 Tìm kiếm
Tìm kiếm
Chương III Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT : Nối đất kết cấu kim loại trong và liền kề hành lang bảo vệ an toàn đường dây dẫn điện trên không điện áp từ 220 kv trở lên phòng tránh nhiễm điện do cảm ứng đo vẽ bản đồ cường độ điện trường Điều 11. Phạm vi nối đất
| Số hiệu: | 05/2021/TT-BCT | Loại văn bản: | Thông tư |
| Nơi ban hành: | Bộ Công thương | Người ký: | Nguyễn Hồng Diên |
| Ngày ban hành: | 02/08/2021 | Ngày hiệu lực: | 22/09/2021 |
| Ngày công báo: | 18/08/2021 | Số công báo: | Từ số 717 đến số 718 |
| Lĩnh vực: | Thương mại | Tình trạng: | Còn hiệu lực |
TÓM TẮT VĂN BẢN
Đối tượng được cấp thẻ an toàn điện
Ngày 02/8/2021, Bộ trưởng Bộ Công Thương ban hành Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT quy định chi tiết một số nội dung về an toàn điện.
Theo đó, các đối tượng được huấn luyện, sát hạch, xếp bậc và cấp thẻ an toàn điện gồm:
- Người làm công việc vận hành, thí nghiệm, xây lắp, sửa chữa đường dây dân điện hoặc thiết bị điện ở doanh nghiệp, bao gồm cả treo, tháo, kiểm tra, kiểm định hệ thống đo, đếm điện năng; điều độ viên.
- Người vận hành, sửa chữa điện ở nông thôn, miền núi, biên giới, hải đảo thuộc tổ chức hoạt động theo Luật Điện lực và các luật khác có liên quan, phạm vi hoạt động tại khu vực nông thôn, miền núi, biên giới, hải đảo.
(Hiện hành là người làm công việc vận hành, sửa chữa điện ở nông thôn, miền núi, biên giới, hải đảo).
- Người lao động làm nghề vận hành, sửa chữa, dịch vụ điện cho các tổ chức, doanh nghiệp. (Nội dung mới bổ sung)
Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT có hiệu lực từ ngày 22/9/2021 và thay thế Thông tư 31/2014/TT-BCT ngày 02/10/2014.
Văn bản tiếng việt
Văn bản tiếng anh
1. Cấp điện áp 220 kV:
Trong và liền kề hành lang bảo vệ an toàn đường dây đến 25 m tính từ mép dây dẫn ngoài hoặc dưới cùng.
2. Cấp điện áp 500 kV:
Liền kề hành lang bảo vệ an toàn đường dây đến 60 m tính từ mép dây dẫn ngoài hoặc dưới cùng.
1. Nhà ở, công trình có mái làm bằng kim loại cách điện với đất: Nối đất mái. Các kết cấu kim loại nằm dưới mái không phải nối đất.
2. Nhà ở, công trình có mái không làm bằng kim loại: Nối đất tất cả các kết cấu kim loại cách điện với đất như vách, tường bao, dầm, xà, vì kèo, khung cửa.
3. Nối đất các kết cấu kim loại cách điện với đất ở bên ngoài nhà ở, công trình như khung sắt, tấm tôn, ăng ten ti vi, dây phơi.
1. Cọc tiếp đất được làm bằng thép tròn đường kính không nhỏ hơn 16 mm hoặc thép vuông có tiết diện tương đương hoặc thép góc có kích thước không nhỏ hơn (40x40x4) mm; chiều dài phần chôn trong đất ít nhất 0,8 m (theo phương thẳng đứng), một đầu cọc nhô lên khỏi mặt đất (không cao quá 0,15 m); nơi đặt cọc tiếp đất không được gây trở ngại cho người sử dụng nhà ở, công trình. Không được sơn phủ các vật liệu cách điện lên bề mặt cọc tiếp đất. Tại những nơi dễ bị ăn mòn, các cọc tiếp đất phải được mạ đồng hoặc mạ kẽm.
2. Dây nối đất có thể được làm bằng thép tròn đường kính không nhỏ hơn 6 mm hoặc thép dẹt kích thước không nhỏ hơn (24x4) mm và phải có biện pháp chống ăn mòn hoặc dây đồng mềm nhiều sợi tiết diện không nhỏ hơn 16 mm2.
3. Dây nối đất được bắt chặt với phần nổi trên mặt đất của cọc tiếp đất và kết cấu kim loại cần nối đất bằng bu lông hoặc hàn.
4. Trường hợp nhà ở, công trình đã có nối đất an toàn đang được sử dụng thì không cần phải làm thêm cọc tiếp đất mà chỉ cần bắt chặt dây nối đất vào nối đất đó bằng bu lông hoặc bằng phương pháp hàn.
1. Trách nhiệm nối đất
a) Đối với nhà ở, công trình có trước khi xây dựng công trình lưới điện cao áp, chủ đầu tư công trình lưới điện cao áp chịu mọi chi phí và lắp đặt hệ thống nối đất;
b) Đối với nhà ở, công trình có sau công trình lưới điện cao áp thì chủ sở hữu, người sử dụng hợp pháp nhà ở, công trình tự lắp đặt hệ thống nối đất hoặc đề nghị đơn vị quản lý vận hành lưới điện cao áp lắp đặt hệ thống nối đất và phải chịu mọi chi phí.
2. Quản lý hệ thống nối đất
Chủ sở hữu, người sử dụng hợp pháp nhà ở, công trình có các kết cấu kim loại nối đất phải quản lý hệ thống nối đất. Khi phát hiện hệ thống nối đất hư hỏng hoặc có hiện tượng bất thường phải báo ngay cho đơn vị quản lý vận hành lưới điện cao áp để phối hợp giải quyết.
1. Chủ đầu tư hoặc đơn vị quản lý vận hành trạm điện có trách nhiệm thực hiện việc đo, vẽ bản đồ cường độ điện trường trên toàn bộ diện tích mặt bằng trạm biến áp và niêm yết tại phòng điều khiển trung tâm của trạm.
2. Bản đồ cường độ điện trường cần được lập lại khi trạm điện có một trong những thay đổi ở phần mang điện từ 220 kV trở lên như sau:
a) Thay đổi phạm vi bố trí trang thiết bị;
b) Thay đổi khoảng cách giữa các vật mang điện;
c) Giảm khoảng cách từ vật mang điện đến mặt đất.
3. Việc đo, kiểm tra trị số cường độ điện trường cần được thực hiện khi đưa công trình vào vận hành và được cập nhật khi có sự thay đổi.
4. Bản đồ cường độ điện trường phải có màu sắc khác nhau để phân biệt được trị số cường độ điện trường tại vị trí công tác. Cụ thể theo bảng sau: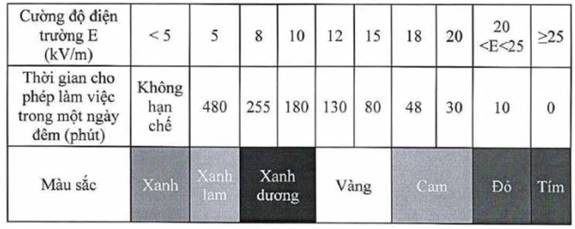
|
MINISTRY OF INDUSTRY AND TRADE |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No. 05/2021/TT-BCT |
Hanoi, August 02, 2021 |
ELABORATING SOME CONTENT ON ELECTRICAL SAFETY
Pursuant to the Electricity Law dated December 03, 2004 and Law on Amendment to Some Articles of Electricity Law dated November 20, 2012;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 14/2014/ND-CP dated February 26, 2014 stipulating in detail the implementation of Electricity Law regarding electricity safety;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 51/2020/ND-CP dated April 21, 2020 amending some Articles of the Government’s Decree No. 14/2014/ND-CP dated February 26, 2014 stipulating in detail the implementation of Electricity Law regarding electricity safety;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 98/2017/ND-CP dated August 18, 2017 on functions, duties, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Industry and Trade;
At the request of Director General of Industrial Safety Techniques and Environment Agency;
The Minister of Industry and Trade hereby promulgates a Circular elaborating some content on electrical safety.
This Circular elaborates some content on electrical safety, specifically:
1. Safety training and assessment, grade assignment and electrical safety card issuance.
2. Grounding of metal structures of housing and works located inside and adjacent to safety corridors of overhead transmission lines of 220 kV and higher to prevent electrostatic induction.
3. Measurement and mapping of electric field intensity.
4. Electrical safety signage.
5. Agreements made upon construction of housing and works located inside safety corridors of overhead transmission lines, violations concerning safety corridors of high-voltage electrical grids, and electrical accident reporting.
This Circular is applicable to organizations and individuals involving in the electricity industry and using electricity; operating electrical equipment requiring safety inspection; electrical equipment inspection service providers on Vietnamese territory and other relevant organizations and individuals.
In this Circular, the terms below are construed as follows:
1. “persons operating, experimenting on, inspecting, building or repairing transmission lines or electrical equipment at enterprises“ refers to employees of units engaging in electricity generation, transmission, distribution, experimentation, inspection or building, providing repair services or using electricity for production (having separate electrical substations).
2. “electricity operators and repairers in rural areas, mountainous areas and border areas and on islands” refers to employees of electricity units operating under the Electricity Law and other relevant laws in rural areas, mountainous areas and border areas and on islands.
3. “employers” refers to the entities mentioned in Clause 2 Article 3 of the Labor Code.
4. "electrical equipment inspection" refers to procedure-based inspection of, experimentation on and assessment of safety level of electrical equipment before it is put to use and during use according to corresponding technical regulations and standards.
5. “authorizing persons” refers to persons permitting work units to work on sites meeting electrical safety requirements.
TRAINING, ASSESSMENT, GRADE ASSIGNMENT AND ELECTRICAL SAFETY CARD ISSUANCE
Article 4. Persons requiring training, assessment, grade assignment and electrical safety card issuance
1. Persons operating, experimenting on, building or repairing transmission lines or electrical equipment at enterprises, including installing, removing and inspecting electrical energy measuring systems; regulators.
2. Electricity operators and repairers in rural areas, mountainous areas and border areas and on islands of organizations operating under the Electricity Law and other relevant laws in rural areas, mountainous areas and border areas and on islands.
3. Electricity operators and repairers and persons providing electricity services for organizations and enterprises.
Article 5. Theoretical training content
1. General training content
a) Electrical system diagrams and electrical system safety requirements;
b) Measures to ensure safety during work: site survey and recording (if needed); planning; work schedule registration; work unit organization; working according to work slip or work order; procedures for granting work permit; safety supervision during work; procedures for ending work and reenergizing;
c) Technical measures to prepare for a safe workplace: cutting off electricity and preventing electricity from entering workplace; checking to ensure that there is no electricity; grounding; setting up barriers, establishing safe task area and placing prohibition signage and information signage.
d) Methods for recognizing and preventing workplace accidents and risks, methods for removing victims from electricity sources and first-aid for victims of electrical accidents;
dd) Functions, uses, instructions for use and storage methods of and regulations on assessment (experimentation and inspection) of safety equipment and working equipment of workers.
2. Training content for transmission line operators
a) Assessment and recognition of risk in transmission line management and operation;
b) Transmission line operating and accident responding procedures;
c) Safety in transmission line inspection; working on offline or online transmission lines; cutting and trimming trees inside and near safety corridors of transmission lines; and working at height.
3. Training content for electrical substation and equipment operators
a) Assessment and recognition of risk in electrical substation management and operation;
b) Electrical substation and equipment operating and accident responding procedures;
c) Safety in electrical equipment inspection; operating or stopping electrical equipment; and working with electrical equipment;
d) Fire safety for electrical substations and equipment.
4. Training content for electrical work constructors
a) Safety in pole foundation digging and filling, and underground cable trench digging;
b) Safety in pole setup;
c) Safety in hanging and stretching transmission lines and lightning arrester wires;
d) Safety in electrical equipment setup.
5. Training content for persons involved in electricity experimentation and inspection
a) Operating procedures, experimenting procedures and safety regulations for equipment of inspection stations and laboratories, and measures to ensure safety in experimentation and inspection;
b) Electrical safety in experimentation and inspection of electrical equipment and materials.
6. Training content for transmission line and electrical equipment repairers
a) For transmission lines: safety in repairing offline or online transmission lines running independently or through areas under the influence of online transmission lines;
b) For electrical equipment: safety in working with each type of electrical equipment.
7. Training content for persons involved in placing, removing and inspecting electrical energy measuring systems where they are installed: safety in placing, removing and inspecting electrical energy measuring systems where they are installed when they are on or off.
8. Training content for electrical system regulators
a) Procedures and regulations related to regulation, operation and incident response;
b) Safety in operation, incident response and handover of transmission lines and electrical equipment under the control of the regulator and on-duty shift of the management unit.
Article 6. Practical training content
1. Instructions for use and methods for storage, experimentation and inspection of safety equipment and working equipment of workers.
2. Methods for removing electric shock victims from electricity sources and first-aid for victims of electrical accidents.
3. Operations related to safety assurance suitable for workers' jobs.
Article 7. Training organization
1. Employers of the persons mentioned in Clause 1 and Clause 3 Article 4 herein shall:
a) Formulate training and assessment documents and stipulate training time as appropriate to safety grades and work positions of workers;
b) Select trainers and assessors according to regulations in Clause 3 of this Article;
c) Organize training, assessment, grade assignment and electrical safety card issuance for workers after they pass assessment. Provide training for whichever part that workers have not passed;
d) Manage and monitor training, assessment, grade assignment and electrical safety card issuance at their units.
2. For the persons mentioned in Clause 2 Article 4 herein, Departments of Industry and Trade shall:
a) Formulate documents and stipulate training and assessment time as appropriate to safety grades and work positions of electricity operators and repairers in rural areas, mountainous areas and border areas and on islands;
b) Select trainers and assessors according to regulations in Clause 3 of this Article;
c) Organize training, assessment, grade assignment and electrical safety card issuance for workers after they pass assessment. Provide training for whichever part that workers have not passed at the request of their employers.
3. Electrical safety trainers and assessors
a) Trainers and assessors of the theoretical training part must have a bachelor’s degree or higher in a major suitable for the training and at least 05 years of experience relevant to the training;
b) Trainers and assessors of the practical training part must have a college degree or higher and at least 05 years of experience relevant to the training.
4. Training and assessment methods and time
a) First-time training shall take place upon a worker’s recruitment and last for at least 24 hours;
b) Periodic training shall take place on an annual basis and last for at least 08 hours;
c) Retraining shall take place when a worker switches to a new position or is assigned with a new safety grade, there is change to equipment or technology, or a worker does not pass a test or has not worked for at least 06 months. Retraining shall last for at least 12 hours.
5. Depending on circumstances, employers may organize training in electrical safety according to regulations of this Circular separately or together with training in occupational safety, occupational safety and hygiene and fire safety or in cooperation with other training units provided for by the law.
6. Employers shall incur training and card issuance costs.
Article 8. Electricity safety grades
Electrical safety grades are divided into 5 grades from 1/5 to 5/5 and require both theoretical and practical assessment results to reach at least 80%.
1. Requirements for grade 1/5:
a) Obtain first-time theoretical and practical training results of at least 80%;
b) Have knowledge about general provisions to maintain safety during work;
c) Use and manage safety equipment and working equipment allocated according to regulations.
2. Requirements for grade 2/5:
a) Grasp knowledge about general provisions and measures to maintain safety during work;
b) Use and manage safety equipment and working equipment allocated according to regulations;
c) Grasp methods for removing victims from electricity sources;
d) Know first-aid for electrical shock victims.
3. Requirements for grade 3/5:
a) Meet requirements for grade 2/5;
b) Be capable of detecting violations and unsafe acts;
c) Have skills in inspecting and supervising workers working on transmission lines or with electrical equipment.
4. Requirements for grade 4/5:
a) Meet requirements for grade 3/5;
b) Understand responsibilities and scope of work of each work unit when working with them;
c) Have skills in developing measures to ensure safety during work and supervising working workers;
d) Be capable of analyzing and investigating electrical accidents.
5. Requirements for grade 5/5:
a) Meet requirements for grade 4/5;
b) Have skills in cooperating with other work units, presiding over work, organizing adoption of safety measures and inspecting and monitoring work.
Article 9. Tasks permitted for each safety grade
1. A person assigned grade 1/5 may perform the following tasks:
a) Tasks without contact with electrical equipment or wires;
b) Assist work units working on transmission lines and electrical equipment.
2. A person assigned grade 2/5 may perform the following tasks:
a) Grade 1/5 tasks;
b) Work at locations where electricity is completely cut off.
3. A person assigned grade 3/5 may perform the following tasks:
a) Grade 2/5 tasks;
b) Work at locations where electricity is cut off in stages;
c) Work directly with online low-voltage transmission lines and electrical equipment;
d) Operate on high-voltage electrical grids;
dd) Inspect operating electrical substations and transmission lines;
e) Issue work orders, give directions directly, permit work units to work, and supervise work units working on low-voltage electrical equipment and transmission lines.
4. A person assigned grade 4/5 may perform the following tasks:
a) Grade 3/5 tasks;
b) Work directly with online high-voltage transmission lines and electrical equipment;
c) Issue work slips and work orders, give directions directly, permit work units to work, and supervise work units working on high-voltage electrical equipment and transmission lines.
5. Persons assigned grade 5/5 may perform all tasks assigned.
Article 10. Electrical safety cards
1. A safety card will be issued in the following cases:
a) After a worker receives first-time training and passes the assessment;
b) When a worker has a new job;
c) When a work loses or damages their card;
d) When a worker's safety grade changes.
2. Electrical safety cards shall be issued to persons mentioned in Clause 2 Article 4 herein within 07 working days after they receive training for the first time, periodic training or retraining or pass an assessment or the Department of Industry and Trade receives an application from their employers if their cards are lost or damaged. Employers of persons mentioned in Clause 2 Article 4 herein shall send an application consisting of the following components for training and card issuance to the Department of Industry and Trade directly or by post:
a) Application from the employer, which contains full name, job and current safety grade of the worker;
b) 02 (2x3) cm pictures and old electrical safety card (if any) of the worker.
3. Electrical safety card specimen is provided in Appendix I enclosed therewith.
4. Card use
a) Time limit for use: from issuance date to revocation date.
b) While working, workers must bring their electrical safety cards and present their cards at the request of authorizing persons, employers and competent persons.
5. An electrical safety card will be revoked in the following cases:
a) The worker has a new job or no longer works for their current employer;
b) The card is old or crumpled or the picture or letters on the card is/are faded;
c) The worker commits a violation against procedures or regulations concerning electrical safety;
d) The worker is issued with a new card.
6. Electrical safety cards shall be revoked by their issuers.
GROUNDING OF METAL STRUCTURES LOCATED INSIDE AND ADJACENT TO SAFETY CORRIDORS OF OVERHEAD TRANSMISSION LINES OF 220 KV AND HIGHER TO PREVENT ELECTROSTATIC INDUCTION; MEASUREMENT AND MAPPING OF ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY
1. At 220 kV:
25 m from the edge of the outer or lowest transmission line inside and adjacent to safety corridors.
2. At 500 kV:
60 m from the edge of the outer or lowest transmission line adjacent to safety corridors.
Article 12. Structures requiring grounding
1. Housing and structures with insulated metal roofs shall have their roofs grounded. Metal structures under the roofs do not require grounding.
2. Housing and structures with non-metal roofs shall ground all insulated metal structures such as walls, girders, beams, rafters and door frames.
3. Insulated metal structures outside of housing and structures such as metal frames, corrugated iron sheets, antennas and clothing wires shall be grounded.
Article 13. Grounding techniques
1. A grounding rod must be made of round steel tubing with a diameter of at least 16mm or square steel tubing with an equivalent cross section or steel angle bar of at least (40x40x4) mm; at least 0,8 m of the rod must be buried underground vertically with one end no more than 0,15 m above the ground; the rod's location must not cause obstruction to the housing or structure user. Do not put insulation paint on the rod. Plate locations prone to corrosion with copper or zinc.
2. Grounding wires may be made of round steel tubing with a diameter of at least 6 mm or steel flat bar of at least (24x4) mm and must be protected from corrosion or flexible multi-strand copper wires with a cross section of at least 16 mm2.
3. Grounding wires shall be connected with the part above the ground of grounding rods and metal structures requiring grounding by bolts or welding.
4. Housing and structures that already have safe grounding structures are not required to place grounding rods and only need to connect grounding wires with such grounding structures by bolts or welding.
Article 14. Responsibility for grounding and grounding system management
1. Responsibility for grounding
a) For housing and structures built before a high-voltage electrical grid, the high-voltage electrical grid investor shall incur all costs and install grounding systems;
b) For housing and structures built after a high-voltage electrical grid, lawful users and owners of those housing and structures shall install grounding systems or request the management unit of the high-voltage electrical grid to install grounding systems and incur all costs.
2. Grounding system management
Lawful users and owners of housing and structures with grounded metal structures must manage their grounding systems and, upon finding damage to their grounding systems or any unusual event, immediately notify the management unit of the high-voltage electrical grid for cooperation in handling.
Article 15. Measurement and mapping of electric field intensity
1. Investors or management units of electrical substations shall measure and map electric field intensity over the whole premises of the substations and post the maps in the central control rooms of the substations.
2. An electric field intensity map shall be revised when any of the following change occurs to the parts carrying 220 kV electricity of the electrical substation:
a) Change to equipment location;
b) Change to distance between electricity carrying objects;
c) Reduction of distance between an electricity carrying object and the ground.
3. Electric field intensity value shall be measured and checked when a work is put to use and updated upon change.
4. Electric field intensity maps must incorporate different colors to differentiate electric field intensity value at work site. To be specific:

Article 16. Classification of electrical safety signage
1. Electrical safety signage shall be classified into 03 types: prohibition signs, warning signage and instruction signage. To be specific:
|
No. |
Type and content of sign |
Picture |
Sign specifications (Picture and font sizes are provided in Appendix II enclosed therewith) |
|
1 |
Prohibition signage |
||
|
A |
“Cấm trèo! Điện cao áp nguy hiểm chết người” (“Do not climb! Fatal high voltage”) |
Pictures 1a and 1b |
Bright red border and lightning symbol, white background and black writing |
|
B |
“Cấm vào! Điện cao áp nguy hiểm chết người” (“Do not enter! Fatal high voltage”) |
Picture 2 |
|
|
C |
“Cấm lại gần! Có điện nguy hiểm chết người“ (“Stay away! Fatal electricity”) |
Picture 3 |
|
|
D |
“Cấm đóng điện! Có người đang làm việc” (“Do not energize! Workers are working”) |
Picture 4 |
Bright red border, white background and black writing |
|
2 |
Warning signage |
||
|
A |
“Dừng lại! Có điện nguy hiểm chết người” (“Stop! Fatal electricity”) |
Picture 5 |
Bright red border and lightning symbol, white background and black writing |
|
B |
“Cáp điện lực” (“Electrical cable”) |
Picture 6 |
Arrow, writing and border in blue-purple or light shade of black 1 , 2 mm in width; white background |
|
3 |
Instruction signage |
||
|
A |
“Làm việc tại đây” (“Work here”) |
Picture 7 |
Green outer background, white inner background and black writing |
|
B |
“Vào hướng này” (“Enter this way”) |
Picture 8 |
|
|
C |
“Đã nối đất” (“Grounded”) |
Picture 9 |
Black border and writing, yellow background |
2. Besides the electrical safety signage mentioned in Clause 1 of this Article, organizations and individuals may have other signage appropriate to their tasks for internal use.
Article 17. Electrical safety signage placement
1. For overhead high-voltage transmission lines, place a “CẤM TRÈO! ĐIỆN CAO ÁP NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“DO NOT CLIMB! FATAL HIGH VOLTAGE”) sign at 2,0 m above ground in a noticeable direction on all poles of the transmission lines (Picture 1a or 1b in Appendix II enclosed therewith).
2. For underground electrical cables not sharing technical infrastructure works with other pipes or cables, place a “CÁP ĐIỆN LỰC” (“ELECTRICAL CABLE”) sign on the ground or markers in the middle of the cable trough at a noticeable location that enables cable search from all locations; and at points where the cable's direction changes; two adjacent signs shall not be more than 30 m apart (Picture 6 in Appendix II enclosed therewith).
3. For electrical substations surrounded by fences, place a “CẤM VÀO! ĐIỆN CAO ÁP NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“DO NOT ENTER! FATAL HIGH VOLTAGE”) on the door or gate to each station (Picture 2 in Appendix II enclosed therewith).
4. For electrical substations hung on poles, signage shall be placed according to regulations applicable to overhead high-voltage transmission lines.
5. Place a “CẤM LẠI GẦN! CÓ ĐIỆN NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“STAY AWAY! FATAL ELECTRICITY”) sign on the covers of kiosk substations, outdoor circuit breaker kiosks and power boxes (feeder pillars) in a noticeable direction (Picture 3 in Appendix II enclosed therewith).
6. Place a “CẤM ĐÓNG ĐIỆN! CÓ NGƯỜI ĐANG LÀM VIỆC” ("DO NOT ENERGIZE! WORKERS ARE WORKING”) sign on control devices, motion drive devices and circuit breakers during power cut.
7. Place a “DỪNG LẠI! CÓ ĐIỆN NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“STOP! FATAL ELECTRICITY”) sign in a noticeable direction (Picture 5 in Appendix II enclosed therewith).
8. At marked work areas, if necessary, place a “LÀM VIỆC TẠI ĐÂY” (“WORK HERE”) sign (Picture 7 in Appendix II enclosed therewith); at entry to work areas, place a “VÀO HƯỚNG NÀY” (“ENTER THIS WAY”) sign (Picture 8 in Appendix II enclosed therewith) and a “ĐÃ NỐI ĐẤT” (“GROUNDED”) sign (Picture 9 in Appendix II enclosed therewith).
9. The “CẤM TRÈO! ĐIỆN ÁP CAO NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“DO NOT CLIMB! FATAL HIGH VOLTAGE”), “CẤM VÀO! ĐIỆN ÁP CAO NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“DO NOT ENTER! FATAL HIGH VOLTAGE”) and “CẤM LẠI GẦN! CÓ ĐIỆN NGUY HIỂM CHẾT NGƯỜI” (“STAY AWAY! FATAL ELECTRICITY”) signs mentioned in Article 16 herein shall be painted (for remote and isolated areas and communes) or placed as separate signs (for towns and cities) at required locations.
Article 18. Responsibilities for electrical safety signage placement
Regulations on responsibilities for signage placement mentioned in Article 17 of this Circular:
1. Investors of new construction works and management units of in-use works shall place signage according to regulations in Clauses 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7 and 9 Article 17 of this Circular.
2. Operation supervisors shall place signage according to regulations in Clause 6 Article 17 of this Circular.
3. Direct commanders of work units or persons authorizing work units to work shall place signage according to regulations in Clause 8 Article 17 of this Circular.
AGREEMENTS MADE UPON CONSTRUCTION INSIDE SAFETY CORRIDORS OF OVERHEAD TRANSMISSION LINES; ELECTRICAL ACCIDENT REPORTING AND VIOLATIONS CONCERNING SAFETY CORRIDORS OF HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRICAL GRIDS
Article 19. Agreements made upon construction or renovation of housing and works inside safety corridors of overhead transmission lines
An agreement on safety measures mentioned in Clause 2 Article 51 of the Electricity Law shall be made as follows:
1. No later than 05 working days after the date of receipt of a written request from the investor, the management unit of the high-voltage electrical grid shall send a written notification about the field survey time to the investor.
2. Survey of the construction/renovation location and the agreement with the investor must be done within 10 working days after the date of receipt of the written request.
3. In case an agreement on safety measures cannot be reached, the management unit of the high-voltage electrical grid must provide the reason for the investor within 05 working days after the survey date in writing.
Article 20. Reporting on electrical accidents and violations concerning safety corridors of high-voltage electrical grids
Besides reporting on accidents according to regulations of law on labor, management units of high-voltage electrical grids shall submit the following reports to their supervisory bodies (if any), Industrial Safety Techniques and Environment Agency and Departments of Industry and Trade:
1. Quick reports on electrical accidents
a) Reporting time: within 24 hours after the accident takes place.
b) Report content and format: use the form in Appendix IV enclosed therewith and send the report by fax or email (PDF file).
2. Semi-annual reports
a) Reporting time:
Before May 30 and November 30 of every year, management units of electrical grids shall submit a report to Departments of Industry and Trade of their provinces.
b) Report content and format: use the form in Appendix IV enclosed therewith and send the report as an official dispatch and by email.
1. This Circular comes into force from September 22, 2021.
2. Circular No. 31/2014/TT-BCT dated October 02, 2014 by the Ministry of Industry and Trade on stipulating certain details of electrical safety is annulled from the date on which this Circular comes into effect.
3. Article 2 of Circular No. 29/2018/TT-BCT is annulled.
4. Transitional provisions
a) In-use electrical safety signage that have similar content but are in different formats from the signage provided in Article 16 of this Circular may be used until they are replaced.
b) Electric field intensity maps currently used at electrical substations and not compliant with regulations in Clause 4 Article 15 herein may be used until they are replaced.
c) For electrical safety cards currently used according to regulations in Circular No. 31/2014/TT-BCT by the Ministry of Industry and Trade, employers may continue to use these cards until they are replaced.
Article 22. Implementing responsibilities
1. Heads of entities affiliated to the Ministry, provincial People’s Committees and relevant organizations and individuals shall implement this Circular.
2. Industrial Safety Techniques and Environment Agency shall provide guidelines for, inspect and resolve difficulties in the implementation of this Circular throughout the country.
3. Departments of Industry and Trade shall:
a) Develop and notify plans for training, assessment, grade assignment and electrical safety card issuance to organizations, individuals and units employing the persons mentioned in Clause 2 Article 4 herein;
b) Provide guidance on and Inspect the implementation of this Circular in areas under their management;
c) Enumerate and monitor electrical accidents and violations concerning safety corridors of high-voltage electrical grids in areas under their management and report to the Ministry of Industry and Trade (via Industrial Safety Techniques and Environment Agency) before June 05 and December 05 of every year.
4. Any difficulty arising during the implementation of this Circular should be reported to the Ministry of Industry and Trade for consideration and/or resolution./.
|
|
THE MINISTER |
Tình trạng hiệu lực: Còn hiệu lực

 Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT (Bản Pdf)
Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT (Bản Pdf)
 Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT (Bản Word)
Thông tư 05/2021/TT-BCT (Bản Word)