 Tìm kiếm
Tìm kiếm
Chương VI Thông tư 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH : Thi, kiểm tra, xét công nhận tốt nghiệp
| Số hiệu: | 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH | Loại văn bản: | Thông tư |
| Nơi ban hành: | Bộ Lao động - Thương binh và Xã hội | Người ký: | Huỳnh Văn Tí |
| Ngày ban hành: | 20/10/2015 | Ngày hiệu lực: | 05/12/2015 |
| Ngày công báo: | 25/12/2015 | Số công báo: | Từ số 1225 đến số 1226 |
| Lĩnh vực: | Lao động - Tiền lương, Giáo dục | Tình trạng: | Còn hiệu lực |
TÓM TẮT VĂN BẢN
Thông tư 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH về đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp quy định chứng chỉ sơ cấp; thi, kiểm tra tốt nghiệp sơ cấp; chương trình đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp; tuyển sinh trình độ sơ cấp; thực hiện chương trình đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp;… được ban hành ngày 20/10/2015.
1. Tuyển sinh đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp
- Thông tư số 42 quy định đối tượng tuyển sinh trình độ sơ cấp là người từ đủ 15 tuổi trở lên, có trình độ học vấn và sức khỏe phù hợp với nghề cần học.
- Hình thức tuyển sinh: Xét tuyển và nhiều lần trong năm.
- Thông báo tuyển sinh sơ cấp: Chậm nhất 03 tháng trước khi tổ chức tuyển sinh, cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp công bố công khai: chỉ tiêu tuyển sinh từng nghề; đối tượng, khu vực tuyển sinh và thời hạn nhận hồ sơ; thời gian xét tuyển và căn cứ xét tuyển trình độ sơ cấp.
2. Tổ chức thực hiện chương trình đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp
- Tổ chức lớp đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp được Thông tư 42/2015 quy định như sau:
+ Lớp học kiến thức nghề, kỹ năng khác trình độ sơ cấp: tối đa 35 người học, đối với lớp cho người dân tộc thiểu số, người khuyết tật tối đa 20 người, riêng lớp cho người mù tối đa 10 người.
+ Lớp học thực hành nghề hoặc học tích hợp đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp: tối đa 18 người học, đối với người dân tộc thiểu số ít người, người khuyết tật, tối đa 10 người, người mù tối đa 8 người học.
+ Mỗi lớp có một giáo viên chủ nhiệm.
- Địa điểm đào tạo đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp linh hoạt tại cơ sở đào tạo, doanh nghiệp, nơi sản xuất, nhưng phải đảm bảo các điều kiện để dạy và học.
3. Thi, kiểm tra, xét công nhận tốt nghiệp đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp
Theo Thông tư số 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH, kiểm tra hoặc thi kết thúc khóa học trình độ sơ cấp được quy định như sau:
- Người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp quy định việc ra đề thi kết thúc khóa học, thể lệ thi, thành lập Hội đồng thi kết thúc khóa học và chỉ đạo thực hiện kỳ thi kết thúc khóa học trình độ sơ cấp.
- Điều kiện dự thi kết thúc khóa học đào tạo sơ cấp theo Thông tư 42 năm 2015 của Bộ Lao động:
+ Các điểm tổng kết môn học, mô - đun >= 5,0 điểm;
+ Không bị truy cứu trách nhiệm hình sự tại thời điểm tổ chức kiểm tra hoặc thi kết thúc khóa học sơ cấp.
- Thi kết thúc khóa học theo hình thức thực hành bài tập kỹ năng tổng hợp để thực hiện các công việc đơn giản của nghề hoặc hoàn thiện một sản phẩm, dịch vụ.
Thông tư 42 còn quy định sổ sách, biểu mẫu quản lý đào tạo và chế độ báo cáo trong đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp; mẫu chứng chỉ sơ cấp, quản lý, cấp phát, thu hồi chứng chỉ sơ cấp; yêu cầu, nội dung, cấu trúc chương trình đào tạo sơ cấp; biên soạn chương trình, giáo trình đào tạo trình độ sơ cấp. Thông tư số 42/2015/BLĐTBXH có hiệu lực từ ngày 05/12/2015.
Văn bản tiếng việt
Văn bản tiếng anh
1. Kiểm tra thường xuyên và kiểm tra định kỳ
a) Kiểm tra đánh giá thường xuyên được thực hiện tại thời điểm bất kỳ trong quá trình học của học sinh theo từng mô - đun cụ thể thông qua việc chấm điểm kiểm tra vấn đáp trong giờ học, kiểm tra viết với thời gian làm bài bằng hoặc dưới 30 phút, kiểm tra một số nội dung thực hành, thực tập, chấm điểm bài tập và các hình thức kiểm tra đánh giá khác.
b) Kiểm tra đánh giá định kỳ được thực hiện tại thời điểm được quy định trong đề cương chi tiết của mô đun, có thể được thực hiện bằng bài kiểm tra viết có thời gian làm bài từ 30 đến 45 phút; làm bài thực hành, thực tập và các hình thức kiểm tra, đánh giá khác.
2. Cách thức thực hiện kiểm tra thường xuyên và kiểm tra định kỳ
a) Kiểm tra đánh giá quá trình học do giáo viên giảng dạy mô - đun thực hiện theo những yêu cầu sau:
- Nội dung kiểm tra là những nội dung được quy định trong mô - đun đào tạo đã giảng dạy cho học sinh;
- Nội dung cụ thể và hình thức kiểm tra thường xuyên do giáo viên tự quyết định;
- Nội dung và hình thức kiểm tra định kỳ được thực hiện theo quy định trong đề cương chi tiết mô - đun của chương trình đào tạo.
b) Các bài kiểm tra theo hình thức kiểm tra viết, tiểu luận, bài tập sau khi chấm phải trả lại cho học sinh ngay sau khi công bố điểm kiểm tra.
3. Quy trình kiểm tra, số bài kiểm tra cho từng mô - đun cụ thể được thực hiện theo quy định của người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp, bảo đảm trong một mô - đun mỗi người học có ít nhất một điểm kiểm tra thường xuyên, một điểm kiểm tra định kỳ.
4. Học sinh không dự kiểm tra nếu không có lý do chính đáng thì phải nhận điểm 0 (không) cho bài kiểm tra đó. Trường hợp có lý do chính đáng thì được giáo viên giảng dạy mô - đun tổ chức làm bài kiểm tra bổ sung.
1. Thể lệ kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun
a) Điều kiện dự kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun: Người học được dự kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun khi có đủ điều kiện sau:
- Tham dự ít nhất 70% thời gian lên lớp lý thuyết, 80% giờ thực hành, thực tập và các yêu cầu của mô - đun được quy định trong đề cương chi tiết của mô - đun.
- Điểm trung bình chung các điểm kiểm tra đạt từ 5,0 điểm trở lên.
Trường hợp người học bị ốm trong quá trình học hoặc trong kỳ kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun, phải viết đơn xin phép gửi cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp trong thời hạn không quá một tuần kể từ ngày ốm, kèm theo giấy chứng nhận của cơ quan y tế trường hoặc cơ quan y tế cấp xã trở lên nhưng phải đảm bảo tham dự lớp học đủ thời gian theo quy định tại điểm này.
b) Hình thức, thời gian kiểm tra
- Hình thức kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun là thực hiện bài kiểm tra kỹ năng tổng hợp, gồm kiến thức và kỹ năng thực hành một hoặc một số khâu công việc của nghề.
- Thời gian làm bài kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun đối với mỗi bài kiểm tra viết từ 60 đến 120 phút, thời gian làm bài kiểm tra đối với các hình thức kiểm tra khác hoặc thời gian làm bài kiểm tra của mô - đun có tính đặc thù của nghề đào tạo do người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp quyết định.
Hình thức kiểm tra, thời gian làm bài kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun phải được quy định trong đề cương chi tiết của mô - đun.
c) Ra đề kiểm tra và chấm điểm
- Người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp tổ chức xây dựng, quản lý và sử dụng ngân hàng đề kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun. Đề kiểm tra phải phù hợp với nội dung mô - đun đã được quy định trong chương trình và phải được bốc thăm ngẫu nhiên từ ngân hàng đề của cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp. Người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp phê duyệt đề trước khi sử dụng.
- Cách chấm và tính điểm kiểm tra
+ Mỗi bài kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun phải do giáo viên chấm điểm và phải ký tên vào bài kiểm tra, phiếu chấm điểm, bảng tổng hợp điểm. Việc chấm điểm bài kiểm tra viết tự luận, chấm điểm vấn đáp, thực hành phải thực hiện trên phiếu chấm thi do người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp quy định.
+ Điểm kiểm tra là điểm trung bình cộng của các giáo viên chấm. Trường hợp điểm của các giáo viên chấm đối với một bài kiểm tra có sự chênh lệch trên 1,0 điểm (theo thang điểm 10) thì phải tổ chức xem xét hoặc chấm lại. Trường hợp chấm lại vẫn không thống nhất được điểm thì trưởng khoa hoặc trưởng bộ môn xem xét, quyết định cuối cùng về cho điểm đối với bài kiểm tra đó. Bài kiểm tra được chấm thông qua máy, phần mềm chuyên dụng và việc chấm phúc khảo do người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp quy định cụ thể và tổ chức thực hiện.
Đối với người học không đủ điều kiện dự kiểm tra hoặc vắng mặt buổi kiểm tra không có lý do chính đáng thì phải nhận điểm 0 cho lần kiểm tra đó; trường hợp có lý do chính đáng thì chưa tính điểm kiểm tra.
- Cách tính điểm mô - đun
+ Điểm mô - đun là điểm trung bình các điểm kiểm tra có trọng số 0,4 và điểm kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun có trọng số 0,6.
+ Điểm trung bình các điểm kiểm tra là trung bình cộng của các điểm kiểm tra thường xuyên, điểm kiểm tra định kỳ theo hệ số của từng loại điểm. Trong đó, điểm kiểm tra thường xuyên tính hệ số 1, điểm kiểm tra định kỳ tính hệ số 2.
d) Kết quả kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun; học và kiểm tra lại
- Người học đủ điều kiện dự kiểm tra sau mỗi lần học, được dự kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun nhưng không quá 02 lần kiểm tra. Cụ thể:
+ Học sinh được dự kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun lần thứ nhất, nếu điểm mô - đun đạt yêu cầu thì không phải dự kiểm tra lần thứ hai; nếu điểm mô - đun chưa đạt yêu cầu thì phải dự kiểm tra thêm một lần nữa do cơ sở tổ chức.
+ Học sinh vắng mặt ở lần kiểm tra nào mà không có lý do chính đáng thì vẫn tính số lần dự kiểm tra đó nhưng điểm số là 0; trường hợp có lý do chính đáng thì chưa tính số lần dự kiểm tra và được người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp bố trí dự kiểm tra.
- Học và kiểm tra lại:
Học sinh phải học và kiểm tra lại mô - đun chưa đạt yêu cầu nếu thuộc một trong các trường hợp sau:
+ Không đủ điều kiện dự kiểm tra lần đầu;
+ Đã hết số lần (02 lần) dự kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun, nhưng điểm mô - đun chưa đạt yêu cầu.
- Học sinh thuộc diện phải học và kiểm tra lại không được bảo lưu điểm, thời gian học tập của mô - đun lần học trước và phải bảo đảm các điều kiện dự kiểm tra được quy định tại Điểm a Khoản 1 của Điều này mới được dự kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun.
- Trường hợp không còn mô - đun do điều chỉnh chương trình thì người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp quyết định chọn mô - đun khác thay thế trên cơ sở phù hợp với mục tiêu của nghề đào tạo.
2. Cách thức tổ chức kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun
a) Cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp tổ chức phổ biến quy chế kiểm tra đối với học sinh tham dự kỳ kiểm tra. Các phiên họp liên quan đến kỳ kiểm tra; việc lựa chọn bốc thăm, bàn giao đề kiểm tra; bài kiểm tra; điểm kiểm tra phải được ghi lại bằng biên bản.
b) Lịch kiểm tra của kỳ kiểm tra chính phải được thông báo trước ngày kiểm tra ít nhất 02 tuần. Lịch kiểm tra của kỳ kiểm tra lại phải được thông báo trước ngày kiểm tra ít nhất 01 tuần. Trong kỳ kiểm tra, từng mô - đun được tổ chức kiểm tra riêng biệt, không bố trí kiểm tra ghép một số mô - đun trong cùng một buổi kiểm tra của một học sinh.
c) Thời gian dành cho ôn kiểm tra mỗi mô - đun tỷ lệ thuận với số giờ của mô - đun đó và bảo đảm ít nhất là 1/2 ngày ôn thi cho 15 giờ thực học. Tất cả các mô - đun phải bố trí giáo viên hướng dẫn ôn kiểm tra, đề cương ôn thi phải được công bố cho người học ngay khi bắt đầu tổ chức ôn kiểm tra.
d) Danh sách học sinh đủ điều kiện dự kiểm tra, không đủ điều kiện dự kiểm tra có nêu rõ lý do phải được công bố công khai trước ngày kiểm tra mô - đun ít nhất 05 ngày làm việc. Danh sách phòng kiểm tra, địa điểm kiểm tra phải được công khai trước ngày kiểm tra kết thúc mô - đun từ 1 - 2 ngày làm việc.
đ) Điểm kiểm tra theo hình thức vấn đáp, thực hành, thực tập hoặc bảo vệ báo cáo thực tập phải được công bố cho học sinh biết ngay sau khi chấm. Đối với các hình thức kiểm tra khác phải được công bố cho học sinh biết muộn nhất sau 05 ngày làm việc kể từ ngày hết hạn nộp kết quả kiểm tra.
e) Người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp quy định cụ thể về tổ chức kiểm tra, kết thúc mô - đun ở cơ sở mình.
1. Người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp có trách nhiệm quy định việc ra đề thi kết thúc khóa học; quy định thể lệ thi (thời gian, hình thức thi; thang điểm và cách tính điểm thi...); thành lập Hội đồng thi kết thúc khóa học và chỉ đạo thực hiện kỳ thi kết thúc khóa học công khai, công bằng, đảm bảo chất lượng, đánh giá đúng kết quả học tập và rèn luyện của người học.
2. Điều kiện để người học được dự thi kết thúc khóa học:
a) Các điểm tổng kết môn học, mô - đun phải đạt từ 5,0 điểm trở lên;
b) Không trong thời gian đang bị truy cứu trách nhiệm hình sự tại thời điểm tổ chức kiểm tra hoặc thi kết thúc khóa học.
3. Hình thức thi kết thúc khóa học:
Thi kết thúc khóa học theo hình thức thực hành bài tập kỹ năng tổng hợp để thực hiện các công việc đơn giản của nghề hoặc hoàn thiện một sản phẩm, dịch vụ.
4. Nhiệm vụ của Hội đồng thi kết thúc khóa học:
a) Thông qua danh sách học sinh được dự thi kết thúc khóa học và thông báo công khai trước kỳ thi 15 ngày;
b) Xây dựng đề, đáp án và quy trình chấm bài thi;
c) Tổ chức thi kết thúc khóa học, xử lý các trường hợp vi phạm nội quy thi và công nhận tốt nghiệp;
d) Tổ chức chấm bài thi;
đ) Đề xuất việc xếp loại tốt nghiệp cho học sinh sau khi kết thúc khóa học.
1. Cách tính điểm tổng kết khóa học
Điểm tổng kết khóa học của người học trình độ sơ cấp được tính theo công thức sau:
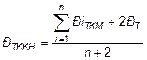
Trong đó:
- ĐTKKH: Điểm tổng kết khóa học
- ĐiTKM: Điểm tổng kết mô - đun thứ i
- ĐT: Điểm thi kết thúc khóa học
- n: Số lượng các mô - đun đào tạo
2. Điều kiện được công nhận tốt nghiệp
Người học trình độ sơ cấp được công nhận tốt nghiệp khi có điểm tổng kết khóa học được tính theo quy định tại khoản 1 của Điều này từ 5,0 trở lên.
3. Xếp loại tốt nghiệp
a) Việc xếp loại tốt nghiệp cho học sinh được căn cứ vào điểm tổng kết khóa học.
b) Các mức xếp loại tốt nghiệp được quy định như sau:
- Loại xuất sắc có điểm tổng kết khóa học từ 9,0 đến 10;
- Loại giỏi có tổng kết khóa học từ 8,0 đến dưới 9,0;
- Loại khá có điểm tổng kết khóa học từ 7,0 đến dưới 8,0;
- Loại trung bình khá có điểm tổng kết khóa học từ 6,0 đến dưới 7,0;
- Loại trung bình có điểm tổng kết khóa học từ 5,0 đến dưới 6,0.
c) Các mức xếp loại tốt nghiệp xuất sắc, giỏi, khá, trung bình khá của học sinh sẽ bị giảm đi một mức nếu học sinh bị kỷ luật từ mức cảnh cáo trở lên trong thời gian học hoặc có một mô - đun trở lên trong khóa học phải thi lại, học lại (không tính mô - đun được tạm hoãn học hoặc được miễn trừ).
d) Mức xếp loại tốt nghiệp được ghi vào chứng chỉ sơ cấp và bảng tổng hợp kết quả học tập của học sinh.
a) Người đứng đầu cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp căn cứ báo cáo của hội đồng kiểm tra hoặc thi kết thúc khóa học ra quyết định công nhận tốt nghiệp và công bố công khai tới người học.
b) Cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp có trách nhiệm báo cáo Sở Lao động - Thương binh và Xã hội nơi cơ sở đào tạo sơ cấp tổ chức đào tạo và cơ quan quản lý cấp trên trực tiếp (nếu có) về kết quả công nhận tốt nghiệp chậm nhất trong thời hạn 30 ngày kể từ khi kết thúc khóa học.
|
MINISTRY OF LABOR - INVALIDS AND SOCIAL AFFAIRS |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No.: 42/2015/TT- BLDTBXH |
Hanoi, October 20, 2015 |
REGULATIONS ON BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING
Pursuant to the Law on vocational education dated November 27, 2014;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 48/2015/ND-CP dated May 15, 2015 detailing certain articles of the Law on vocational education;
Pursuant to Government’s Decree No. 106/2012/ND-CP dated December 20, 2012 defining functions, duties, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs;
At the request of the Director General of the General Directorate of Vocational Training;
Ministry of Labour - Invalids and Social Affairs promulgates this Circular to provide for the basic-level training,
This Circular provides for the basic-level training, including: the minimum body of knowledge and skills, and required capacity of graduates; requirements, contents and structure of training programs and textbooks, and procedures for establishment, compilation, appraisal and issuance of training programs and textbooks; determination of enrolment criteria, enrolment plans and organization of the enrolment; the execution of training programs; test, examinations, evaluation, and recognition of graduation; the form of basic-level training certificate, and printing, management, issuance, revocation and cancellation of basic-level training certificate; forms and records for managing basic-level teaching and learning activities.
This Circular provides for the basic-level training and applies to vocational training institutions, enterprises that have registered for basic-level vocational education (hereinafter referred to as basic-level training institutions), and relevant agencies, organizations and individuals.
Article 3. Interpretation of terms
In this Circular, these terms are construed as follows:
1. Minimum body of knowledge and skills for basic-level training is the compulsory number of modules which a learner must earn to be qualified for graduating from the basic-level training.
2. Module is a learning unit which is the complete integration between professional knowledge, practical skills and professional attitude to help learners acquire integral competency of practice in one or certain tasks of a profession.
3. Basic-level training program refers to the system of knowledge, skills, responsibility and autonomy that is suitable for the methods of teaching, teaching and learning facilities, and the evaluation of study results to ensure that learners earn necessary knowledge, skills, responsibility and autonomy to perform simple jobs of their professions.
4. Outcome standard is the required knowledge, skills, responsibility and autonomy a learner shall obtain when he complete the training program that the training institution has undertaken and published together with conditions for implementation.
MINIMUM BODY OF KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS; REQUIRED CAPACITY OF GRADUATES AT BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING
Article 4. Minimum body of knowledge and skills at basic-level training
The minimum body of knowledge and skills at basic-level training is 03 (three) modules with at least 300 hours of the actual study duration which is performed from 03 (three) months to less than 01 (one) year.
Article 5. Required capacity of graduates at basic-level training
1. Knowledge:
a) Understand and have foundation knowledge of requirements and standards of each task of their professions; are able to apply certain knowledge to practice and continue the study at a higher level;
b) Understand and have knowledge of occupational safety and hygiene for their jobs, job positions and working places.
2. Skills: Are able to perform simple or repetitive tasks of a profession and other necessary skills for such profession;
3. Autonomy and responsibility: Are able to receive, record and transmit information as requested; have ability to know requirements, standards and results of surrounding job positions or related tasks; assume responsibility for their working results and products.
PROCEDURES FOR ESTABLISHMENT, PREPARATION, APPRAISAL AND ISSUANCE OF TRAINING PROGRAMS AND TEXTBOOKS AT BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING
Section 1. CONTENTS AND STRUCTURE OF TRAINING PROGRAMS AND TEXTBOOKS
Article 6. Requirements on training programs and textbooks
1. Requirements on training programs
a) In a training program, the name of training profession must be determined and such name of training profession must be included in the list of professions and jobs of enterprises and employers’ business and production sectors/fields in a given region or in the list of intermediate-level and college-level training professions promulgated by central-level vocational education authority;
b) Contents of training programs must comply with basic-level training objectives as regulated in Clause 1 and Point 1 Clause 2 Article 4 of the Law on vocational education, satisfy requirements on the body of knowledge, vocational skills, other necessary skills, required capacity of graduates for each training profession and be in conformity with the national qualifications framework and national standards of vocational skills;
c) The training program must specify the number of modules and training duration of each module in correspondence with training method; periods of theoretical training, practice and internship;
d) The training program must be scientific, accurate, systematic, practical and suitable to manufacturing/service technology; flexible to adapt to changes of technology and labour market. The training program must use consistent and understandable language;
dd) Duration of the training program and procedures for performing modules must be arranged suitably for executing vocational education objectives in an effective manner;
e) The training program must set forth requirements training facilities and teaching staff for executing such training program and ensuring training quality;
g) The training program must specify the method for evaluating study results and determining the level of outcome standard of modules and that of the training program;
h) The training must ensure the connectivity between levels of vocational education.
2. Requirements on training textbooks
a) Comply with objectives and contents of modules specified in the training program;
b) Ensure the accuracy, systematic and pedagogic quality; ensure the balance and conformity between texts and pictures;
c) Contents of knowledge and skills must ensure objectives of headings, subheadings/sections, subsections in lessons/chapters of modules;
d) Each lesson/chapter of the textbook must include questions or exercises; each textbook must be enclosed with the list of reference documents whose reliability and origin must be specified;
dd) The textbook must be presented in a brief, simple and easily understandable manner; use general and consistent professional terms; illustrative pictures must clarify knowledge and skills thereof;
e) The textbook must be in conformity with teaching devices, sources of educational materials and other teaching facilities.
Article 7. Contents and structure of training programs and textbooks
1. Contents and structure of the training program at basic-level training for each training profession must include the following contents:
a) Name and code of the training profession;
b) Subjects of enrolment and entry requirements;
c) Description about the training course and training objectives;
d) The list of the number of modules, and duration of each module;
dd) The body of knowledge, vocational skills and other necessary skills, the autonomy and responsibility;
e) Duration of the training course, including: Total duration of the training course, the actual study duration, periods of theoretical training, practice and internship, period for reviewing, test or taking final exams of modules and the training course; in which, the period for practice and internship must be from 70% of the actual study duration.
g) Training process, and requirements on graduation;
h) Methods and grading system for evaluating study results;
i) Guidance on the application of training program.
2. Contents and structure of the training textbooks at basic-level training for each training profession must include the following contents:
a) General information about the textbook (name of module, name of training profession, training level; announcement of the copyright; introduction; table of contents, etc.);
b) Module’s code, order, nature, meaning and roles thereof; objectives of the modular textbook;
c) Contents of the modular textbook; name, code, introduction and objectives of lessons/chapters; contents of knowledge and skills of headings, subheadings/sections, subsections of each lesson/chapter (including: knowledge, skills, procedures, methods of performing tasks; drawings, pictures, exercises and contents that learners should remember);
d) Requirements on evaluation of study results upon the end of each lesson/chapter and the end of each module.
Section 2. PROCEDURES FOR ESTABLISHMENT, APPRAISAL AND ISSUANCE OF TRAINING PROGRAMS
Article 8. Procedures and organization of the establishment of training program
1. Procedures for the establishment of the training program
a) Step 1: Make a survey to determine demands on basic-level human resources, demands of employers towards graduates of basic-level training course according to each profession, and determine basic-level training professions to establish or select training programs.
b) Step 2: Design the training program:
- Establish general and detailed outlines of basic-level training program;
- Do study on national standards of vocational skills of the training profession or carry out the analysis on the profession or works in accordance with regulations on the establishment of national standards of vocational skills (if national standards of vocational skills are not yet promulgated) for determining outcome standard and the body of knowledge, skills and contents which must be included in the training program;
- Determine the importance of selected knowledge and skills in the basic-level training program according to the following levels: Mandatory - Crucial - Recommended;
- Design the structure of the training program; compare such structure of training program with that of the same profession at the same training level of other domestic and foreign training institutions for referring and selecting a suitable structure of training program;
- Determine requirements, contents and methods for evaluating study results of learners;
- Organize conference to collect suggestions of experts about the structure of training program;
- Summarize collected suggestions and perfect the structure of training program.
c) Step 3: Compile the training program according to determined contents and structure in which each module shall be detailed; conditions for doing each module; evaluation methods and contents.
d) Step 4: Complete the draft of the training program
- Organize a conference of experts (composing of: technical experts of enterprises, managers, researchers, and lecturers, teachers of vocational training institutions, artisans and individuals who possess knowledge and experience in relevant training profession).
- Complete the draft of the training program.
dd) Step 5: Appraise and issue the training program
- Complete documents and the draft of the training program.
- The steering board of the training program shall report and defend the training program before the training program appraisal council.
- The training program appraisal council convenes and carries out the appraisal of the training program to use as the basis for requesting the competent authority to consider, approve and make decision on the issuance of training program.
e) Step 6: Evaluate and revise contents of the training program.
2. Organization of the establishment of the training program
a) The head of the basic-level training institution assigns its affiliated units to perform the tasks stated in Point a and Point e Clause 1 of this Article and makes decision on the establishment of the steering board in charge of establishing the training program (hereinafter referred to as the steering board) to perform the tasks stated in Point b, Point c, Point d and Point dd Clause 1 of this Article.
b) The steering board shall, depending on the workload of each training program which must be established, include from 5 to 7 members who are teachers, vocational education managers, or technicians of enterprises. In which, at least one-third of members are teachers in corresponding profession. The steering board composes of the head of the board, deputy head, secretary and members.
- Standards for selecting members of the steering board:
+ Possess intermediate-level degree or higher;
+ Have at least 3 years of experience in teaching or participating in the production or business in the field of the profession whose training program is established;
- Rights and responsibilities of the steering board:
+ Organize the establishment of training program of the assigned profession in conformity with regulations of this Circular;
+ The steering board may establish its sub-boards to do each task of the establishment of the training program;
+ Assume responsibility for contents and quality of the training program of the assigned profession.
Article 9. Procedures for appraising and issuing the training program
1. Step 1: Establish the training program appraisal council.
a) The head of the training institution shall make decision on the establishment of the training program appraisal council (hereinafter referred to as the program appraisal council).
b) The program appraisal council shall, depending on the workload of each training program which must be appraised, include from 5 to 7 members who are teachers, vocational education managers, or technicians of enterprises. At least one member of the program appraisal council is appointed by the employer that shall employ graduates of the training profession, and at least one-third of total members of the program appraisal council are teachers in corresponding basic-level training profession. The program appraisal council includes the council’s chairman who is the representative of heads of the training institution, deputy chairman, secretary and members.
c) Standards for selecting members of the program appraisal council
- Possess college degree or higher;
- Have at least 5 years of experience in teaching or participating in the production or business in the field of the profession whose training program must be appraised.
d) Rights and responsibilities of the program appraisal council:
- The program appraisal council is the professional advisory organization that assists the head of the training institution in appraising the training program.
- Comment and appraise the quality of the training program; assume responsibility for the appraisal quality; give recommendations for approving the training program.
- Organize the appraisal of the training program and make report on the appraisal results which shall be used as the basis for approving the training program.
dd) Principles of operation of the program appraisal council:
- The program appraisal council works under the management of the council’s chairman;
- The meeting of the program appraisal council is considered valid if at least two-thirds of the council’s members, including the council’s chairman, secretary and members who act as criticizers, are present at the meeting; members who are absent from the meeting must submit their written evaluation of the training program to the program appraisal council before the date of meeting;
- The program appraisal council shall openly discuss, and each council’s member shall state his analytical opinions and evaluation of the training program; vote on each content of the training program and come to conclusion according to majority (according to suggestion of at least two-thirds of the council’s members);
- Contents of the meeting of the program appraisal council must be recorded in the minutes of the meeting (the minutes of the meeting must include opinions of each member and voting result of each content which is concluded by the council). The minutes of the meeting shall be unanimously approved and signed by participants of the meeting.
e) The program appraisal council may establish its sub-boards to assist it in appraising one or certain modules of the training program which must be appraised.
2. Step 2: Appraise the training program
a) The program appraisal council shall appraise the training program on the basis of current regulations on the training program; requirements on the training profession according to the national qualifications framework or the national standards of vocational skills, and determined training objectives or outcome standard.
b) The program appraisal council shall come to obvious conclusion by specifying one of the following contents: the training program is approved without any modification or amendment, or the training program is approved with request for modification or amendment and specifying contents that must be modified or amended, or the training program is unapproved and reasons thereof.
3. Step 3: Report on appraisal results
Chairman of the program appraisal council submits the report on the training program appraisal results, enclosed with the minutes of council’s meeting and appraisal documents in order that the head of the training institution can consider and make decision on the issuance of the training program.
4. Step 4: Issue the training program
The head of the basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of the training program appraisal results submitted by the program appraisal council, take the autonomy in approving and issuing the basic-level training program which applies to such training institution.
Article 10. Selection of training programs; evaluation and revision of training programs, and announcement of training programs and outcome standards
1. Selection of training programs
The head of the basic-level training institution may select training programs provided that the appraisal of such training programs must be carried out as regulated in Article 9 of this Circular to form the basis for approving and applying such training programs to such training institution.
2. Evaluation and revision of training programs
a) The basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of at least every 3 years, conduct the evaluation of the training program to evaluate the completion of determined outcome standards, and the conformity of such training program to demands of employers and manufacturing technological changes relating to the training profession; changes in state regulations and the training institution's regulations on training program; the unification and connection between contents of the training program, training methods, test and evaluation of study results, and planned effects of change or revision of such training program.
b) Draft contents of the training program that must be modified or revised and carry out the appraisal thereof as regulated in Article 9 of this Circular.
c) The head of the basic-level training institution shall issue the revised training program on the basis of proposals submitted by the program appraisal council after the training program has been evaluated as regulated in Point a and Point b Clause 2 of this Article.
3. The basic-level training institution must announce training programs and outcome standards of each training program to learners and their families, if the enrolment is made by posting a notice at the head office of the training institution, or specify those in the enrolment notice, or post those on the website of the training institution, or via means of the mass media. Contents that must be announced include:
a) Announced contents of the training program: name of the training program, subjects of the enrolment, period of the enrolment, training duration and place of training; knowledge and skills that learners shall learn and practice; basic-level certificate; tuition payable; support policies (if any).
b) Announced contents of outcome standards: required knowledge and skills of graduates; types of works of the training profession or job positions that learners are able to perform upon the completion of the basic-level training program.
Section 3. PROCEDURES FOR COMPILATION, APPRAISAL AND ISSUANCE OF TRAINING TEXTBOOKS
Article 11. Procedures for compiling training textbooks
1. Step 1. Establish the training textbook compilation team
a) The head of the basic-level training institution shall make decision on the establishment of the training textbook compilation team (hereinafter referred to as the compilation team).
b) The compilation team shall include from 5 to 7 members, including team leader, secretary and members who are teachers, lecturers, experts or managers who are experienced in relevant training profession.
c) Standards for selecting members of the compilation team: possess intermediate-level degree of higher; have at least 3 years of experience in teaching or participating in the production or business in the field of the profession whose training textbooks must be compiled.
d) Rights and responsibilities of the compilation team:
- The compilation team may establish groups to compile textbooks for certain modules of the training profession; each group shall include from 3 to 5 members who are teachers or lecturers who have teaching experience in the training profession whose textbooks must be compiled. Groups shall assist the compilation team in performing the compilation of training textbooks of the assigned profession;
- Assign tasks to training textbook compilation groups;
- Provide guidance on methods and procedures for compiling training textbooks to members of compilation groups;
- Assume responsibility for contents and quality of training textbooks; report to the appraisal council and perfect the draft thereof according to ideas contributed by the appraisal council.
2. Step 2: Design the structure of training textbooks
The compilation team shall carry out a study on the training program of a relevant profession and detailed programs of modules; Collect and refer to relevant documents to use as the basis for compiling training textbooks. To be specific:
a) Determine objectives of headings, subheadings/sections, subsections in lessons/chapters of modules;
b) Determine core and typical knowledge; the structure and types of exercises/products for forming vocational skills for the purpose of obtaining objectives of headings, subheadings/sections, subsections in lessons/chapters of modules;
c) Organize conference to collect suggestions of experts about the structure of training textbooks;
d) Summarize collected suggestions and perfect the structure of training textbooks.
3. Step 3. Compile training textbooks
a) Compile detailed contents of modular textbooks;
b) Organize a conference to collect suggestions of experts, including teachers, lecturers, managers, researchers and experts in the training profession, about contents of each modular textbook;
c) Summarize collected suggestions of experts and perfect the structure of training textbooks.
4. Step 4: Review, compile and complete drafts of training textbooks
a) Review and compile training textbooks in a general manner;
b) Consult experts, who are specialized engineers working in local enterprises or agencies, about training textbooks;
c) Complete of the training program.
5. Step 5: Appraise and issue training textbooks
a) Send drafts of training textbooks to the textbook appraisal council, enclosed with summarized reports on the compilation process and core contents of each training textbook;
b) Defend the compiled training textbooks before the textbook appraisal council;
c) Perfect the training textbooks according to ideas contributed by the textbook appraisal council;
d) Submit the perfect textbooks to the head of the basic-level training institution (enclosed with report on the appraisal made by the textbook appraisal council) for considering and making decision on the issuance of training textbooks.
6. Step 6: Appraise and revise contents of the training textbooks.
Article 12. Procedures for appraising and issuing the training textbooks
a) Step 1: Establish the textbook appraisal council
a) The head of the basic-level training institution shall make decision on the establishment of the textbook appraisal council.
b) The textbook appraisal council includes from 5 to 7 members. There are the council’s chairman, deputy chairman, secretary and members. The council's members are teachers, lecturers, experts, or managers who are experienced in relevant training profession, and appointed according to each specialized area of the training profession. At least one member of the council is appointed by the employer who shall employ graduates.
c) Members of the textbook appraisal council must possess college degree of higher; have at least 5 years of experience in teaching or participating in the production or business in the field of the training profession whose training textbook must be appraised.
d) The textbook appraisal council may establish and entrust its sub-boards with tasks in appraising certain modular textbooks which must be appraised of relevant training profession. Each sub-board shall include from 3 to 5 members who are teachers or lecturers who have teaching experience in corresponding modules of the training profession.
dd) Duties of the textbook appraisal council: Appraise training textbooks which are drafted and submitted by the compilation team; Submit reports to the head of the basic-level training institution on appraisal results to use as the basis for considering and making decision on issuance of training textbooks.
2. Step 2: Organize the appraisal of training textbooks
a) The textbook appraisal council shall appraise each training textbook on the basis of the training program and current requirements on training textbooks. To be specific:
- Organize the meeting under the management of the council’s chairman and the presence of all members of the council on the principle of open discussion in which each council’s member shall state his analytical opinions and evaluation of each compiled textbook, and vote on each content of such textbook, then the council may come to conclusions. Any opinion is brought to the conclusion if it has been approved by at least two-thirds of total members of the council.
- Submit the report on appraisal results, enclosed with the minutes of the council’s meeting (in which, opinions of each member, voting result of each content which is concluded by the council and signatures of members), to the head of the training institution for considering and making decisions on approval and application of training textbooks.
b) Training textbook compilation team must respond to any queries of members of the textbook appraisal council.
c) The textbook appraisal council shall come to obvious conclusion by specifying one of the following contents: the training textbook is approved without any modification or amendment, or the training textbook is approved with request for modification or amendment and specifying contents that must be modified or amended, or the training textbook is unapproved and reasons thereof.
3. Step 3: Report on appraisal results
Chairman of the textbook appraisal council submits the report on the training textbook appraisal results, enclosed with the minutes of council’s meeting and appraisal documents in order that the head of the training institution can consider and make decision on the issuance of training textbooks.
4. Step 4: Issue training textbooks
The head of the basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of the training textbook appraisal results submitted by the textbook appraisal council, take the autonomy in approving and issuing the basic-level training textbooks which apply to such training institution.
Article 13. Selection, revision and evaluation of contents of training textbooks
1. Selection of training textbooks
The head of the basic-level training institution may select training textbooks of other training institutions provided that the appraisal of such training textbooks must be carried out as regulated in Article 12 of this Circular to form the basis for approval and application of such training textbooks.
2. Revision and evaluation of training textbooks
a) The head of the basic-level training institution must, on the basis of at least every 3 years, conduct the evaluation of training textbooks that are being used at such training institution.
b) Draft contents of training textbooks that must be modified or revised and carry out the appraisal of training textbooks as regulated in Article 12 of this Circular.
c) The head of the basic-level training institution shall issue revised training textbooks on the basis of proposals submitted by the appraisal council after training textbooks have been evaluated as regulated in Point a and Point b Clause 2 of this Article.
ENROLMENT FOR BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING
Article 14. Determination of enrolment target, enrolment plan and announcement of enrolment
1. Determination of enrolment target
The basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of its enrolment scale defined in the certificate of registration of basic-level training activities and certificate of registration of additional basic-level training activities which have been issued by competent authorities, take the autonomy in determining its annual enrolment targets for basic-level training.
2. Enrolment plan
a) Annually, the basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of enrolment targets determined as regulated in Clause 1 of this Article, and enterprises and employers’ demands on labour, demands of learners, and its enrolment and training results during the year, prepare and send its annual enrolment plan of the following year, in which, the number of learners, training professions, subjects of enrolment, period and areas of enrolments must be specified, to the department of labour - invalids and social affairs where the basic-level training is organized, and relevant ministries or regulatory bodies that direct supervise such training institution (if any) ahead of October 31st.
b) Annually, department of labour - invalids and social affairs shall summarize and send enrolment plans submitted by local basic-level training institutions; relevant ministries or regulatory bodies shall summarize and send enrolment plans submitted by their affiliated basic-level training institutions (if any) to Ministry of Labour - Invalids and Social Affairs ahead of November 30th.
3. Announcement of the enrolment
Within 03 (three) months before the enrolment is organized, the basic-level training institution must publicly announce the following contents: the enrolment target of each training profession; subjects of the enrolment, enrolment areas, and period for receiving applications for admission; period for considering and accepting applications for admission and grounds thereof.
Article 15. Subjects and methods of enrolment
1. Subjects of the enrolment
Subjects of the enrolment are those who are enough 15 (fifteen) years of age or older, have level of education and health suitable for their registered professions.
2. Enrolment method: Consideration of applications for admission which shall be made in several times per year.
Article 16. Registration for admission to basic-level training
1. Learners may register for admission to basic-level training at one or several basic-level training institutions. Learners shall submit their applications to basic-level training institutions where they register for admission.
2. Heads of basic-level training institutions shall regulates procedures and application for registration, the consideration for admission, and sending notice of admission to candidates who are eligible for basic-level training.
3. If all requirements on admission to basic-level training have been satisfied by successful candidates, the training department shall request the head of the training institution to sign decision on certification of official students of such training institution, placement and issuance of student’s cards.
4. Learners are provided by the basic-level training institution with sufficient information about objectives, contents and teaching plans of training programs, training regulations, duties and rights of learners.
5. Admission documents of each learner must be stored in a document bag and managed by the training department of the basic-level training institution.
EXECUTION OF BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING PROGRAMS
Article 17. Duration of training activities
1. The head of the basic-level training institution shall, depending on requirements and characteristics of each training profession, and its actual conditions, regulate specific duration of its training activities.
2. Unit of duration of training activities
a) Duration of a training course may be year-based, month-based or week-based duration.
b) One session of practice or module-based study is 60 minutes. One session of theoretical instruction is 45 minutes.
c) One day of practice, internship or module-based study shall consist of up to 8 sessions. One day of theoretical instruction shall consist of up to 6 sessions.
d) One week of module-based study or practice shall consist of up to 40 (forty) sessions. One week of theoretical instruction shall consist of up to 30 (thirty) sessions.
3. The individual in charge of training affairs of the basic-level training institution shall, depending on the number of learners, the number of classes and facilities of such training institution, arrange daily schedule for each class.
Article 18. Training duration and division of training duration
1. Basic-level training duration must be enough for accumulating the number of modules required for each training program. The head of the basic-level training institution shall, depending on its training conditions, regulate the maximum training duration of each training program provided that it must not exceed twice the designed duration of such training program.
2. The basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of the training program, divide training duration and arrange training plan for each training profession; maximum and minimum number of modules that must be accumulated for each semester or study stage provided that the following requirements must be satisfied:
a) The minimum study duration of each training program is 10 (ten) weeks and the maximum study duration of the same is 42 (forty-two) weeks. The minimum duration for reviewing, test or taking final exam of each training course is 01 (one) week and the maximum duration for the same is 02 (two) weeks.
b) The minimum duration for general activities of the training program is 01 (one) week and the maximum duration for the same is 02 (two) weeks.
3. The head of the basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of contents and the minimum body of knowledge and skills, required capacity of graduates prescribed in the training program of each training profession, decide the number of modules for each semester or study stage.
Article 19. Execution and management of training program
1. Preparation of the training plan
a) The training plan of the course must include the following contents: training objectives, the number of modules, name of each training module; time for test or taking final exam of the course; location for executing the training program.
b) The training plan for semester or study stage must include the following contents: name of training modules; period for execution, starting time and ending time; time of test; teachers and teaching location.
At the beginning of each course, the basic-level training institution must inform learners of training regulations; training plan of the course, that of semester or study stage; mandatory and optional contents of the training program for the whole course, each semester or study stage; list of modules that shall be taught; schedule for tests and exams, and forms of test or final exam or recognizing study results; learners' rights and duties.
2. Requirements on teachers
a) Teachers must meet standards of professional qualifications as regulated.
b) The basic-level training institution must arrange qualified teachers to teach contents of the training program.
3. Organization of classes and training location
a) Organization of classes:
- The maximum number of learners of a class in professional knowledge and other necessary skills is 35 persons. The maximum number of learners who are ethnics or persons with disabilities of a class in professional knowledge and other necessary skills is 20 persons. Especially, the maximum number of learners who are blind of a class in professional knowledge and other necessary skills is 10 persons.
- The maximum number of learners of a practice class or integrative learning class is 18 persons. The maximum number of learners who are ethnics or persons with disabilities of a practice class or integrative learning class is 10 persons. Especially, the maximum number of learners who are blind of a practice class or integrative learning class is 8 persons.
- Each class shall be managed by a head teacher.
b) Training location
The training may be executed in a flexible manner at the training institution, enterprises or manufacturing establishments provided that teaching and learning conditions, location for learning vocational knowledge, location for learning vocational skills, training facilities and materials, etc. must be ensured in conformity with requirements of each training module or training program.
4. Organization of instruction
a) At the beginning of each course, semester or study stage, and before the program of each module starts, teachers shall test and evaluate knowledge and vocational skills as well as learning attitude of each learner (evaluation of learner’s capacity) in order to prepare suitable teaching contents and methods.
b) Only knowledge and skills that learners have not learned or grasped or mastered shall be taught. A test is conducted for evaluating study results of the module that has been taught, and then, the instruction of the following module of the training program shall be executed.
c) In case the basic-level training is continuously conducted, learners may, upon the completion of each semester or study stage, do jobs which they have learned at their residential areas or working places, or themselves review for the test of learned module and continue the following module, semester or study stage.
Article 20. Interruption of studies
1. A learner may suspend his/her studies and reserve study results in the following cases:
a) The learner is conscripted into the army or the police, or participates in the volunteer youth force;
b) The learner is sick or has an accident that needs to receive long-term treatment provided that a certificate made by the hospital or authorized medical facility is submitted;
c) In case of temporary suspension due to personal demands, the following requirements must be satisfied:
- At least one module or a semester or study stage of the training program has been completed at the basic-level training institution;
- The learner does not fall in cases of expulsion as regulated in Article 21 of this Circular.
2. A learner who wishes to resume studies at the basic-level training institution must give a prior notice of at least 5 (five) working days before a new semester or study stage starts.
3. The head of the basic-level training institution shall regulate procedures for temporary suspension, preservation of study results and resumption of studies, and announce such procedures at that basic-level training institution.
Article 21. Expulsion and withdrawal from studies
1. A learner may be expelled from the training institution in the following cases:
a) Learner is disciplined at expulsion level.
b) The maximum training duration of the training program comes to an end as regulated in Section 1 Article 18 of this Circular.
2. A learner who is not in the cases of expulsion as regulated in Clause 1 of this Article, and has fulfilled all obligations as regulated, can request the head of the basic-level training institution to approve his withdrawing from the training institution in the following cases:
a) The learner himself finds that he is unable to complete the training program.
b) The learner must withdraw due to other reasons, enclosed with unambiguous evidences, and such withdrawal is approved by the head of the training institution.
3. The head of the basic-level training institution shall regulate procedures, responsibilities of the training institution, those of the learner, and grant decision on the expulsion or the withdrawal from studies to relevant learner.
4. Within one month from the date on which the decision on the expulsion or the withdrawal from studies is granted to the learner, the basic-level training institution must inform the local authorities where the learner registers for permanent residence and temporary residence (if any).
Article 22. Transfer between basic-level training institutions
1. During the training duration, due to personal demands and family's demands (change of family’s residence, or due to family or personal background), a learner’s transfer between basic-level training institutions may be considered and his/her study results shall be approved if the following requirements are satisfied:
a) The learner must submit an application for transfer between training institutions, enclosed with the application for admission as regulated by the transfer-in training institution;
b) The transfer-in training institution has the training profession that the learner is studying;
c) The learner is not disciplined or under the disciplinary probation;
d) The transfer must be approved by both current training institution and transfer-in training institution.
2. The head of the transfer-in training institution may, on the basis of training programs of two training institutions, decide to grant permission to the learner to continue his/her studies and recognize previous study results of the learner or modules whose results are converted and the number of modules which the learner must complete.
Article 23. Evaluation and recognition of study results
1. The evaluation of study results at basic-level training is carried out by the combination of test marks during the study process and test mark of each module. Module mark is the sum of test marks during the study process of such module (including marks of regular tests and periodical test mark) and the mark of the final test of such module.
2. Mark for evaluating study results of a learner shall be out of 10 (from 1 to 10) and rounded to the nearest tenth.
3. The study results are evaluated according to the number of accumulated modules. Upon the end of the basic-level training program, if the learner who has sufficiently accumulated the required number of modules and satisfied all requirements shall be granted with an basic-level training certificate by the head of the vocational training institution. Accumulated modules shall be recognized and must not be repeated if the learner registers for other training programs or such modules shall be preserved for attending the bridge program to higher level.
EXAMS, TESTS AND RECOGNITION OF GRADUATION
Article 24. Regular test and periodical test
1. Regular test and periodical test
a) The regular test is carried out at anytime during the learners’ study process according to each specific module by marking oral tests during class hours, paper tests with the testing period equal or under 30 minutes, tests in certain contents of practice or internship, marking exercises and other testing forms.
b) The periodical test is carried out at a given period defined in the detailed outline of relevant module; the periodical test may be carried out in writing with testing period from 30 to 45 minutes; doing practice or internship exercises and other testing forms.
2. Methods of organizing regular test and periodical test
a) The module teacher shall give tests for evaluating learners’ study results in conformity with the following requirements:
- Test questions must be related to contents of the training module which have been taught to learners;
- Module teacher shall decide specific test questions and the form of regular test;
- Test questions and the form of periodical test shall comply with regulations stated in the detailed outlines of relevant module of the training program;
b) Tests that are given in the form of paper test, essay or exercise must be given back to learners immediately after test marks are announced.
3. The head of the basic-level training institution shall promulgates regulations on testing procedures and the number of tests for each module, ensuring that a learner must have at least one mark of regular test and the same of periodical test for each module.
4. A learner who fails to sit for a test without stating legitimate reasons shall get 0 (zero) mark on such test. If a learner who is absent with legitimate reasons may make up the test as arranged by the module teacher.
Article 25. Final test at the end of each module
1. Regulations on the final test at the end of each module
a) To sit for the final test at the end of each module, learners must meet the following requirements:
- Learners must attend a minimum of 70% of theoretical hours and 80% of practical/internship hours, and meet requirements of such module as prescribed in the detailed outline of such module.
- Learners must get an overall average mark of all tests of 5.0 or higher.
A learner who got ill during study process or the testing period at the end of a module must submit an application for sick leave to the basic-level training institution within one week from the date on which he got ill, enclosed with certificate of illness granted by the medical agency of the training institution or the medical agency at communal level or higher but such learner is required to maintain his/her attendance rate as regulated in this point.
b) Testing forms and testing period
- The final test at the end of a module is a test on general skills, including knowledge and skills in practicing one or certain tasks of the training profession.
- The period of a paper test at the end of a module is from 60 to 120 minutes. The head of the basic-level training institution shall decide testing periods for other testing forms or the testing period of the module that has specific characteristics of the training profession.
The testing form and the testing period of the final test at the end of a module must be specified in the detailed outline of such module.
c) Preparing test questions and mark scheme
- The head of the basic-level training institution shall establish, manage and use the question bank for final tests at the end of modules. Test questions must be in conformity with the module’s contents that have been prescribed in the training program and randomly selected from the question bank of the basic-level training institution. The test questions must be approved by the head of the basic-level training institution before using.
- Marking methods
+ Each test at the end of a module must be marked by teacher who must sign on the marked paper test, marking sheet or summary table of scores. The marking of essay tests, oral tests and practice tests must be made in marking sheets stipulated by the head of the basic-level training institution.
+ Test mark is the average of marks awarded by teachers. If there is a difference of more than 1.0 mark (according to 10-grading system) between marks awarded by teachers to the same test, it must be considered or the mark review of such test must be carried out. If it still has the difference in marks awarded by teachers after the mark review has been carried out, the faculty dean or the head teacher of such subject shall consider and make final decision on the mark awarded to such test. The head of the basic-level training institution shall provide specific regulations on tests which are marked via computers or specialized software and the mark review, and organize the implementation thereof.
A learner who fails to meet requirements to sit a test or is absent from the testing session without legitimate reasons must get zero mark. If a learner is absent with legitimate reasons, the mark of such test is not yet determined.
- Methods of calculating module mark
+ Module mark is the average of test marks with a weighing factor of 0.4 and the mark of the final test at the end of such module shall be given a weighing factor of 0.6.
+ The average mark of test marks is the arithmetic mean of marks of regular tests and periodical tests according to specific coefficient of each type of mark. Where, regular tests shall be given the coefficient of 1, and periodical tests shall be given the coefficient of 2.
d) Result of the final test at the end of each module; repeating a module and retaking a test
- A learner who has met all requirements to sit a test is entitled to sit the final test at the end of a module but a learner shall not sit the final test more than two times. To be specific:
+ A learner who has passed the first test at the end of a module must not sit for the second test. A learner who failed in the first test must sit for the second test organized by the training institution.
+ If a learner fails to sit a final test without legitimate reasons, it will be considered that he/she has taken the test and received the zero mark. If a learner is absent with legitimate reasons, he/she may sit another test as arranged by the head of the basic-level training institution.
- Repeating a module and retaking a test:
A learner must repeat and retake a test of a failed module in the following cases:
+ The learner fails to meet requirements to sit the initial test;
+ The learner failed in all tests (02 times) stipulated for a module.
- A learner who must repeat and retake a test of a given module may not preserve previously awarded marks and study period of such module, and can sit the final test of a module if having satisfied all requirements to sit a test as prescribed in Point a Clause 1 of this Article.
- If the module in which the learner failed is not yet organized due to the modification of the training program, the head of the basic-level training institution shall decide a substitute module which must be conformable to objectives of the training profession.
2. Method of conducting the final test of a module
a) The basic-level training institution shall disseminate testing regulations to learners attending such test. Meetings relating to the test, selection and delivery of test questions, test papers, and test marks must be recorded in writing.
b) The schedule of the main test must be announced at least 02 weeks before the testing date. The schedule of the re-take must be announced at least 01 weeks before the testing date. One test shall be separately organized for one module. The combination of certain modules in a test is not allowed.
c) The duration for reviewing for a final test of a given module shall be directly proportional to total hours of such module. At least a half of a day is given for reviewing for the test for the actual study duration of 15 hours. The training institution must arrange teachers to provide guidance to learners to review for their tests. The review outline must be provided to learners immediately when such review starts.
d) The list of learners eligible to sit the test of a given module and the list of learners ineligible to sit the test of the same and reasons thereof must be publicly announced at least 05 working days before the testing date of such module. The list of testing rooms and testing locations must be publicly announced from 01 to 02 working days before the testing date of relevant module.
dd) Marks of oral tests, practice/internship test or mark of defense of internship report must be announced immediately after such marks are awarded. Marks of other tests must be announced within 05 working days from the end of the deadline for submitting testing results expires.
e) The head of the basic-level training institution shall promulgate regulations on the organization of final tests of modules of such training institution.
Article 26. End-of-course test or exam (referred to as the end-of-course exam)
1. The head of the basic-level training institution shall provide for the preparation of end-of-course exam questions; exam regulations (period, the form of the exam; grading system and marking method, etc.); the establishment of the end-of-course exam board, and direct the performance of the end-of-course exam in a transparent and fair manner for the purpose of ensuring the quality of the end-of-course exam, and the appreciation of study and training results of learners.
2. To sit the end-of-course exam, learners must meet the following requirements:
a) Learners must get an overall total mark of a subject or module of 5.0 or higher;
b) Learners must not face criminal prosecutions at the time of organizing the end-of-course test or exam.
3. Form of the end-of-course exam:
The end-of-course exam is organized by doing exercises in general skills for performing simple tasks of the training profession or finishing certain products or services.
4. Duties of the end-of-course exam board:
a) Approve the list of learners who are eligible to sit the end-of-course exam and announce such list in at least 15 days before the exam date;
b) Prepare exam questions and answers, and marking procedures;
c) Organize the end-of-course exam, handle acts in breach of exam regulations and assume responsibility for the graduation recognition;
d) Organize the marking of exam papers;
dd) Suggest the ranking of graduates at the end of the course.
Article 27. Graduation recognition for graduates of basic-level training course
1. Method of calculating GPA of the course
The GPA of a learner at basic level shall apply the following formula:

Where:
- DTKKH: GPA of the course
- DiTKM: Overall total mark of the module i
- DT: The end-of-course exam mark
- n: The number of training modules
2. Requirements for the graduation recognition
A learner at basic level shall be certified for graduation when he attains a GPA from 5.0 as per Clause 1 of this Article.
3. Graduation ranking
a) Graduates shall be ranked according to their GPAs.
b) A graduate may be ranked according to the following ranks:
- Excellent: The GPA is from 9.0 to 10;
- Very good: The GPA is from 8.0 to less than 9.0;
- Good: The GPA is from 7.0 to less than 8.0;
- Above average: The GPA is from 6.0 to less than 7.0;
- Average: The GPA is from 5.0 to less than 6.0;
c) The graduation rank, if above average, shall be lowered to the immediate lower rank if the student receives a disciplinary warning or harsher penalties, or he must repeat or retake one or certain modules during the course (excluding suspended or exempted modules).
d) The graduation rank shall be specified in the basic-level training certificate and the record of study results of relevant graduate.
4. Graduation recognition
a) The head of the basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of the report submitted by the end-of-course test or exam board, decide the graduation recognition and inform it to learners.
b) The basic-level training institution shall submit reports to the department of labour - invalids and social affairs where it organizes the basic-level training and relevant managing agency (if any) on the graduation recognition results within 30 days from the end of the training course.
FORM OF BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING CERTIFICATE; PRINTING, MANAGEMENT, ISSUANCE, REVOCATION AND CANCELLATION OF BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING CERTIFICATES
Article 28. Form of basic-level training certificate
1. The basic-level training certificate shall include two sides with the size of 19cm x 18cm.
2. The front side of the basic-level training certificate has the red background, the national emblem, and words in the front side are printed in yellow; the back side of the basic-level training certificate shall has the white background, the light yellow bronze-drum pattern, words in the back side are printed in black. Particularly, the phrase “BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING CERTIFICATE” is printed in red color, Times New Roman font, bold and uppercase.
3. Specific contents of the basic-level training certificate are as per the form No. 1 of this Circular.
Article 29. Form of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate
1. The form of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate shall be the same with that of the basic-level training certificate as per Article 28 of this Circular but the word “DUPLICATE” is additionally printed in red color, Times New Roman font, uppercase and no bold.
2. Specific contents of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate are as per the form No. 2 of this Circular.
Article 30. Printing, management and issuance of basic-level training certificates
1. Printing and management of basic-level training certificates
a) The basic-level training institution shall, on the basis of the form of the basic-level training certificate and that of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate as per Article 28 and Article 29 of this Circular, design or select forms of unnamed templates of basic-level training certificate, and those of unnamed templates of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate, with the logo of such training institution, if any.
b) The basic-level training institution shall send an official dispatch, enclosed with forms of unnamed templates of basic-level training certificate and those of unnamed templates of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate (03 copies each), to the department of labour - invalids and social affairs where its head office locates for endorsement.
Within 5 (five) working days from the date on which the said documents are received, the department of labour - invalids and social affairs must certify each form of the unnamed templates of basic-level training certificate and that of the unnamed templates of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate. In case of refusal, a written notice specifying reasons thereof shall be granted to the basic-level training institution.
Over the said time-limit, if the department of labour - invalids and social affairs neither certifies nor responds to the basic-level training institution, such basic-level training institution is entitled to printed and use basic-level training certificates and duplicates of basic-level training certificate according to the unnamed templates submitted.
d) The form of the unnamed templates of basic-level training certificate and that of the unnamed templates of the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate which have been certified shall be retained in the basic-level training institution and relevant department of labour - invalids and social affairs.
dd) The basic-level training institution shall print and issue basic-level training certificates and duplicates of basic-level training certificate according to the unnamed templates as per Point b Clause 1 of this Article to graduates.
2. Issuance of basic-level training certificates
a) The head of the basic-level training institution shall sign and issue the basic-level training certificate to each graduate who has been certified for graduation as per Article 27 of this Circular,
b) The basic-level training certificate is issued only once, no re-issuance made. The duplicate of the basic-level training certificate is issued as requested by the relevant graduate.
c) The basic-level training institution shall record in the register of basic-level training certificates and the register of duplicates of basic-level training certificates.
Article 31. Revocation and cancellation of basic-level training certificates
1. The head of the basic-level training institution may revoke the basic-level training certificate and the duplicate of the basic-level training certificate in the following cases:
a) Any fraudulent act during the study process, leading to the false assessment of study results, is discovered.
b) The printing, management and issuance of basic-level training certificates and duplicates of basic-level training certificates are not performed as regulated.
c) A basic-level training certificate or the duplicate of basic-level training certificate is issued to unqualified learners; the basic-level training certificate or the duplicate of basic-level training certificate is issued by an incompetent individual; the basic-level training certificate is erased or altered
d) The holder of the basic-level training certificate and the duplicate of basic-level training certificate lends his/her basic-level training certificate or the duplicate of basic-level training certificate to another person.
2. The head of the basic-level training institution shall consider and make decision on the cancellation of the graduation recognition and the revocation of the issued basic-level training certificate and the issued duplicate of basic-level training certificate. The revocation of the basic-level training certificate may be announced on the mass media, where necessary.
FORMS AND RECORDS FOR MANAGING BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING, AND REPORTING OF BASIC-LEVEL TRAINING
Article 32. Forms and records for managing basic-level training
Forms and records for managing basic-level training, which are promulgated under this Circular, consist of:
|
1. Training progress |
Form No. 3. |
|
2. Teacher’s plan |
Form No. 4. |
|
3. Class record book |
Form No. 5. |
|
4. Teacher handbook |
Form No. 6. |
|
5. Training plan |
Form No. 7. |
|
6. Register of basic-level training certificates |
Form No. 8. |
|
7. Register of duplicates of basic-level training certificates |
Form No. 9. |
|
8. Student management book |
Form No. 10. |
1. Basic-level training institutions shall submit reports to departments of labour - invalids and social affairs, and ministries or regulatory bodies that directly manage relevant training institutions (if any), on the enrolment for basic-level vocational training and training results on the periodical basis of every 6 months (ahead of June 30th) or 01 year (ahead of December 31st) by using the form No. 11 enclosed to this Circular.
2. Department of labour - invalids and social affairs shall summarize the enrolment and training results at basic level in provinces under their authorities; relevant ministries or regulatory bodies shall summarize the enrolment and training results at basic level of their affiliated training institutions (if any), on the periodical basis of every 6 months (ahead of July 31st) or 01 year (ahead of January 31st of the following year), to the Ministry of Labour - Invalids and Social Affairs in conformity with the form No. 12 enclosed to this Circular.
Article 34. Responsibilities of Ministry of Labor - Invalids and Social Affairs
1. Take the prime responsibility and coordinate with agencies that are in charge of managing vocational training institutions, and affiliated to relevant ministries and local governments, to direct and provide guidance on the implementation of regulations on the basic-level training.
2. Inspect and summarize reports on the implementation of regulations on the basic-level training.
Article 35. Responsibilities of the people’s committees of central-affiliated cities and provinces
1. Instruct basic-level training institutions in their provinces to execute basic-level training programs as regulated.
2. Direct, inspect and summarize reports on the execution of basic-level training programs by basic-level training institutions in their provinces as regulated.
Article 36. Responsibilities of ministries and regulatory bodies that have affiliated basic-level training institutions
1. Direct and provide guidance to their affiliated basic-level training institutions on the execution of basic-level training programs.
2. Direct, inspect and summarize reports on the execution of basic-level training programs by basic-level training institutions under their authority as regulated.
1. This Circular shall take effect as of December 05, 2015.
2. Basic-level training institutions that carry out the enrolment and execute basic-level vocational training before the date on which this Circular takes effect shall continue their execution of current training courses until such courses are completed as regulated by relevant training programs and regulations on the basic-level vocational training.
3. The Circular No. 31/2010/TT-BLDTBXH dated October 08, 2010 of the Ministry of Labour - Invalids and Social Affairs providing guidance on the establishment of programs and the compilation of textbooks for basic-level vocational training and regulations on vocational education which are contrary to regulations of this Circular shall be abrogated.
4. Difficulties that arise during the implementation of this Circular should be reported to the Ministry of Labour - Invalids and Social Affairs for consideration./.
|
|
FOR MINISTER |
Tình trạng hiệu lực: Còn hiệu lực

 Thông tư 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH (Bản Pdf)
Thông tư 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH (Bản Pdf)
 Thông tư 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH (Bản Word)
Thông tư 42/2015/TT-BLĐTBXH (Bản Word)