuance of a certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business upon damage to the certificate or change to the service business’s name includes the documents mentioned in Point a Clause 1 herein and the issued certificate of eligibility of fire prevention and fighting service business.
5. Application for reissuance of a lost certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business includes the documents mentioned in Point a Clause 1 herein and a declaration of loss of the certificate with confirmation of the police authority of the locality where the certificate is lost.
6. Documents included in applications for issuance or reissuance of certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business submitted to police authorities shall be the authentic copy or notarized or certified true copy or copy/photocopy submitted together with its authentic copy for comparison.
7. The applicant shall submit 01 application prepared according to Clause 12 herein to the competent authority in one of the following ways:
a) Directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority;
b) Online via the public service portal of the competent authority (documents included in state secret lists shall be submitted in compliance with regulations of laws on state secret protection);
c) By public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law.
8. The official receiving the application shall check its components and validity and perform the following tasks:
a) If the application is adequate and valid according to regulations, receive it and fill out 02 copies of the acknowledgement of application receipt (using Form No. PC03);
b) If the application is inadequate or invalid according to regulations in Clause 4 herein, instruct the applicant on how to complete the application as per regulations and fill out the application revision instruction (using Form No. PC04).
9. Announcement of application processing results:
a) If the application is submitted directly at the single-window unit of the competent authority, the official receiving it shall give 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy;
b) If the application is submitted via the public service portal of the competent authority, the official receiving the application shall send a notification of application receipt or instruction on application revision to the applicant via email or text message;
c) If the application is submitted by public postal service, the service of an enterprise and individual or authorization as per the law, the official receiving it shall send 01 copy of the acknowledgement of application receipt or application revision instruction to the applicant and retain 01 copy.
10. The person sent to submit the application by the applicant must have a letter of introduction or letter of authorization and present their unexpired identity card or passport.
11. Within 07 working days from the date of receipt of a valid application, the competent authority shall consider and issue or reissue the certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business (using Form No. PC34). If the application is rejected, the competent authority must send a written explanation to the applicant.
12. Competence in issuance and reissuance of certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business
a) Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue has the power to issue and reissue certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business to service businesses providing technical fire prevention and fighting inspection consultancy, service businesses engaging in production and assembling of fire prevention and fighting equipment; service businesses established according to a ministerial-level decision; and foreign-invested service businesses;
b) Fire departments have the power to issue and reissue certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business to service businesses in localities under their management, excluding service businesses issuance of certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business of which is within the competence of Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue.
13. Service businesses may engage in fire prevention and fighting service business only after they are granted a certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business by the police authority.
Article 46. Management, use and revocation of certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business
1. The head/legal representative of a service business shall manage the certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business issued to their business and perform the following tasks:
a) Return the certificate to the issuing police authority for revocation when their business is dissolved or goes bankrupt as per the law or no longer engages in fire prevention and fighting service business;
b) Notify the issuing police authority of the reason for and duration of temporary suspension of their business’s operations in writing when their business’s operations are temporarily suspended;
c) Carry out procedure for reissuance of the certificate when the certificate is lost or damaged, or the name, address or head/legal representative of their business is changed as per the law, or there is change or addition to the fire prevention and fighting service business lines of their business;
d) Present the certificate to the competent state agencies and police authority upon request.
2. A service business will have its certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business revoked when it fails to satisfy conditions for fire prevention and fighting service business after the certificate is issued. The certificate shall be revoked in compliance with regulations in Clause 4 Article 16 herein. After revocation, the police authority shall notify the revocation to the enterprise registration authority or competent authority permitting the service business to operate in writing.
FUNDING FOR FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHTING OPERATIONS
Article 47. Use of funding for fire prevention and fighting operations
1. Funding for fire prevention and fighting operations shall be distributed to the following activities:
a) Investment in fire prevention and fighting operations, facilities and equipment and equipment for firefighting authorities;
b) Assistance for operations of the neighborhood watch, internal firefighting forces and specialized firefighting forces;
c) Assistance for communication and establishment of the all people’s fire prevention and fighting movement;
d) Assistance for commendation in relation to fire prevention and fighting operations;
dd) Assistance for other fire prevention and fighting operations.
2. Funding for fire prevention and fighting operations shall be managed and used as prescribed by law.
Article 48. Funding for fire prevention and fighting operations
1. Funding for fire prevention and fighting operations of firefighting authorities, state agencies, service providers, armed forces and other units funded by central and local government budgets shall be covered by state budget in accordance with existing state budget decentralization and other legal funding sources as per the law.
On an annual basis, the Ministry of Public Security shall formulate a plan for budget for fire prevention and fighting operations and assign Police Department of Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue to carry out this plan; People's Committees at all levels must formulate a plan for funding for fire prevention and fighting operations in their localities.
2. Regulatory bodies and organizations not funded by state budget, households, individuals and foreign organizations in Vietnam shall cover their fire prevention and fighting operations according to regulations.
3. Funding from state budget for operations of firefighting authorities shall be distributed to the following activities:
a) Regular operations of firefighting authorities;
b) Provision, renovation and modernization of fire prevention and fighting equipment and technical facilities; and scientific and technological research on fire prevention and fighting according to regulations.
4. Expenditure items for fire prevention and fighting operations of People's Committees at all levels:
a) Assistance for building, conversion and repair of work premises, purchase, provision, maintenance, repair, renovation and modernization of fire prevention and fighting equipment and technical facilities for firefighting authorities stationed in their localities;
b) Regular operations of the neighborhood watch; regular assistance for the leader and vice leaders of the neighborhood watch;
c) Purchase of protective equipment and fire prevention and fighting equipment for the neighborhood watch and internal firefighting forces of regulatory bodies and organizations funded by state budget.
Article 49. Encouraging investment in fire prevention and fighting
1. The State shall encourage and enable Vietnamese regulatory bodies, organizations and individuals, overseas Vietnameses, foreign organizations and individuals and international organizations to invest in and sponsor the following:
a) Fire prevention and fighting operations;
b) Fire prevention and fighting equipment;
c) Training and refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting;
d) Application of scientific and technological advancements in fire prevention and fighting;
dd) Building and development of facilities and technologies supporting fire prevention and fighting.
2. The State shall encourage research, domestic manufacturing and assembling and export of fire prevention and fighting equipment.
3. Regulatory bodies, organizations and individuals involved in domestic manufacturing and assembling, import and export of fire prevention and fighting equipment are entitled to tax incentives as per the State’s regulations.
RESPONSIBILITIES OF MINISTRIES, MINISTERIAL-LEVEL AGENCIES, GOVERNMENTAL AGENCIES AND PEOPLE’S COMMITTEES AT ALL LEVELS FOR FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHTING
Article 50. Responsibilities of ministries, ministerial-level agencies and Governmental agencies
1. Within their competence, ministries, ministerial-level agencies and Governmental agencies shall perform the following tasks:
a) Promulgate legislative documents and regulations on fire prevention and fighting applicable to areas under their management;
b) Organize dissemination of law and education on fire prevention and fighting; direct launch and preservation of the all people’s fire prevention and fighting movement;
c) Direct investment of funding in fire prevention and fighting and provision of fire prevention and fighting equipment;
d) Direct firefighting operations and recovery from fire damage;
dd) Assign personnel for fire prevention and fighting; produce statistics and submit reports on fire prevention and fighting to the Government and Ministry of Public Security.
2. The Ministry of Education and Training shall take charge and cooperate with the Ministry of Public Security and relevant ministries, central authorities and units in formulating content of training in fire prevention, firefighting and rescue, deciding training time and stipulating incorporation of training into subject-centered curricula and educational activities of the general education curricula and extracurricular activities as suitable for each educational stage and qualification.
3. The Ministry of Information and Communications shall take charge and cooperate with the Ministry of Public Security and relevant regulatory bodies in promoting dissemination of and education on law and providing knowledge and skills concerning fire prevention, firefighting and rescue.
4. The Ministry of Construction shall take charge and cooperate with the Ministry of Public Security and relevant ministries and central authorities in reviewing and amending construction planning, urban planning and planning under its management connected to planning for fire prevention and fighting infrastructures as appropriate to actual situation; researching, amending and formulating technical regulations and standards related to fire prevention and fighting for types of works lacking technical regulations and standards.
5. The Ministry of Finance shall take charge of allocating funding for recurrent expenditure to ministries and central government authorities in charge of fire prevention and fighting according to regulations of the Law on State Budget and guidelines thereof.
6. The Ministry of Planning and Investment shall take charge and cooperate with the Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Public Security and relevant ministries and central authorities in incorporating plans for 5-year and annual investment in development of fire prevention and fighting of ministries, central authorities and local governments into 5-year and annual socio - economic development plans of the state to ensure socio - economic development is connected with strengthening of national defense and security; appraising funding sources and ability to balance funding for projects on investment in construction of facilities and manufacturing and procurement of equipment for fire prevention and fighting according to regulations of the Law on Public Investment; and proposing the consolidated plans to the Government and the National Assembly for approval.
7. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs shall take charge and cooperate with the Ministry of Public Security in fire prevention and fighting for premises of diplomatic missions, consular missions and representatives of international organizations and houses of members thereof; post information on Vietnam-based international organizations and foreign organizations and individuals entitled to privileges and immunities concerning exemption from firefighting mobilization; notify the Ministry of Public Security of premises of consular missions of countries with which Vietnam has signed a consular agreement, premises of representatives of international organizations affiliated to the United Nations, premises of representatives of intergovernmental international organizations not affiliated to the United Nations, and mass organizations of international organizations where Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter for firefighting purpose at the request or with the permission of the heads or authorized persons of these entities; notify the Ministry of Public Security of houses of members of consular posts who do not have Vietnamese nationality or permanently reside in Vietnam where Vietnamese firefighting forces may enter for firefighting purpose at their request or with their permission as stipulated by consular agreements between Vietnam and their countries.
8. The Ministry of Labor - War Invalids and Social Affairs shall provide guidelines for benefits offered to persons mobilized to directly participate in or support firefighting operations as per a mobilization order by the competent person and involved in an accident, or suffering from reduced work capacity due to an accident as per the conclusion of the medical examination council, or sustaining an injury, or sustaining an injury mentioned in the Ordinance on Benefits for People with Meritorious Services to Revolutions, or deceased, or deceased in a manner mentioned in the Ordinance on Benefits for People with Meritorious Services to Revolutions; benefits offered to members of the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces upon participation in a training or refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations; and benefits offered to members of the neighborhood watch and internal and specialized firefighting forces involved in an accident, suffering from bodily harm or deceased during a refresher or training course on fire prevention and fighting operations as agreed upon with the Ministry of Public Security and Ministry of Finance.
9. The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development shall take charge and cooperate with the Ministry of Public Security, ministries, central authorities, local governments and relevant regulatory bodies in developing and implementing plans for force mobilization in forest fire prevention and fighting in an effective manner.
Article 51. Responsibilities of Ministry of Public Security
The Ministry of Public Security shall exercise unified state management of fire prevention and fighting throughout the country and perform the following tasks:
1. Propose and implement fire prevention and fighting strategies, planning and plans nationwide.
2. Promulgate or propose legislative documents, regulations and standards on fire prevention and fighting for promulgation; stipulate decentralization of fire prevention and fighting management, decentralization of training in fire prevention and fighting operations in police authorities and issuance of certificate thereof; stipulate content and duration of refresher courses on fire prevention and fighting; and provide guidelines for inspection of and training in fire safety design inspection and appraisal.
3. Provide guidance and direction on dissemination of law and education on fire prevention and fighting; establishment of the all people’s fire prevention and fighting movement;
4. Carry out fire management of motor vehicles and facilities under its management; inspect fire prevention and fighting; handle complaints and denunciations related to fire prevention and fighting intra vires.
5. Appraise and inspect fire safety commissioning results of investors and vehicle owners for projects, construction works and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements and provide for performance of these tasks by the police; inspect and issue certificate of compliance for fire prevention and fighting equipment; provide for, manage, print and distribute inspection stamps used for fire prevention and fighting equipment.
6. Investigate and handle fire incidents and handle violations against fire prevention and fighting regulations.
7. Provide regulations, guidelines and directions on receipt and handling of fire incident reports, firefighting operations direction, combat-ready firefighters, and firefighting plan formulation and drills according to regulations.
8. Develop and perform projects on investment in fire prevention and fighting equipment for firefighting authorities; promulgate and organize implementation of regulations on norms and standards for provision, management, preservation, maintenance and use of fire prevention and fighting equipment.
9. Develop firefighting authorities; organize training for fire prevention and fighting officials.
10. Organize research, distribution and application of scientific and technological advances in fire prevention and fighting.
11. Produce state statistics on fire prevention and fighting.
12. Organize an information system for management and command of fire prevention and fighting operations.
13. Inspect fire and explosion insurance connected with fire prevention and fighting.
14. Propose participation in international organizations and signing or participation in conventions on fire prevention and fighting to the Government; carry out international activities related to fire prevention and fighting intra vires.
Article 52. Responsibilities of People’s Committees at all levels
1. Provincial and district-level People’s Committees shall exercise state management of fire prevention and fighting in their provinces and districts and perform the following tasks intra vires:
a) Promulgate regulations on fire prevention and fighting in their provinces and cities;
b) Direct, inspect and organize implementation of regulations of law on fire prevention and fighting in their provinces and districts; handle violations against fire prevention and fighting regulations intra vires;
c) Provide guidance and direction on dissemination of law and education on fire prevention and fighting for the people; develop the all people’s fire prevention and fighting movement;
d) Allocate funding from budget to fire prevention and fighting and provision of fire prevention and fighting equipment;
dd) Ensure conditions for fire incident reporting and roads and water supply for firefighting purpose;
e) Develop planning for barracks of firefighting authorities, propose land allocation and build these barracks;
g) Direct formulation and drills of firefighting plans involving mobilization of multiple forces and equipment;
h) Direct firefighting operations and recovery from fire damage;
i) Produce statistics and submit reports on fire prevention and fighting to the supervisory People's Committees, the Government and Ministry of Public Security.
2. Commune-level People’s Committees shall exercise state management of fire prevention and fighting in their communes and perform the following tasks intra vires:
a) Promulgate, direct, inspect and organize implementation of regulations of law on fire prevention and fighting; inspect fire safety of residential areas, households, household businesses and facilities under their management; and handle violations against fire prevention and fighting regulations intra vires;
b) Organize dissemination of law and education on fire prevention and fighting; establish the all people’s fire prevention and fighting movement;
c) Organize management of the neighborhood watch of villages;
d) Direct investment of funding in fire prevention and fighting and provision of fire prevention and fighting equipment;
dd) Direct firefighting plan formulation and drills;;
e) Organize firefighting operations and recovery from fire damage;
g) Produce statistics and submit reports on fire prevention and fighting to district-level People's Committees.
1. This Decree takes effect from January 10, 2021 and supersedes the Government’s Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP dated July 31, 2014 providing guidelines for a number of Articles of Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting and Law on Amendments to Law on Fire Prevention and Fighting (hereinafter referred to as “Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP”).
2. In the cases where any of the legislative documents referred to in this Decree is amended or replaced, the newest one shall apply.
3. Handling of administrative procedures via the public service portal:
a) In the event where public service portals of competent authorities have not satisfied conditions for handling of administrative procedures by electronic means, application submission and announcement of application processing results shall be carried out directly at single-window units of competent authorities or by public postal service, service provided by an enterprise or individual or authorization as prescribed by law;
b) Application submission and announcement of application processing results when public service portals of competent authorities have satisfied conditions for handling of administrative procedures by electronic means shall be carried out in accordance with regulations of the Government’s Decree No.45/2020/ND-CP dated April 08, 2020 on administrative procedures by electronic means.
4. Transitional provisions:
a) For projects and works included in the list in Appendix IV and motor vehicles subject to special fire safety requirements mentioned in Clause 2 Article 10 of Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP and issued with the certificate of design appraisal but not mentioned in the list in Appendix V enclosed therewith, their construction and commissioning of their fire safety shall conform to regulations in Articles 14 and 15 of this Decree;
b) For projects and works excluded from the list in Appendix IV enclosed with Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP and having been appraised and issued with the construction permit by construction authorities or currently under construction, if they are included in the list in Appendix V enclosed with this Decree, their investors may continue the construction, carry out commissioning and take responsibility for their fire safety;
c) For facility firefighting plans formulated using Form No. PC11 enclosed with Circular No. 66/2014/TT-BCA dated December 16m 2014 by the Ministry of Public Security detailing implementation of a number of Articles of Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP dated July 31, 2014 (hereinafter referred to as “Circular No. 66/2014/TT-BCA”) and approved by competent authorities, if there is no change to the dangers posed by fire, explosion and toxic hazards and firefighting-related conditions, these plans may continue to be adopted and do not require reformulation or reapproval;
d) Applicants whose applications for the following procedures have been received before the entry into force of this Decree shall continue to follow regulations in Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP: issuance of the permit for transport of goods posing fire or explosion hazard; fire safety design appraisal and inspection of fire safety commissioning results; firefighting plan approval; issuance of the certificate of training in fire prevention and fighting operations; inspection of fire prevention and fighting equipment; and issuance of the practitioner certificate in fire safety consultancy and certificate of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business;
dd) Permits to transport goods posing fire or explosion hazard; fire safety design appraisal certificates, fire safety design appraisal documents; records of fire safety commissioning; inspection certificates of motor vehicles; practitioner certificates in fire safety consultancy; certificates of eligibility for fire prevention and fighting service business; and certificates of completion of refresher course on fire prevention and fighting operations issued according to regulations of Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP may continue to be used until their expiry dates (if any) as prescribed by law;
e) Units permitted to inspect fire prevention and fighting equipment by the Ministry of Public Security may continue to perform such inspection according to regulations of Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP, and must satisfy all requirements for inspection of fire prevention and fighting equipment provided for in this Decree within 24 months after the entry into force of this Decree. Inspection stamps used for fire prevention and fighting equipment shall be printed using Form No. PC20 promulgated together with Circular No. 36/2018/TT-BCA dated December 05, 2018 by the Ministry of Public Security amending some Articles of Circular No. 66/2014/TT-BCA until the Ministry of Public Security provides new regulations on inspection stamps used for fire prevention and fighting equipment.
Article 54. Implementing responsibilities
Ministers, heads of ministerial-level agencies, heads of Governmental agencies, Chairpersons of People’s Committees of provinces and central-affiliated cities and relevant organizations and individuals shall implement this Decree./.
|
|
P.P. THE GOVERNMENT |
LIST OF FACILITIES REQUIRING FIRE MANAGEMENT
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Premises of regulatory bodies at all levels.
2. Apartment buildings; tenement houses, dormitories; mixed-use buildings.
3. Junior kindergartens, senior kindergartens; primary schools, lower secondary schools; upper secondary schools, multi-level secondary schools; colleges, universities, academies; post-secondary schools; vocational schools; continuing education institutions; other educational institutions established under the Education Law.
4. Hospitals; polyclinics, clinics, sanitariums, physical rehabilitation facilities, orthopedic facilities, nursing homes, epidemic prevention and control facilities, medical centers, other healthcare facilities established under the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment.
5. Theaters, cinemas, circuses; convention centers; cultural centers, karaoke facilities, night clubs; bars, clubs, beauty clinics, massage shops, theme parks, zoos, aquariums.
6. Markets; shopping malls; supermarkets; department stores; convenience stores; restaurants and eateries.
7. Hotels, guesthouses; rented houses and other types of lodgings established under the Law on Tourism.
8. Workplaces of enterprises and socio - political organizations.
9. Museums, libraries; exhibits; storage facilities, bookstores, fair facilities; religious establishments.
10. Post offices, broadcasting and telecommunications facilities; information equipment housing units; data storage and management centers.
11. Stadiums; arenas; sports centers; racing tracks, shooting ranges; other sports facilities established under the Law on Physical Training and Sports.
12. Airports, air traffic control towers; wharves of seaports; dry ports; inland ports; coach stations; rest stops; rail stations; aerial passenger tramway terminals; subway facilities; motor vehicle registration facilities; automobile, motorcycle and moped trading and maintenance facilities.
13. Automobile garages and parking lots established under the law.
14. Road tunnels and railway tunnels of at least 500 m.
15. Nuclear facilities; facilities for producing, trading, preserving and using industrial explosives and explosive precursors; industrial explosive and explosive precursor storage; industrial explosive and explosive precursor import and export ports; weapon and combat gear storage.
16. Facilities for extracting, processing, producing, transporting, trading and preserving petroleum, petroleum products and gas on land; petroleum and petroleum product terminals, gas terminals; petroleum, petroleum product and gas import and export ports; filling stations, flammable liquid stations; gas stations.
17. Industrial facilities with grade A, B, C, D or E risk of fire and explosion.
18. Power plants; electrical substations with voltage of at least 110 kV.
19. Tunnels with production, storage and use of flammable materials and explosives; storage of flammable goods or non-flammable goods contained in flammable packaging; flammable goods and scrap yards with area of at least 500 m2.
20. Facilities besides those mentioned from section 1 to section 19 that have internal filling stations or use internal gas supply systems with total weight of gas used of at least 70 kg.
21. Mixed-use houses involved in trade of flammable goods or substances or goods contained in flammable packaging of household./.
LIST OF FACILITIES AT RISK OF FIRE OR EXPLOSION
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Premises of regulatory bodies at all levels with at least 10 stories or total volume of all work buildings of at least 25.000 m3.
2. Apartment buildings, tenement houses and dormitories with at least 7 stories or total volume of at least 10.000 m3; mixed-use buildings with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
3. Junior kindergartens and senior kindergartens with at least 350 students or total volume of all educational buildings of at least 5.000 m3; primary schools, lower secondary schools; upper secondary schools and multi-level secondary schools with total volume of all educational buildings of at least 5.000 m3; colleges, universities, academies, post-secondary schools, vocational schools and continuing education institutions with at least 7 stories or total volume of all educational buildings of at least 10.000 m3; other educational institutions established under the Education Law with total volume of at least 5.000m3.
4. Hospitals with at least 250 beds; polyclinics, clinics, sanitariums, physical rehabilitation facilities, orthopedic facilities, nursing homes, epidemic prevention and control facilities, medical centers and other healthcare facilities established under the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
5. Theaters, cinemas and circuses with at least 600 seats; convention centers with at least 5 stories or total volume of all convention buildings of at least 10.000 m3; cultural centers, karaoke facilities, night clubs; bars, clubs, beauty clinics, massage shops, theme parks, zoos and aquariums with volume of at least 5.000 m3.
6. Classes 1 and 2 markets; shopping malls; supermarkets; department stores; convenience stores; restaurants and eateries with total business space of at least 500 m2 or volume of at least 5.000 m3.
7. Hotels, guesthouses; rented houses and other types of lodgings established under the Law on Tourism with at least 7 stories or total volume of all lodgings of at least 10.000 m3.
8. Workplaces of enterprises and socio - political organizations with at least 7 stories or total volume of all work buildings of at least 10.000 m3.
9. Museums, libraries; exhibits; storage facilities, bookstores and fair facilities with volume of at least 10.000 m3.
10. Post offices and broadcasting and telecommunications facilities with at least 5 stories or volume of the main building of at least 10.000 m3; information equipment housing units and data storage and management centers with volume of at least 5.000 m3.
11. Stadiums with at least 40.000 seats; arenas with at least 500 seats; sports centers; racing tracks and shooting ranges with total volume of all sport buildings of at least 10.000 m3 or at least 5.000 seats; other sports facilities established under the Law on Physical Training and Sports with volume of at least 5.000 m3.
12. Airports, air traffic control towers; wharves of seaports; dry ports; classes I and II inland ports; classes 1 and 2 coach stations; class 1 rest stops; rail stations; and aerial passenger tramway terminals with volume of at least 5.000 m3; subway facilities; motor vehicle registration facilities; and automobile, motorcycle and moped trading and maintenance facilities with business space of at least 500 m2 or volume of at least 5.000 m3.
13. Garages capable of accommodating at least 10 automobiles.
14. Nuclear facilities; facilities producing, trading, preserving and using industrial explosives and explosive precursors; industrial explosive and explosive precursor storage; industrial explosive and explosive precursor import and export ports; weapon and combat gear storage.
15. Facilities for extracting, processing, producing, transporting, trading and preserving petroleum, petroleum products and gas on land; petroleum and petroleum product terminals, gas terminals; petroleum, petroleum product and gas import and export ports; filling stations, flammable liquid stations; and gas stations with total gas storage of at least 200 kg.
16. Industrial facilities with grade A or B risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of at least 5.000 m3; grade C risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of at least 10.000 m3; grade D or E risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of at least 15.000 m3.
17. Power plants; electrical substations with voltage of at least 110 kV.
18. Tunnels with production, storage and use of flammable materials and explosives and total volume of at least 5.000 m3; storage of flammable goods or non-flammable goods contained in flammable packaging with total volume of at least 5.000 m3./.
LIST OF FACILITIES UNDER POLICE MANAGEMENT
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Premises of regulatory bodies at district level and higher.
2. Apartment buildings with at least 5 stories or volume of at least 5.000m3, tenement houses and dormitories with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 2.500 m3; mixed-use buildings with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 1.500 m3.
3. Junior kindergartens and senior kindergartens with at least 100 students or total volume of at least 1.000 m3; primary schools and lower secondary schools with total volume of at least 2.000 m3; upper secondary schools and multi-level secondary schools; colleges, universities, academies; post-secondary schools; vocational schools; continuing education institutions; and other educational institutions established under the Education Law with total volume of at least 1.000 m3.
4. Hospitals; polyclinics, clinics, sanitariums, physical rehabilitation facilities, orthopedic facilities, nursing homes, epidemic prevention and control facilities, medical centers and other healthcare facilities established under the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment with at least 3 stories or total volume of at least 1.000 m3.
5. Theaters, cinemas, circuses; convention centers with at least 3 stories or total volume of at least 1.500 m3; cultural centers, karaoke facilities and night clubs with at least 3 stories or volume of at least 1.000 m3; bars, clubs, beauty clinics, massage shops, theme parks, zoos and aquariums with at least 3 stories or total volume of at least 1.500 m3.
6. Classes 1 and 2 markets; shopping malls; supermarkets; department stores; convenience stores; restaurants and eateries with total business space of at least 300 m2 or volume of at least 1.000 m3.
7. Hotels and guest houses with at least 5 stories or volume of at least 1.500 m3; rented houses and other types of lodgings established under the Law on Tourism with at least 3 stories or volume of at least 1.000 m3.
8. Workplaces of enterprises and socio - political organizations with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 1.500 m3.
9. Museums, libraries; exhibits; storage facilities, bookstores and fair facilities with volume of at least 1.500 m3; religious establishments with volume of at least 5.000 m3.
10. Post offices and broadcasting and telecommunications facilities with at least 3 stories or volume of at least 1.500 m3; information equipment housing units and data storage and management centers with volume of at least 1.000 m3.
11. Stadiums; arenas; sports centers; racing tracks, shooting ranges; other sports facilities established under the Law on Physical Training and Sports with volume of at least 1.500 m3.
12. Airports, air traffic control towers; wharves of seaports; dry ports; inland ports; coach stations; rest stops; rail stations; aerial passenger tramway terminals; subway facilities; motor vehicle registration facilities; and automobile, motorcycle and moped trading and maintenance facilities with business space of at least 500 m2 or volume of at least 5.000 m3.
13. Garages capable of accommodating at least 10 automobiles; parking lots established under the law and capable of accommodating at least 20 automobiles.
14. Road tunnels and railway tunnels of at least 500 m.
15. Nuclear facilities; facilities producing, trading, preserving and using industrial explosives and explosive precursors; industrial explosive and explosive precursor storage; industrial explosive and explosive precursor import and export ports; weapon and combat gear storage.
16. Facilities for extracting, processing, producing, transporting, trading and preserving petroleum, petroleum products and gas on land; petroleum and petroleum product terminals, gas terminals; petroleum, petroleum product and gas import and export ports; filling stations, flammable liquid stations; and gas stations with total gas storage of at least 150 kg.
17. Industrial facilities with grade A or B risk of fire and explosion; grade C risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of at least 2.500 m3; grade D or E risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of at least 5.000 m3.
18. Power plants; electrical substations with voltage of at least 110 kV.
19. Tunnels with production, storage and use of flammable materials and explosives and total volume of at least 1.500 m3; storage of flammable goods or non-flammable goods contained in flammable packaging with total volume of at least 1.500 m3; flammable goods and scrap yards with area of at least 1000 m2.
20. Facilities besides those mentioned from section 1 to section 19 that have internal filling stations or use internal gas supply systems with total weight of gas used of at least 70 kg.
21. Mixed-use houses involved in trade of flammable goods or substances or goods contained in flammable packaging of household with total business space of at least 300 m2./.
LIST OF FACILITIES UNDER MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNE-LEVEL PEOPLE’S COMMITTEES
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Premises of regulatory bodies at commune level.
2. Apartment buildings with less than 5 stories and volume of less than 5.000 m3, tenement houses and dormitories with less than 5 stories and total volume of less than 2.500 m3; mixed-use buildings with less than 5 stories and total volume of less than 1.500 m3.
3. Junior kindergartens and senior kindergartens with less than 100 students or total volume of less than 1.000 m3; primary schools and lower secondary schools with total volume of all educational buildings of less than 2.000 m3; other educational institutions established under the Education Law with volume of less than 1.000 m3.
4. Polyclinics, clinics, sanitariums, physical rehabilitation facilities, orthopedic facilities, nursing homes, epidemic prevention and control facilities, medical centers and other healthcare facilities established under the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment with less than 3 stories and total volume of less than 1.000 m3.
5. Convention centers with less than 3 stories or total volume of less than 1.500 m3; cultural centers, karaoke facilities and night clubs with less than 3 stories and volume of less than 1.000 m3; bars, clubs, beauty clinics, massage shops, theme parks, zoos and aquariums with volume of less than 1.500 m3.
6. Class 3 markets; shopping malls; supermarkets; department stores; convenience stores; restaurants and eateries with business space of less than 300 m2 and volume of less than 1.000 m3.
7. Hotels and guest houses with less than 5 stories and total volume of less than 1.500 m3; rented houses and other types of lodgings established under the Law on Tourism with less than 3 stories and total volume of less than 1.000 m3.
8. Workplaces of enterprises and socio - political organizations with less than 5 stories and volume of less than 1.500 m3.
9. Museums, libraries; exhibits; storage facilities, bookstores and fair facilities with volume of less than 1.500 m3; religious establishments with volume of less than 5.000 m3.
10. Post offices and broadcasting and telecommunications facilities with less than 3 stories and volume of less than 1.500 m3; information equipment housing units and data storage and management centers with volume of less than 1.000 m3.
11. Sports facilities established under the Law on Physical Training and Sports with volume of less than 1.500 m3.
12. Automobile, motorcycle and moped trading and maintenance facilities with business space of less than 500 m2 and volume of less than 5.000 m3.
13. Indoor garages capable of accommodating less than 10 automobiles; parking lots established under the law and capable of accommodating less than 20 automobiles.
14. Flammable liquid stations and gas stations with total gas storage of less than 150 kg.
15. Industrial facilities with grade C risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of less than 2.500 m3; and grade D or E risk of fire and explosion and total volume of all buildings housing the main production lines of less than 5.000 m3.
16. Tunnels with production, storage and use of flammable materials and explosives and total volume of less than 1.500 m3; storage of flammable goods or non-flammable goods contained in flammable packaging with total volume of less than 1.500 m3; flammable goods and scrap yards with area of less than 1000 m2.
17. Mixed-use houses involved in trade of flammable goods or substances or goods contained in flammable packaging of household with total business space of less than 300 m2./.
LIST OF PROJECTS, WORKS AND MOTOR VEHICLES REQUIRING APPRAISAL OF FIRE SAFETY DESIGN
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Premises of regulatory bodies at all levels with at least 7 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
2. Apartment buildings, tenement houses and dormitories with at least 7 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3; mixed-use buildings with at least 7 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
3. Junior kindergartens and senior kindergartens with at least 100 students or total volume of at least 3.000 m3; primary schools, lower secondary schools, upper secondary schools and multi-level secondary schools with total volume of at least 5.000 m3; colleges, universities, academies; post-secondary schools; vocational schools; continuing education institutions; and other educational institutions established under the Education Law with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
4. Hospitals; polyclinics, clinics, sanitariums, physical rehabilitation facilities, orthopedic facilities, nursing homes, epidemic prevention and control facilities, medical centers and other healthcare facilities established under the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 3.000 m3.
5. Theaters, cinemas and circuses with at least 300 seats; convention centers with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3; cultural centers, karaoke facilities and night clubs with at least 3 stories or volume of at least 1.000 m3; bars, clubs, beauty clinics, massage shops, theme parks, zoos and aquariums with at least 3 stories or total volume of at least 1.500 m3.
6. Markets; shopping malls; supermarkets; department stores; convenience stores; restaurants and eateries with total volume of at least 3.000 m3.
7. Hotels, guest houses, rented houses and other types of lodgings established under the Law on Tourism with at least 7 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
8. Workplaces of enterprises and socio - political organizations with at least 7 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
9. Museums, libraries; exhibits; storage facilities, bookstores and fair facilities with total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
10. Post offices and broadcasting and telecommunications facilities; information equipment housing units and data storage and management centers with at least 5 stories or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
11. Stadiums with at least 5.000 seats; arenas, sports centers racing tracks, shooting ranges and other sports facilities established under the Law on Physical Training and Sports with at least 5.000 seats or total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
12. Airports, air traffic control towers; wharves of seaports; dry ports; inland ports; coach stations; rail stations; aerial passenger tramway terminals and rest stops with total volume of at least 1.500 m3; subway facilities; motor vehicle registration facilities; and automobile, motorcycle and moped trading and maintenance facilities with business space of at least 500 m2 or volume of at least 5.000 m3.
13. Indoor garages with total volume of at least 3.000 m3.
14. Road tunnels of at least 500 m; railway tunnels of at least 1.000 m.
15. Nuclear facilities; facilities producing, trading and preserving industrial explosives and explosive precursors; industrial explosive and explosive precursor storage; industrial explosive and explosive precursor import and export ports; weapon and combat gear storage.
16. Facilities for extracting, processing, producing, transporting, trading and preserving petroleum, petroleum products and gas on land; petroleum and petroleum product terminals, gas terminals; petroleum, petroleum product and gas import and export ports; filling stations, internal filling stations with at least 01 fuel dispenser; gas stations and internal gas supply systems with total gas storage of at least 200 kg.
17. Industrial facilities with grade A or B risk of fire and explosion and total volume of at least 1.500 m3; and grade C, D or E risk of fire and explosion and total volume of at least 5.000 m3.
18. Power plants; electrical substations with voltage of at least 110 kV.
19. Tunnels with production, storage and use of flammable materials and explosives and total volume of at least 1.000 m3. Warehouses of flammable goods or non-flammable goods contained in flammable packaging with total volume of at least 3.000 m3.
20. Technical infrastructures related to fire prevention and fighting of cities, economic zones, industrial parks, industry clusters, export-processing zones, hi-tech parks and other functional zones according to the Law on Planning requiring approval from authority at district level or higher.
21. Motor vehicles subject to special requirements for fire safety. Railway vehicles and watercrafts at least 20 m in length transporting passengers, gasoline, oil, flammable liquids, flammable gas, explosives and chemicals posing fire and explosion hazards./.
LIST OF FIRE PREVENTION AND FIGHTING EQUIPMENT
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Motor firefighting equipment
a) Fire trucks: fire trucks with tanks, fire trucks without tanks, airport fire trucks, forest fire trucks, chemical (powder, foaming agent, gas) fire trucks, tunnel fire trucks, railway fire trucks and amphibious fire trucks;
b) Firefighting vehicles: ladder trucks; bucket trucks; command vehicles; command center vehicles; fire scene examination vehicles; lighting vehicles; pumpers; water tenders; equipment carriers; firefighter carriers; chemical carriers; rescue vehicles; smoke removal vehicles; technical maintenance vehicles; logistics vehicles; crane trucks; chemical, biological and nuclear hazard handling vehicles; extinguishant carriers; breathing apparatus transport and charging vehicles; fire hose carriers; fuel carriers; ambulances; and fire bikes;
c) Firefighting aircrafts; firefighting boats; firefighting canoes; firefighting motorboats; other firefighting floating structures with motor;
d) Firefighting pumps;
dd) Other motor equipment: air charging machines; sawing, cutting, drilling, hammering, winching, pulling and spreading equipment (with motor), power inverters, bucket equipment, vegetation processing equipment (vegetation cutters, grass cutters); PPV fans; smoke extract fans; power generators; air blowers; and shoulder-supported fire extinguishers with motor.
2. Common firefighting equipment
a) Fire hoses and suction hoses;
b) Hose nuzzles;
c) Dividing breechings, ejectors;
d) Fire hydrants;
dd) Fire ladders;
e) Powder, foam, gas and water-based fire extinguishers.
3. Extinguishants: water-based firefighting chemicals, firefighting powder, firefighting gas and firefighting foaming agents.
4. Fire-resistant substances or materials; fire protection materials, fire protection doors, fire protection glass, fire protection dividers, fire dampers; and fire curtains.
5. Equipment of fire alarm systems: fire alarm control panels, detectors of all types, early warning equipment, modules of all types, fire alarm bells, fire alarm lights, fire alarm pull stations, fire alarm buttons, fire alarm sound systems and evacuation instructions.
6. Equipment of firefighting systems (by gas, aerosol, water, powder, foam): firefighting control panels; extinguishant releasing bells, horns, lights and signs; alarm valves, deluge valves, supervisory valves, selector valves, pressure switches, flow switches; non-metal pipes in automated firefighting water supply systems, soft pipes used for fire hoses; hose connections of fire hydrants, extinguishant hoses of all types; bottles and equipment containing firefighting gas, aerosol, powder and foam of all types.
7. Escape lights, emergency lights.
8. Personal protective clothing and equipment
a) Firefighting trousers, tops, hats, boots, gloves, shoes, belts, glasses and face masks; heat-resistant trousers, tops, hats, boots, gloves and shoes; insulated boots and gloves; personal lighting equipment;
b) Toxic-filtering respirators; respiratory protective devices; self-contained breathing apparatus.
9. Human rescue equipment: human rescue ropes; rescue belts; human rescue mattresses; human rescue ladders; evacuation slides; human detectors; high-altitude rescue equipment; underwater rescue equipment; confined space rescue equipment; equipment for rescue during events of chemical and radiation hazards; first-aid equipment.
10. Forcible entry tools: pliers, saws, hammers, axes, hoes, shovel, crowbars, multi-purpose forcible entry tools, long-handled sickles, machete, rakes, flappers.
11. Equipment for communication, commanding of firefighting operations and rescue
a) Command tables, command tents, command flags, incident commander armbands;
b) Wired communication systems;
c) Radio communication systems, surveillance equipment supporting commanding of forest and aerial firefighting operations, handheld GPS devices.
12. Equipment for inspection of fire safety and fire prevention and fighting equipment./.
LIST OF FIRE PREVENTION AND FIREFIGHTING EQUIPMENT REQUIRING INSPECTION
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Fire trucks; rescue vehicles; ladder trucks; pumpers; extinguishant carriers; breathing apparatus transport and charging vehicles; smoke removal vehicles; firefighting boats, canoes and motorboats; air charging machines.
2. Firefighting pumps.
3. Common firefighting equipment: fire hoses; hose nuzzles; dividing breechings, fire hydrants; extinguishers of all types.
4. Water-based firefighting chemicals, firefighting foaming agents.
5. Specimens of structures covered by fire-resistant substances or materials; specimens of fire protection structural components (fire protection doors,, fire protection dividers, fire dampers, fire curtains).
6. Equipment of fire alarm systems: fire alarm control panels, detectors of all types, fire alarm bells, fire alarm lights, fire alarm buttons.
7. Equipment of firefighting systems (by gas, aerosol, water-based extinguishant, powder, foam): automated firefighting system control panels; extinguishant releasing bells, horns and lights, extinguishant manual release buttons; alarm valves, deluge valves, selector valves, pressure switches, flow switches; non-metal pipes in firefighting water supply systems, soft pipes used for fire hoses; extinguishant hoses of all types; gas bottles.
8. Escape lights, emergency lights.
9. Specialized firefighting trousers, tops, hats, boots and gloves./.
SPECIFICATIONS OF SIGNAL FLAGS, SIGNAGE, ARMBAND AND TAPE USED IN FIREFIGHTING OPERATIONS
(Enclosed with the Government's Decree No. 136/2020/ND-CP dated November 24, 2020)
1. Fire truck priority flag
The flag has the shape of an isosceles triangle with a width of 270 mm and a height of 370 mm and a green background with yellow border. In the middle of the flag is a printed or embroidered yellow arrow with a length of 235 mm, a tail of 50 mm in length and 30 mm in width, a body of 5 mm in width and a head 20 mm away from the flag’s border. In the middle of the arrow are the printed or embroidered “CHỮA CHÁY" ("FIRE FIGHTING") words in yellow capitalized Times New Roman font and of 30 mm in height. The flag handle is 500 mm in height and 15 mm in diameter.
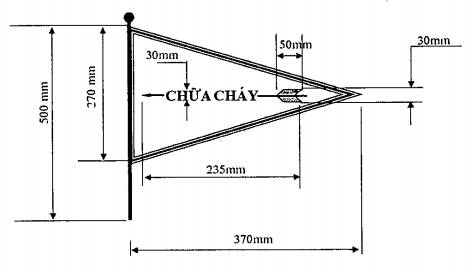
2. Fire area barricade tape
The tape has a yellow background, a width of 80 mm and a length of from 50 to 100 m. 2 lines of words run along the length of the tape repeatedly. The first line contains the words “KHU VỰC CHỮA CHÁY” (“FIRE AREA”) and the second line contains the words “FIRE AREA” of 20 mm in height and in capitalized Times New Roman font.

3. Signal flag of firefighting command team
The flag has the shape of an isosceles triangle with a width of 300 mm and a height of 400 mm and a red background with yellow border. The flag contains printed or embroidered words “BAN CHỈ HUY CHỮA CHÁY” (“FIREFIGHTING COMMAND TEAM”) in yellow capitalized Times New Roman font and of 40 mm in height. The flag handle is pushed through a 20 mm hole at the top of the flag for hanging.
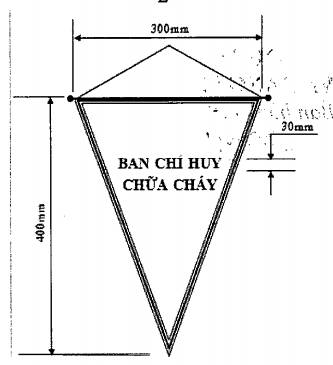
4. Incident commander armband
The incident commander armband is made from fabric with a red background with yellow border, a width of 100 mm and a circumference of from 350 to 450 mm. The armband contains the words “CHỈ HUY CHỮA CHÁY” (“INCIDENT COMMANDER”) in yellow capitalized Times New Roman font and of 40 mm in height.

5. Fire area no entry sign
The yellow sign is made from plastic, can be folded neatly, and contains the silver reflective words “KHU vực CHỮA CHÁY” (“FIRE AREA”), “KHÔNG NHIỆM VỤ CẤM VÀO” (“NO ENTRY”), “FIRE AREA” and “NO ENTRY” of 30 mm in height and in capitalized Times New Roman font on both sides./.
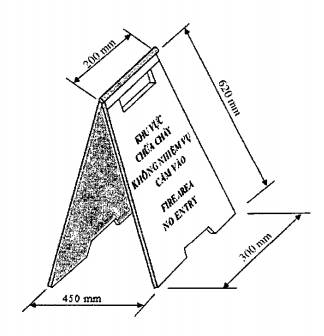
Văn bản liên quan
Cập nhật
Điều 4. Cơ sở thuộc diện quản lý về phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 7. Điều kiện an toàn về phòng cháy và chữa cháy đối với hộ gia đình
Điều 20. Trách nhiệm báo cháy, chữa cháy và tham gia chữa cháy
Điều 21. Người chỉ huy chữa cháy
Điều 22. Nhiệm vụ chỉ huy, chỉ đạo chữa cháy
Điều 27. Hoàn trả và bồi thường thiệt hại phương tiện, tài sản được huy động để chữa cháy
Điều 33. Huấn luyện, bồi dưỡng nghiệp vụ phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 37. Nâng lương đối với quân nhân chuyên nghiệp, công nhân và viên chức quốc phòng
Điều 4. Cơ sở thuộc diện quản lý về phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 5. Điều kiện an toàn về phòng cháy và chữa cháy đối với cơ sở
Điều 8. Điều kiện an toàn về phòng cháy và chữa cháy đối với phương tiện giao thông cơ giới
Điều 9. Cấp phép, vận chuyển hàng hóa nguy hiểm về cháy, nổ
Điều 13. Thiết kế và thẩm duyệt thiết kế về phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 15. Nghiệm thu, kiểm tra kết quả nghiệm thu về phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 16. Kiểm tra về phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 18. Phục hồi hoạt động của cơ sở, phương tiện giao thông cơ giới, hộ gia đình và cá nhân
Điều 33. Huấn luyện, bồi dưỡng nghiệp vụ phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 38. Kiểm định phương tiện phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 41. Điều kiện đối với cơ sở kinh doanh dịch vụ phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 44. Chứng chỉ hành nghề tư vấn về phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 45. Giấy xác nhận đủ điều kiện kinh doanh dịch vụ phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Điều 47. Sử dụng nguồn tài chính cho hoạt động phòng cháy và chữa cháy
Bài viết liên quan
Mức phạt quán karaoke vi phạm phòng cháy chữa cháy mới nhất 2025

Mức phạt quán karaoke vi phạm phòng cháy chữa cháy mới nhất 2025
Thời gian gần đây, liên tiếp xuất hiện nhiều vụ cháy lớn tại các phòng karaoke khiến nhiều người tử vong. Vậy mức phạt quán karaoke vi phạm phòng cháy chữa cháy mới nhất 2025 được quy định ra sao? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các quy định về vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Lối ra thoát nạn quán karaoke phải đáp ứng điều kiện gì?

Lối ra thoát nạn quán karaoke phải đáp ứng điều kiện gì?
Thời gian gần đây, liên tiếp xuất hiện nhiều vụ cháy lớn tại các phòng karaoke khiến nhiều người tử vong. Vậy lối ra thoát nạn quán karaoke phải đáp ứng điều kiện gì? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các quy định về vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Mẫu quyết định thành lập đội PCCC cơ sở mới nhất 2025

Mẫu quyết định thành lập đội PCCC cơ sở mới nhất 2025
Phòng cháy chữa cháy (viết tắt là PCCC) là tổng hợp các biện pháp, giải pháp kỹ thuật nhằm loại trừ hoặc hạn chế đến mức tối đa các nguy cơ xảy ra cháy, nổ, đồng thời tạo các điều kiện thuận lợi, phù hợp cho công tác cứu người, cứu tài sản, chữa cháy, chống cháy lan hiệu quả và làm giảm thiểu tối đa các thiệt hại do cháy, nổ gây ra. Vậy mẫu quyết định thành lập đội PCCC cơ sở mới nhất 2025 là mẫu nào? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Phụ cấp phòng cháy chữa cháy cơ sở là bao nhiêu?

Phụ cấp phòng cháy chữa cháy cơ sở là bao nhiêu?
Phòng cháy chữa cháy (viết tắt là PCCC) là tổng hợp các biện pháp, giải pháp kỹ thuật nhằm loại trừ hoặc hạn chế đến mức tối đa các nguy cơ xảy ra cháy, nổ, đồng thời tạo các điều kiện thuận lợi, phù hợp cho công tác cứu người, cứu tài sản, chữa cháy, chống cháy lan hiệu quả và làm giảm thiểu tối đa các thiệt hại do cháy, nổ gây ra. Vậy phụ cấp phòng cháy chữa cháy cơ sở là bao nhiêu? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Số người trong đội phòng cháy chữa cháy cơ sở là bao nhiêu?

Số người trong đội phòng cháy chữa cháy cơ sở là bao nhiêu?
Phòng cháy chữa cháy (viết tắt là PCCC) là tổng hợp các biện pháp, giải pháp kỹ thuật nhằm loại trừ hoặc hạn chế đến mức tối đa các nguy cơ xảy ra cháy, nổ, đồng thời tạo các điều kiện thuận lợi, phù hợp cho công tác cứu người, cứu tài sản, chữa cháy, chống cháy lan hiệu quả và làm giảm thiểu tối đa các thiệt hại do cháy, nổ gây ra. Vậy số người trong đội phòng cháy chữa cháy cơ sở là bao nhiêu? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Karaoke tuân thủ PCCC phải đáp ứng điều kiện gì?

Karaoke tuân thủ PCCC phải đáp ứng điều kiện gì?
Thời gian gần đây, liên tiếp xuất hiện nhiều vụ cháy lớn tại các phòng karaoke khiến nhiều người tử vong. Vậy quán karaoke tuân thủ PCCC phải đáp ứng điều kiện gì? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các quy định về vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Đối tượng nào có trách nhiệm tham gia vào đội dân phòng đội PCCC cơ sở?

Đối tượng nào có trách nhiệm tham gia vào đội dân phòng đội PCCC cơ sở?
Phòng cháy chữa cháy (viết tắt là PCCC) là tổng hợp các biện pháp, giải pháp kỹ thuật nhằm loại trừ hoặc hạn chế đến mức tối đa các nguy cơ xảy ra cháy, nổ, đồng thời tạo các điều kiện thuận lợi, phù hợp cho công tác cứu người, cứu tài sản, chữa cháy, chống cháy lan hiệu quả và làm giảm thiểu tối đa các thiệt hại do cháy, nổ gây ra. Vậy đối tượng nào có trách nhiệm tham gia vào đội dân phòng đội PCCC cơ sở? Bài viết sau đây sẽ làm rõ các vấn đề này. 11/01/2025Mẫu báo cáo công tác PCCC trường học mới nhất 2025

Mẫu báo cáo công tác PCCC trường học mới nhất 2025
Báo cáo công tác phòng cháy chữa cháy là một trong những nội dung mà các cơ sở có trách nhiệm phải thực hiện khi kiểm tra công tác phòng cháy chữa cháy thường xuyên, định kỳ và đột xuất. Vậy mẫu báo cáo phòng cháy chữa cháy trường học hiện nay thế nào? 09/01/2025Mẫu báo cáo công tác PCCC 6 tháng đầu năm mới nhất 2025

Mẫu báo cáo công tác PCCC 6 tháng đầu năm mới nhất 2025
Báo cáo công tác phòng cháy chữa cháy là một trong những nội dung mà các cơ sở có trách nhiệm phải thực hiện khi kiểm tra công tác phòng cháy chữa cháy thường xuyên, định kỳ và đột xuất. Bài viết sau đây sẽ là mẫu báo cáo công tác PCCC 6 tháng đầu năm mới nhất. 09/01/2025Khi nào cần báo cáo công tác PCCC?


 Nghị định 136/2020/NĐ-CP (Bản Word)
Nghị định 136/2020/NĐ-CP (Bản Word)
 Nghị định 136/2020/NĐ-CP (Bản Pdf)
Nghị định 136/2020/NĐ-CP (Bản Pdf)