Tìm kiếm
Tìm kiếm
Thông tư số 22/2015/TT-BTNMT của Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường: Quy định về bảo vệ môi trường trong sử dụng dung dịch khoan; quản lý chất thải và quan trắc môi trường đối với các hoạt động dầu khí trên biển
| Số hiệu: | 22/2015/TT-BTNMT | Loại văn bản: | Thông tư |
| Nơi ban hành: | Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường | Người ký: | Bùi Cách Tuyến |
| Ngày ban hành: | 28/05/2015 | Ngày hiệu lực: | 20/07/2015 |
| Ngày công báo: | 12/06/2015 | Số công báo: | Từ số 593 đến số 594 |
| Lĩnh vực: | Tài nguyên - Môi trường | Tình trạng: |
Hết hiệu lực
10/01/2022 |
TÓM TẮT VĂN BẢN
Văn bản tiếng việt
|
BỘ TÀI NGUYÊN VÀ |
CỘNG HÒA XÃ HỘI CHỦ NGHĨA VIỆT NAM |
|
Số: 22/2015/TT-BTNMT |
Hà Nội, ngày 28 tháng 5 năm 2015 |
QUY ĐỊNH VỀ BẢO VỆ MÔI TRƯỜNG TRONG SỬ DỤNG DUNG DỊCH KHOAN; QUẢN LÝ CHẤT THẢI VÀ QUAN TRẮC MÔI TRƯỜNG ĐỐI VỚI CÁC HOẠT ĐỘNG DẦU KHÍ TRÊN BIỂN
Căn cứ Luật bảo vệ môi trường năm 2014;
Căn cứ Luật dầu khí năm 1993; Luật sửa đổi, bổ sung một số điều của Luật dầu khí năm 2000; Luật sửa đổi, bổ sung một số điều của Luật dầu khí năm 2008;
Căn cứ Nghị định số 21/2013/NĐ-CP ngày 04 tháng 3 năm 2013 của Chính phủ quy định chức năng, nhiệm vụ, quyền hạn và cơ cấu tổ chức của Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường;
Xét đề nghị của Tổng cục trưởng Tổng cục Môi trường và Vụ trưởng Vụ Pháp chế;
Bộ trưởng Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường ban hành Thông tư quy định về bảo vệ môi trường trong sử dụng dung dịch khoan; quản lý chất thải và quan trắc môi trường đối với các hoạt động dầu khí trên biển,
Điều 1. Phạm vi điều chỉnh và đối tượng áp dụng
1. Thông tư này quy định về bảo vệ môi trường trong sử dụng dung dịch khoan; quản lý chất thải và quan trắc môi trường đối với các hoạt động dầu khí trên biển.
2. Thông tư này áp dụng đối với các cơ quan quản lý về môi trường, tổ chức, cá nhân có hoạt động liên quan đến hoạt động dầu khí trong phạm vi lãnh thổ, vùng đặc quyền kinh tế và thềm lục địa của nước Cộng hòa xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam.
Trong Thông tư này các từ ngữ dưới đây được hiểu như sau:
1. Hoạt động dầu khí trên biển là các hoạt động tìm kiếm, thăm dò, khai thác dầu khí; vận chuyển, lưu trữ, chế biến dầu khí và các dịch vụ kỹ thuật khác liên quan trực tiếp cho các hoạt động này mà được thực hiện trên biển.
2. Tổ chức dầu khí là các cá nhân, tổ chức được phép hoạt động dầu khí trên biển theo quy định của pháp luật.
3. Công trình dầu khí là các loại giàn, công trình di động hay cố định, phương tiện và các kết cấu khác được sử dụng nhằm phục vụ cho hoạt động dầu khí trên biển.
4. Dung dịch khoan là dung dịch tuần hoàn được sử dụng trong quá trình khoan thăm dò, khai thác dầu khí để đưa mùn khoan lên khỏi giếng khoan và cân bằng áp suất trong giếng khoan, làm mát, bôi trơn mũi khoan, truyền năng lượng thuỷ lực đến mũi khoan, trám kín các chỗ thấm và bảo trì thành giếng.
5. Dung dịch khoan nền nước (Water - Based Drilling Fluids - WBDF) là dung dịch khoan sử dụng nước làm pha liên tục và một số phụ gia khác.
6. Dung dịch khoan nền không nước: (Non – Aqueous Drilling Fluids - NADF) là dung dịch khoan sử dụng dung dịch nền là dầu tổng hợp làm pha liên tục và một số phụ gia khác.
7. Rác thực phẩm là thức ăn thừa phát sinh từ quá trình sinh hoạt hàng ngày trên các giàn khoan, giàn khai thác và trên tàu.
8. Khu vực nhạy cảm môi trường bao gồm khu bảo tồn thiên nhiên, vườn quốc gia, khu di tích lịch sử văn hóa, khu di sản thế giới, khu dự trữ sinh quyển và khu danh lam thắng cảnh đã được xếp hạng.
9. Công ước Marpol hay Marpol 73/78 là tên gọi tắt của Công ước quốc tế về ngăn ngừa ô nhiễm biển từ tàu.
Điều 3. Sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước
1. Dung dịch khoan nền không nước được sử dụng khi khoan các đoạn thân giếng gặp khó khăn về mặt kỹ thuật mà dung dịch khoan nền nước không thể thực hiện được, bao gồm một trong các trường hợp dưới đây:
a) Khoan các phân đoạn địa tầng phức tạp, dự kiến phát sinh nhiều rủi ro như các khoảng địa tầng dễ sập lở, kẹt cần khoan, mất dung dịch khoan, phun trào giếng khoan;
b) Xử lý sự cố trong quá trình khoan;
c) Gọi dòng.
2. Tổng cục Môi trường xem xét, cho phép sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước đối với từng trường hợp cụ thể.
3. Trước khi sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước, tổ chức dầu khí gửi hồ sơ đề nghị sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước đến Văn phòng Tiếp nhận và Trả kết quả giải quyết thủ tục hành chính của Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường, hồ sơ bao gồm:
a) Văn bản đề nghị sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước, nêu rõ lý do bắt buộc phải sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước, phương án sử dụng, phương án xử lý và các biện pháp giám sát theo mẫu tại Phụ lục 1 của Thông tư này;
b) Trường hợp dung dịch khoan nền không nước lần đầu tiên sử dụng tại Việt Nam: hồ sơ phải có bản gốc Kết quả phân tích dung dịch khoan nền không nước theo các quy định của Quy chuẩn kỹ thuật quốc gia về dung dịch khoan và mùn khoan thải từ các công trình dầu khí trên biển. Các thí nghiệm được tiến hành ở điều kiện môi trường Việt Nam do phòng thí nghiệm được Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường chứng nhận đủ điều kiện hoạt động dịch vụ quan trắc môi trường hoặc phòng thí nghiệm được công nhận chất lượng;
c) Các hồ sơ khác liên quan đến dung dịch khoan nền không nước (nếu có);
d) Trong thời hạn 03 (ba) ngày làm việc kể từ ngày nhận được hồ sơ, Tổng cục Môi trường có trách nhiệm thông báo cho tổ chức, cá nhân để bổ sung, hoàn thiện hồ sơ nếu hồ sơ không đầy đủ, hợp lệ theo quy định;
đ) Trong thời hạn 10 (mười) ngày làm việc, kể từ ngày nhận được hồ sơ đầy đủ, hợp lệ, Tổng cục Môi trường lấy ý kiến Tổng cục Biển và Hải đảo Việt Nam về hồ sơ đề nghị sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước; xem xét hồ sơ, ý kiến của Tổng cục Biển và Hải đảo Việt Nam và có văn bản trả lời tổ chức dầu khí về việc sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước. Nội dung văn bản trả lời nêu rõ chấp thuận hoặc không chấp thuận.
4. Tổng cục Môi trường lập, đăng tải và cập nhật danh sách các dung dịch khoan nền không nước đã được chấp thuận sử dụng trên cổng Thông tin điện tử của Tổng cục Môi trường.
5. Tổ chức dầu khí khi sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước tuân thủ đúng phương án đã được cơ quan quản lý nhà nước về môi trường chấp thuận, gửi báo cáo quá trình sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước đến Tổng cục Môi trường, chậm nhất là sau 30 ngày sau khi kết thúc đợt sử dụng.
1. Nước khai thác thải từ công trình dầu khí trên biển được xử lý và thải bỏ tuân thủ Quy chuẩn kỹ thuật quốc gia về nước khai thác thải từ các công trình dầu khí trên biển.
2. Các nguồn nước thải khác phát sinh từ công trình dầu khí trên biển được thu gom, xử lý và thải bỏ theo quy định tại Bảng 1 Thông tư này.
Bảng 1:
Yêu cầu về thu gom, xử lý và thải bỏ đối với các nguồn nước thải phát sinh từ công trình dầu khí trên biển
|
STT |
Vị trí thải |
Nguồn nước thải |
Yêu cầu |
|
1 |
Cách bờ nhỏ hơn 03 (ba) hải lý |
Nước rửa máy móc thiết bị, nước rửa khoang chứa dầu. |
Thu gom, xử lý và thải bỏ bảo đảm đạt quy chuẩn kỹ thuật quốc gia về nước thải công nghiệp. |
|
Nước thải sinh hoạt |
Thu gom, xử lý và thải bỏ bảo đảm đạt quy chuẩn kỹ thuật quốc gia về nước thải sinh hoạt. |
||
|
2 |
Cách bờ từ 03 (ba) đến 12 (mười hai) hải lý |
Nước rửa máy móc thiết bị, nước rửa khoang chứa dầu. |
Thu gom, xử lý, thải bỏ và có giấy chứng nhận ngăn ngừa ô nhiễm dầu tuân thủ các yêu cầu quy định tại Phụ lục I của Công ước Marpol. |
|
Nước thải sinh hoạt |
Thu gom, xử lý, thải bỏ và có giấy chứng nhận ngăn ngừa ô nhiễm nước thải sinh hoạt tuân thủ các yêu cầu quy định tại Phụ lục IV của Công ước Marpol. |
||
|
3 |
Cách bờ lớn hơn 12 (mười hai) hải lý |
Nước rửa máy móc thiết bị, nước rửa khoang chứa dầu. |
Thu gom, xử lý đạt hàm lượng dầu tối đa không vượt quá 15 mg/l trước khi thải xuống biển. |
|
Nước thải sinh hoạt |
Thu gom, thải xuống biển. |
3. Phân loại, thu gom, lưu giữ và quản lý chất thải không nguy hại trên công trình dầu khí trên biển:
a) Chất thải rắn sinh hoạt và chất thải rắn công nghiệp thông thường được thu gom và phân loại thành 03 nhóm bao gồm: nhóm rác thực phẩm, nhóm phế liệu để thu hồi tái chế và nhóm chất thải thông thường còn lại;
b) Nhóm rác thực phẩm được thải xuống biển sau khi nghiền đến kích thước nhỏ hơn 25 mm;
c) Các chất thải là gỗ, giấy, bìa được phép đốt và tro được phép thải xuống biển;
d) Nhóm phế liệu để thu hồi, tái chế và nhóm chất thải thông thường còn lại phải thu gom và vận chuyển vào bờ.
4. Phân loại, thu gom và lưu giữ chất thải nguy hại trên công trình dầu khí ngoài khơi:
a) Chất thải nguy hại phải phân loại theo tính chất nguy hại;
b) Các loại chất thải nguy hại có cùng tính chất nguy hại, cùng biện pháp xử lý và không phản ứng với nhau được để chung trong một dụng cụ kín;
c) Dụng cụ chứa chất thải nguy hại phải có nhãn rõ ràng để nhận biết loại chất thải được thu gom.
5. Vận chuyển chất thải về đất liền:
a) Chất thải nguy hại và không nguy hại sau khi được phân loại, lưu trữ riêng trong các thùng chứa (skip) được vận chuyển riêng lẻ hoặc được đặt chung trong công-ten-nơ để đưa về đất liền bằng các tàu dịch vụ;
b) Vận chuyển chất thải bằng các tàu dịch vụ phải tuân thủ các quy định hiện hành về quản lý chất thải nguy hại.
1. Tổ chức dầu khí chỉ sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền nước trong hoạt động khoan thăm dò dầu khí trên biển không phải thực hiện quan trắc môi trường trước và sau khi kết thúc khoan thăm dò.
2. Đối với hoạt động khoan thăm dò dầu khí có sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước ở khu vực cách bờ nhỏ hơn 3 hải lý và khu vực nhạy cảm môi trường phải thực hiện quan trắc môi trường nền 01 lần trước khi thực hiện chương trình khoan thăm dò và 01 lần trong thời gian 01 năm kể từ khi kết thúc hoạt động khoan thăm dò.
3. Quan trắc môi trường trong hoạt động khoan phát triển mỏ:
Tổ chức dầu khí trong hoạt động khoan phát triển mỏ phải thực hiện quan trắc môi trường như sau:
a) Quan trắc môi trường công trình hoặc cụm công trình: thực hiện quan trắc môi trường nền 01 lần trước khi tiến hành các hoạt động khoan phát triển và khai thác mỏ; quan trắc môi trường 01 lần trong thời gian 01 năm kể từ thời điểm thu được dòng dầu hoặc khí thương mại đầu tiên từ mỏ. Thực hiện chương trình quan trắc định kỳ 3 năm/lần tính từ thời điểm thực hiện chương trình quan trắc môi trường đầu tiên sau khoan phát triển mỏ;
b) Quan trắc môi trường đường ống chính dẫn dầu hoặc dẫn khí: thực hiện quan trắc môi trường nền 01 lần trước khi lắp đặt; không phải thực hiện quan trắc môi trường định kỳ, trừ trường hợp xảy ra rò rỉ, cháy, nổ.
4. Địa điểm, vị trí, thời gian, tần suất, thông số quan trắc thực hiện theo quy định tại Phụ lục 2 của Thông tư này.
5. Trong thời hạn một trăm hai mươi ngày (120) ngày, kể từ ngày kết thúc đợt quan trắc, tổ chức dầu khí gửi Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường, Sở Tài nguyên và Môi trường nơi có hoạt động dầu khí: 01 bản in báo cáo quan trắc đợt và 01 đĩa CD báo cáo kết quả quan trắc.
Điều 6. Tổ chức thực hiện và điều khoản thi hành
1. Thông tư này có hiệu lực thi hành kể từ ngày 20 tháng 7 năm 2015.
2. Tổng cục Môi trường có trách nhiệm hướng dẫn, kiểm tra việc thực hiện Thông tư này.
3. Trong quá trình thực hiện Thông tư này nếu phát sinh những khó khăn, vướng mắc, các Bộ, ngành, địa phương, tổ chức, cá nhân kịp thời phản ánh về Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường để tổng hợp, trình Bộ trưởng xem xét, quyết định./.
|
Nơi nhận: |
KT.BỘ TRƯỞNG |
MẪU VĂN BẢN ĐỀ NGHỊ SỬ DỤNG DUNG DỊCH KHOAN NỀN KHÔNG NƯỚC1
(Ban hành kèm theo Thông tư số 22/2015/TT-BTNMT ngày 28 tháng 05 năm 2015 của Bộ trưởng Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường)
|
(Tên tổ chức, cá nhân) |
CỘNG HÒA XÃ HỘI CHỦ NGHĨA VIỆT NAM |
|
Số: |
Địa danh, ngày…tháng …năm … |
Kính gửi: Tổng cục Môi trường
1. Thông tin chung:
Tên tổ chức, cá nhân đề nghị:
Chứng minh thư/hộ chiếu (đối với cá nhân):
Địa chỉ văn phòng:
Điện thoại: Fax:
Loại hình hoạt động:
Tên người liên hệ:
2. Mô tả tóm tắt dự án/hoạt động dự kiến sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước:
3. Thông tin về dung dịch khoan nền không nước đăng ký sử dụng:
3.1. Danh mục đăng ký sử dụng:
|
TT |
Tên dung dịch khoan |
Khối lượng của dung dịch nền bám dính theo mùn khoan thải (ước tính) |
Phương pháp xử lý |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2. Đặc điểm, đặc tính của dung dịch khoan nền không nước dự kiến sử dụng
- Tên thương mại:
- Tên công thức hóa học:
- Phân loại hóa chất:
- Mã SICC:
- Nhà sản xuất:
- Mã hóa chất:
- Đặc điểm lý hóa: (màu sắc, mùi vị, độ nhớt…)
- Thành phần hóa học của dung dịch khoan nền không nước
- Tính chất vật lý của dung dịch khoan nền không nước
4. Phương án sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước:
- Vị trí:
- Thời gian dự kiến:
- Lý do cần phải sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước
- Các kết quả phân tích thử nghiệm tại Việt Nam của dung dịch khoan nền không nước;
- Khối lượng dự kiến sử dụng;
- Cách thức sử dụng và các biện pháp giám sát, giảm thiểu tác động môi trường do việc sử dụng;
- Cam kết thực hiện chương trình giám sát môi trường đối với việc sử dụng dung dịch khoan nền không nước.
5. Danh mục các hồ sơ, giấy tờ đi kèm:
- Bản sao hồ sơ có các thông tin về dung dịch khoan nền không nước của nhà sản xuất;
- Bản gốc các kết quả phân tích thử nghiệm tại Việt Nam của dung dịch khoan nền không nước (đối với trường hợp lần đầu sử dụng tại Việt Nam).
Tôi xin cam đoan rằng những thông tin cung cấp ở trên là đúng sự thật. Đề nghị quý Cơ quan xem xét hồ sơ và đồng ý sử dụng.
|
|
Tổ chức, cá nhân (Ký tên, đóng dấu (nếu có)) |
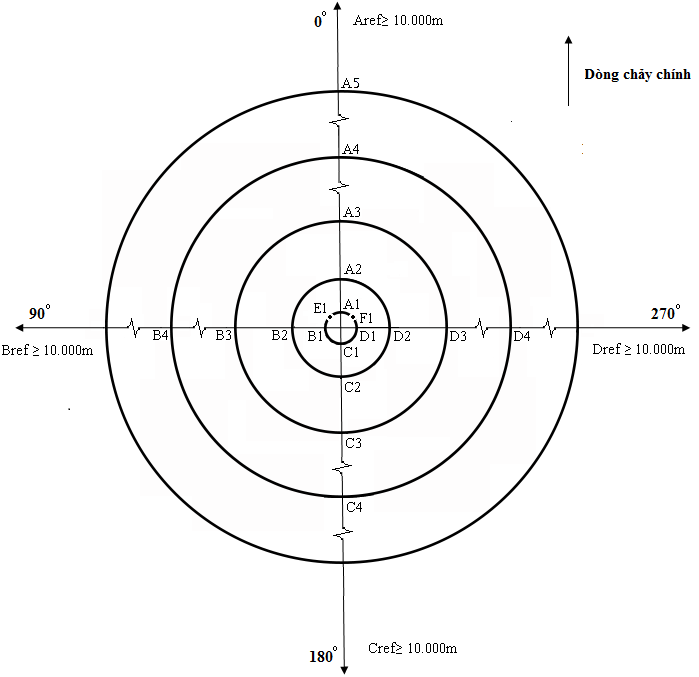
ĐỊA ĐIỂM, THỜI GIAN, TẦN SUẤT, THÔNG SỐ QUAN TRẮC MÔI TRƯỜNG ĐỐI VỚI CÁC HOẠT ĐỘNG DẦU KHÍ NGOÀI KHƠI
(Ban hành kèm theo Thông tư số 22/2015/TT-BTNMT ngày 28 tháng 05 năm 2015 của Bộ trưởng Bộ Tài nguyên và Môi trường)
1. Địa điểm, thời gian, tần suất, thông số quan trắc:
Bảng 1: Tần suất, loại mẫu và vị trí (số lượng) mẫu quan trắc theo từng hoạt động
|
TT |
Hoạt động |
Loại mẫu |
Tần suất |
Các điểm quan trắc, được thể hiện tại Hình 1 và Bảng 2 |
Thông số quan trắc |
|
|
1 |
Khoan thăm dò dung dịch khoan nền nước |
Không cần thực hiện quan trắc môi trường |
||||
|
2 |
Khoan thăm dò bằng dung dịch khoan nền không nước mới |
Quan trắc môi trường trước thăm dò |
Mẫu nước |
01 lần trước khi khoan thăm dò |
A3, B3, C3, D3 |
Quy định tại mục: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
|
Mẫu Trầm tích |
A3, B3, C3, D3 |
Quy định tại mục: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5. |
||||
|
Quan trắc môi trường sau khoan thăm dò |
Mẫu nước |
01 lần sau khi khoan thăm dò |
A1, A2, Aref, C1, Cref, |
Quy định tại mục: 2.2.1, 2.2.2 |
||
|
Mẫu Trầm tích |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 |
Quy định tại mục: 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 2.1.3, 2.1.4, 2.1.5, 2.1.6. |
||||
|
3 |
Khoan phát triển và khai thác mỏ |
Quan trắc môi trường trước khi phát triển và khai thác mỏ |
Mẫu nước |
01 lần trước khi khoan phát triển và khai thác mỏ |
A1, A2, Aref, C1, Cref, |
Quy định tại mục: 2.2.1, 2.2.2 |
|
Mẫu trầm tích |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 |
Quy định tại mục: 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 2.1.3, 2.1.4, 2.1.5, 2.1.6. |
||||
|
Quan trắc môi trường sau khi phát triển và khai thác mỏ |
Mẫu nước |
01 lần đầu sau 1 năm khai thác dòng dầu/khí thương mại đầu tiên, các lần quan trắc sau tiến hành 3 năm/lần |
A1, A2, Aref, B1, Bref, |
Quy định tại mục: 2.2.1, 2.2.2. |
||
|
Mẫu trầm tích |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 Trong trường hợp kết quả THC của mẫu trầm tích đáy ghi nhận tại 1 trong các điểm A1, B1, C1, D1 vượt quá 50 mg/kg khô, cần bổ sung thêm hai điểm quan trắc E và F trong vòng bán kính 250 m.Trong trường hợp có những mỏ có nhiều nguồn thải từ các công trình tương đối gần nhau (cụm các công trình). Khi khoảng cách giữa 2 điểm thuộc 2 mạng lưới lấy mẫu nhỏ hơn 500 m, chỉ cần tiến hành lấy mẫu tại điểm thuộc mạng lưới có khả năng phát sinh lượng thải nhiều hơn. |
Quy định tại mục: 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 2.1.3, 2.1.4, 2.1.5, 2.1.6. |
||||
|
Quan trắc đường ống chính dẫn dầu /khí |
Mẫu nước |
01 lần trước khi lắp đặt |
Ít nhất 03 điểm lấy mẫu đáy bao gồm điểm đầu điểm cuối, bố trí dọc theo tuyến ống, nằm xuôi hướng dòng chảy chiếm ưu thế cách đường ống khoảng 250 m, khoảng cách tối đa giữa các điểm là 20 km |
Quy định tại mục: 2.2.1, 2.2.2 |
||
|
Mẫu trầm tích |
Quy định tại mục: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5; 2.1.6. |
|||||
|
4 |
Hoạt động tháo dỡ công trình dầu khí |
Quan trắc sau tháo dỡ |
Mẫu nước |
01 lần trước tháo dỡ và 01 lần sau khi tháo dỡ xong |
A1, A2, Aref, B1, Bref, |
Quy định tại mục: 2.2.1, 2.2.2. |
|
Mẫu trầm tích |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 |
Quy định tại mục: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5; 2.1.6 |
||||
Hình 1. Sơ đồ mạng lưới các điểm lấy mẫu quan trắc môi trường
Bảng 2. Mạng lưới lấy mẫu trầm tích và mẫu nước biển
(00 là hướng của dòng chảy chính kể từ tâm của hệ trục tỏa tròn)
|
Vị trí |
Khoảng cách kể từ tâm (m) |
00 |
900 |
1800 |
2700 |
450 |
3150 |
Ghi chú |
|
1 |
250 |
A1 |
B1 |
C1 |
D1 |
E1 |
F1 |
|
|
2 |
500 |
A2 |
B2 |
C2 |
D2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
1.000 |
A3 |
B3 |
C3 |
D3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
2.000 |
A4 |
B4 |
C4 |
D4 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
4.000 |
A5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Tối thiểu 10.000 |
Aref |
Bref |
Cref |
(Hoặc Dref) |
|
|
Vị trí đối chiếu |
2. Các thông số quan trắc
2.1. Quan trắc trầm tích đáy
2.1.1. Đặc điểm trầm tích đáy: Mô tả bề mặt trầm tích đáy, các loài động vật sống, màu sắc, mùi (nếu có).
2.1.2. Tổng hàm lượng vật chất hữu cơ (TOM)
2.1.3. Phân bố độ hạt, nhiệt độ, độ ẩm, pH, Eh hoặc ORP
2.1.4. Hydrocacbon và dung dịch khoan nền không nước
- Tổng hàm lượng hydrocacbon (THC)
- Hàm lượng của 16 hydrocacbon thơm đa vòng (tại Bảng 3) và các đồng đẳng alkyl C1 – C3 của chúng (NPD) được phân tích tại tất cả điểm thuộc vòng 250 m, một điểm thuộc vòng 1.000 m, các điểm đối chiếu và các điểm khi có hàm lượng THC lớn hơn 50 mg/kg khô.
2.1.5. Kim loại nặng
- Phân tích các kim loại As, Ba, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn và Hg.
2.1.6. Quần xã động vật đáy (quy định tại Bảng 4)
- Số loài trên diện tích lấy mẫu 0,5 m2 (ở mỗi điểm lấy mẫu);
- Mật độ (số cá thể/đơn vị diện tích) quy về diện tích 1,0 m2 (ở mỗi trạm lấy mẫu);
- Danh sách đầy đủ các loài; hoặc các cấp độ phân loại tới mức thấp nhất có thể (giống, họ, bộ…) trong trường hợp không thể định danh được đến mức loài;
- Bảng danh mục các loài chiếm ưu thế ở mỗi điểm lấy mẫu;
- Tính đa dạng, được thể hiện bằng chỉ số đa dạng sinh học (Chỉ số Shannon Wiener) - Hs trên cơ sở log2;
- Chỉ số tương đồng Pielou (J);
- Chỉ số Hulbert ES100 khi số cá thể lớn hơn 100.
2.2. Quan trắc chất lượng môi trường nước
2.2.1. Các thông số đo đạc tại hiện trường
Nhiệt độ, pH, hàm lượng oxy hòa tan (DO), độ mặn.
2.2.2. Các thông số phân tích trong phòng thí nghiệm
Tổng cacbon hữu cơ (TOC), tổng hydrocacbon (THC), tổng chất rắn lơ lửng (TSS), Zn, Hg, Cd, tổng Cr, Cu, As, Pb và Ba.
Bảng 3. Danh mục 16 hydrocacbon thơm đa vòng (PAH)
|
STT |
Tên hợp chất |
|
1 |
Acenaphthene |
|
2 |
Acenaphthylene |
|
3 |
Anthracene |
|
4 |
Benzo (a) anthracene |
|
5 |
Benzo (a) pyrene |
|
6 |
Benzo (b) fluoranthene |
|
7 |
Benzo (ghi) perylene |
|
8 |
Benzo (k) fluoranthene |
|
9 |
Chrysene |
|
10 |
Dibenzo (a,h) anthracene |
|
11 |
Fluoranthene |
|
12 |
Fluorene |
|
13 |
Indeno (1,2,3-cd) pyrene |
|
14 |
Naphthalene |
|
15 |
Phenanthrene |
|
16 |
Pyrene |
Bảng 4. Đánh giá mức độ đa dạng của quần xã động vật đáy
|
Đa dạng động vật đáy Hs = 1 – 5 (Theo chỉ số đa dạng Shannon Weiner) |
|
|
Hs = 0 – 0,99 |
1 |
|
Hs = 1 – 1,99 |
2 |
|
Hs = 2 – 2,99 |
3 |
|
Hs = 3 – 3,99 |
4 |
|
Hs >4 |
5 |
|
THE MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT |
THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No. 22/2015/TT-BTNMT |
Hanoi, May 28, 2015 |
STIPULATING THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION IN THE PROCESS OF USING DRILLING FLUIDS; WASTE MANAGEMENT AND ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FOR OFFSHORE OIL AND GAS OPERATIONS
Pursuant to the Law on Environmental Protection adopted in 2014;
Pursuant to the Law on Petroleum adopted in 1993; the Law on Amendment and Supplementation to the Law on Petroleum adopted in 2000; the Law on Amendment and Supplementation to the Law on Petroleum adopted in 2008;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 21/2013/NĐ-CP dated March 4, 2013 on defining the functions, tasks, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment;
After considering the request made by the Director of the General Department of Environment and the Director of the Department of Legal Affairs;
The Minister of Natural Resources and Environment hereby provides regulations on the environmental protection in the process of using drilling fluids; waste management and environmental monitoring for offshore oil and gas operations,
Article 1. Scope of application and applicable entities
1. This Circular provides regulations on the environmental protection in the process of using drilling fluids; waste management and environmental monitoring for offshore oil and gas operations.
2. This Circular shall apply to the environment administration agency, organization or individual engaged in gas and oil-related operations within territorial waters, exclusive economic zones and continental shelves of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Article 2. Interpretation of terms
Terms used herein shall be construed as follows:
1. Offshore oil and gas operations refer to exploration, extraction, transportation, storage and processing of gas and oil as well as rendering of other technical services directly related to these operations which take place on the sea.
2. Petroleum organization refers to any individual or organization carrying out oil and gas operations on the sea in accordance with legal regulations.
3. Oil and gas facilities refer to a wide range of mobile or fixed drilling rigs, works, equipment and other structures used for offshore oil and gas operations.
4. Drilling fluid refers to circulated fluids used in the process of oil and gas exploration and extraction drilling in order to remove drill cuttings from drilled wells and control formation pressures, cool and lubricate drill bits, transmit hydraulic energy to drill bits, seal permeable formations and maintain well bores.
5. Water - based drilling fluid – WBDF refers to the drilling mud containing water as the continuous phase and other additives.
6. Non – aqueous drilling fluid – NADF refers to the drilling mud containing the synthetic oil as the continuous phase and other additives.
7. Food waste refers to leftovers generated during daily activities that occur on drilling rigs and extraction rigs and aboard ships.
8. Environmentally sensitive area includes natural sanctuaries, national parks, museums, world heritage sites, biosphere reserves and scenic beauty sites which have been ranked.
9. MARPOL convention or MARPOL 73/78 is short for the International Convention for the prevention of marine pollution from ships.
Article 3. Using non – aqueous drilling fluids
1. Non-aquerous drilling fluids are used as a replacement for water-based drilling fluids to aid the technically difficult drilling of boreholes, including one of the following circumstances:
a) Drilling through geological layers which are complex and exposed to a lot of risks such as easy corrosion, drill suspension, drilling fluid loss and well blowout;
b) Dealing with problems that may arise during the drilling process;
c) Providing flow assurance.
2. Vietnam Environment Administration shall consider and permit non-aquerous drilling fluids to be used in specific situations.
3. Before using non-aquerous drilling fluids, the oil and gas organization shall file application for use of non-aquerous drilling fluids to the division for administrative receipt and result response affiliated to the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. This application includes the following documents:
a) Application for use of non-aquerous drilling fluids in which the reasons why they have to use these non-aquerous drilling fluids, plans to use or treat such fluids as well as controlling measures by completing the form given in the Appendix 1 hereof;
b) If non-aquerous drilling fluids are used for the first time in Vietnam, documentation submitted to apply for permission to use non-aquerous drilling fluids must include the original of the analysis result as prescribed in the national technical regulations on discharge of drilling fluids and drilling cuttings from offshore oil and gas facilities. Tests conducted in Vietnam’s environmental conditions in laboratory rooms of which the conformity to accepted standards for environmental monitoring service has been accredited by the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, or in those which achieve the quality standard;
c) Other documents relating to non-aquerous drilling fluids (if available);
d) Within 03 (three) working days from the receipt of all necessary documents, Vietnam Environment Administration shall be responsible for advising organizations or individuals to improve their documentation if their submitted documents are insufficient or illegitimate in accordance with regulations;
dd) Within 10 (ten) working days from the receipt of all sufficient and valid documents, Vietnam Environment Administration shall confer with the General Department of Vietnam’s Sea and Islands on applications for use of non-aquerous drilling fluids; review these applications, opinions from the General Department of Vietnam’s Sea and Islands and respond in writing to petroleum organizations with use of non-aquerous drilling fluids. The written response must clearly state consent or refusal.
4. Vietnam Environment Administration shall compile, post and update the list of non-aquerous drilling fluids which have been approved for use on their website.
5. Petroleum organizations, when using non-aquerous drilling fluids, must stick to the plan approved by environmental administration agencies, and send a report on the process of using non-aquerous drilling fluids to Vietnam Environment Administration within a maximum of 30 days after each time such fluids are used.
1. Effluents discharged from offshore oil and gas extraction facilities shall be treated and disposed of in compliance with the national technical regulation on effluents discharged from offshore oil and gas extraction facilities.
2. Other sources of effluents coming from offshore oil and gas extraction facilities shall be collected, treated and disposed of in accordance with regulations given in the Table 1 hereof.
Table 1:
Requirements for collection, treatment and disposal of effluents discharged from offshore oil and gas extraction facilities
|
No. |
Discharge position |
Effluent discharge source |
Requirement |
|
1 |
Less than 03 (three) nautical miles away from the shore |
Water used for cleaning machinery, equipment and oil hold. |
Collection, treatment and disposal in conformity with national technical regulations on industrial effluent wastewater |
|
Domestic wastewater |
Collection, treatment and disposal in conformity with national technical regulations on domestic wastewater |
||
|
2 |
From 03 (three) to 12 (twelve) nautical miles away from the shore |
Water used for cleaning machinery, equipment and oil hold. |
Collection, treatment, disposal and certificate of oil pollution prevention in compliance with requirements stipulated in the Appendix I given in the MARPOL convention. |
|
Domestic wastewater |
Collection, treatment, disposal and certificate of domestic wastewater pollution prevention in compliance with requirements stipulated in the Appendix IV given in the MARPOL convention. |
||
|
3 |
More than 12 (twelve) nautical miles away from the shore |
Water used for cleaning machinery, equipment and oil hold. |
Collection, treatment in conformity with the maximum oil content of 15 mg/l before discharge into the sea. |
|
Domestic wastewater |
Collection and discharge into the sea. |
3. Classification, collection, storage and management of wastes without harm to offshore oil and gas extraction facilities:
a) Common domestic and industrial solid wastes are collected and classified into 03 groups, including food wastes, waste materials for reuse or recycling and the rest of normal wastes;
b) Waste food before being dumped into the sea must be ground into objects with less than 25 mm in size;
c) Wastes being items made from wood, paper or cartons are burned to ash before being discharged into the sea;
d) Waste materials for reuse or recycling and the rest of normal wastes must be collected and carried ashore.
4. Classification, collection, storage of hazardous wastes within offshore oil and gas extraction facilities:
a) Hazardous wastes must be classified by the nature of hazard;
b) Hazardous wastes with the same nature of hazard, the same treatment method and without producing reactions, must be stored in the same sealed instrument;
c) Instruments containing hazardous wastes must have clear labels that help to distinguish which types of wastes have been collected.
5. Carriage of wastes to the mainland:
a) Hazardous and non-hazardous wastes, after being classified, stored in skips shall be separately transported or grouped into the same container to carry them to the mainland by service vessels;
b) Transportation of wastes by service vessels must conform to applicable laws on hazardous waste management.
Article 5. Environmental monitoring
1. Petroleum organizations are only allowed to use water-based drilling fluids in offshore oil and gas exploration drilling operations that do not require the environmental monitoring before and after completion of such exploration drilling.
2. As for oil and gas exploration drilling operations using non-aquerous drilling fluids in the waters which are 3 nautical miles away from the shore and environmentally sensitive area, the background environmental monitoring must be performed once before each exploration drilling and once within 01 year from completion of such exploration drilling.
3. Environmental monitoring for development stage drilling:
During the development stage drilling process, petroleum organizations must perform environmental monitoring as follows:
a) Environmental monitoring for a facility or a complex of facilities: the background environmental monitoring is performed once before the commencement of development and extraction drilling; once within 01 year from the time of gaining the first commercial oil or gas flow. Executing the environmental monitoring program on a triennial basis that begins on the time of commencing the first environmental monitoring program in the post-development drilling stage;
b) Environmental monitoring for main oil or gas pipeline: performing once before installation; requiring none of periodic environmental monitoring, except when leakage, fire or explosion occurs.
4. Monitoring area, position, time, frequency and parameter shall be governed by regulations laid down in the Appendix 2 hereof.
5. Within one hundred twenty (120) days from the date on which one monitoring is completed, the petroleum organization shall provide the Ministry and the Department of Natural Resources and Environment where oil and gas operations occur with 01 printed report of one monitoring and 01 CD of monitoring result report.
Article 6. Implementation and implementary provisions
1. This Circular shall come into force from July 20, 2015.
2. Vietnam Environment Administration shall be responsible for providing guidance on and inspecting implementation of this Circular.
3. In the course of implementation, if there is any difficulty that may arise, Ministries, departments and local authorities, organizations or individuals, should send timely feedbacks to the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment for the purpose of compiling a general report for submission to the Minister for consideration and decision./.
|
|
PP. THE MNISTER |
APPLICATION FORM FOR USE OF NON-AQUEROUS DRILLING FLUIDS
(Issued together with the Circular No. 22/2015/TT-BTNMT of the Minister of Natural Resources and Environment dated May 28, 2015)
|
(Name of applicant) |
THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No.: |
……….., date…… … |
Dear Vietnam Environment Administration,
1. General information:
Name of applicant:
ID card/Passport number (applicable to individual):
Office address:
Telephone: Fax:
Scope of operations:
Contact person:
2. Brief description of project/ proposed activities using non-aquerous drilling fluids:
3. Information about non-aquerous drilling fluids to be registered for use:
3.1. List of fluids to be registered for use:
|
No. |
Name of drilling fluids |
Weight of base fluid adhering to drilling cuttings (estimated) |
Treatment method |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2. Characteristics and features of non-aquerous drilling fluids proposed for use
- Commercial name:
- Chemical formula name:
- Chemical classification:
- SICC code:
- Manufacturer:
- Chemical code:
- Physicochemical characteristics: (color, odor, viscosity, etc.)
- Chemical ingredients of non – aqueous drilling fluid
- Physical properties of non – aqueous drilling fluid
4. Plan to use non – aqueous drilling fluid:
- Location:
- Proposed time:
- Reasons for using non – aqueous drilling fluids
- Result of non-aquerous drilling fluid testing and analysis conducted in Vietnam;
- Proposed use weight;
- Manners of use and methods for supervision and minimization of environmental impacts due to use of such fluid;
- Commitment to executing environmental control program for use of non-aquerous drilling fluids.
5. List of attached documents:
- Copy of manufacturer’s documentation containing information about non-aquerous drilling fluids;
- Original copy of the result of testing and analysis of non-aquerous drilling fluid conducted in Vietnam (applicable to those used in Vietnam for the first time).
I hereby undertake that the abovementioned information is true and accurate. I would like to ask for your kind consideration and permission to use such fluid.
|
|
Name of applicant (Signature and seal (if available)) |
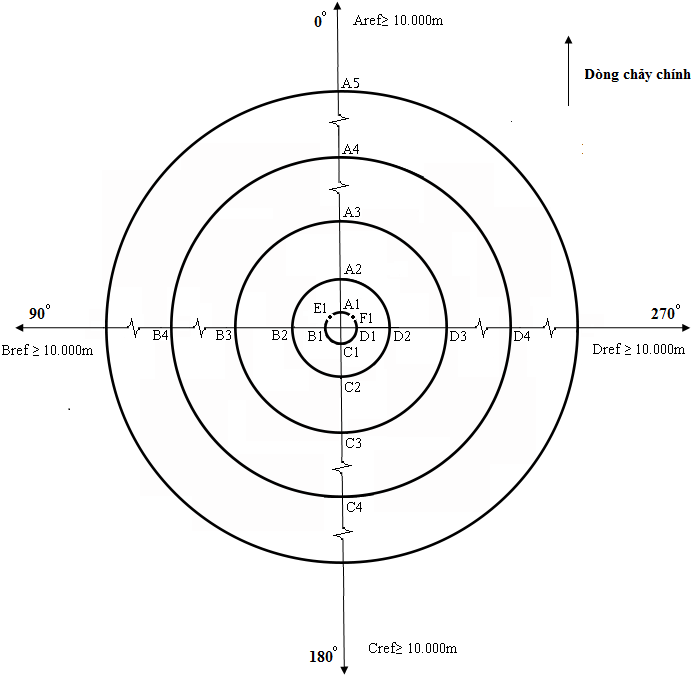
LOCATION, TIME, FREQUENCY AND PARAMETERS OF ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FOR OFFSHORE OIL AND GAS OPERATIONS
(Issued together with the Circular No. 22/2015/TT-BTNMT of the Minister of Natural Resources and Environment dated May 28, 2015)
1. Location, time, frequency and parameters environmental monitoring:
Table 1: Frequency, sample type and location (quantity) of environmental monitoring samples by specific operations
|
No. |
Operation |
Sample type |
Frequency |
Environmental monitoring locations shown at Picture 1 and Table 2 |
Parameter |
|
|
1 |
Exploration drilling using water-based drilling fluid |
Environmental monitoring is not required |
||||
|
2 |
Exploration drilling using new non-aquerous drilling fluid |
Pre-exploration environmental monitoring |
Water sample |
Once before the exploration drilling |
A3, B3, C3, D3 |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
|
Sediment sample |
A3, B3, C3, D3 |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5. |
||||
|
Post-exploration environmental monitoring |
Water sample |
Once after the exploration drilling |
A1, A2, Aref, C1, Cref, |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
||
|
Sediment sample |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5, 2.1.6. |
||||
|
3 |
Mine development and extraction drilling |
Environmental monitoring before mine development and extraction |
Water sample |
Once before mine development and extraction drilling |
A1, A2, Aref, C1, Cref, |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
|
Sediment sample |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5, 2.1.6. |
||||
|
Environmental monitoring after mine development and extraction |
Water sample |
For the first time, once after 1 year of first commercial oil or gas flow extraction. Performing the following environmental monitoring on a triennial basis |
A1, A2, Aref, B1, Bref, |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
||
|
Sediment sample |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 If the THC result of bottom sediment sampling at one of A1, B1, C1, D1 positions exceeds 50 dry mg/kg, the environmental monitoring should be additionally conducted at the position E and F within a radius of 250m. As for mines with many sources of discharge from relatively near facilities (a complex of facilities, if the distance between 2 positions within 2 sampling networks is less than 500m, the sampling is only required at the network with greater possibility of generating discharge volume. |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5, 2.1.6. |
||||
|
Environmental monitoring of the main oil or gas pipeline |
Water sample |
Once before installation |
At least 03 bottom sediment sampling positions, including terminal points, points along the piping route, and points along the dominant current which are about 250m away from the main pipeline. The maximum distance between points is 20 km |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
||
|
Sediment sample |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5; 2.1.6. |
|||||
|
4 |
Oil and gas facility demolition |
Post-demolition environmental monitoring |
Water sample |
Once before demolition and once after completion of demolition |
A1, A2, Aref, B1, Bref, |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.2.1; 2.2.2. |
|
Sediment sample |
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Aref, B1, B2, B3, B4, Bref, C1, C2, C3, C4, Cref, D1, D2, D3, D4 |
Stipulated in paragraphs: 2.1.1; 2.1.2; 2.1.3; 2.1.4; 2.1.5; 2.1.6. |
||||
Picture 1. Diagram of network of sampling points for the environmental monitoring
Table 2. Network of sediment and seawater sampling
(00 means the main current flowing from the radial symmetry center)
|
Position |
Distance from the center (m) |
00 |
900 |
1800 |
2700 |
450 |
3150 |
Note |
|
1 |
250 |
A1 |
B1 |
C1 |
D1 |
E1 |
F1 |
|
|
2 |
500 |
A2 |
B2 |
C2 |
D2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
1,000 |
A3 |
B3 |
C3 |
D3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
2,000 |
A4 |
B4 |
C4 |
D4 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
4,000 |
A5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Not less than 10,000 |
Aref |
Bref |
Cref |
(Or Dref) |
|
|
Reference position |
2. Environmental monitoring parameters
2.1. Bottom sediment monitoring
2.1.1. Characteristics of bottom sediments: Description of the uppermost layer of bottom sediment, living animals, color and odor (if any).
2.1.2. Total organic matter (TOM)
2.1.3. Particle density, temperature, humidity, pH, Eh or ORP
2.1.4. Hydrocarbon and non-aquerous drilling fluid
- Total hydrocarbons (THC)
- Content of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (at Table 3) and its C1 - C3 alkyl homologs (NPD) are alanyzed at all points inside the circle of 250 m, one point inside the circle of 1,000m, reference points and points where THC content is greater than 50 dry mg/kg.
2.1.5. Heavy metal
- Analysis of metals such as As, Ba, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn and Hg.
2.1.6. Benthic communities (stipulated at Table 4)
- A number of species on a sampling area of 0.5 m2 (at each sampling point);
- Density (a number of individuals/an area unit) converted into an area of 1.0 m2 (defined at each sampling station);
- Comprehensive list of species; or lowest possible taxonomy (genus, order, family, etc), in case it is impossible to define species in the nomenclature;
- List of dominant species at each sampling point;
- Diversity shown by biodiversity index (Shannon Wiener index) - log2 – based coefficient;
- Pielou’s evenness index (J);
- Hulbert index, when a number of individuals are greater than 100.
2.2. Monitoring of water environment quality
2.2.1. Parameters defined at the monitoring position
Temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen content and salinity.
2.2.2. Parameters defined inside the laboratory room
Total organic carbons (TOC), total hydrocarbons (THC), total suspended solids (TSS), Zn, Hg, Cd, total Cr, Cu, As, Pb and Ba.
Table 3. List of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH)
|
No. |
Name of compounds |
|
1 |
Acenaphthene |
|
2 |
Acenaphthylene |
|
3 |
Anthracene |
|
4 |
Benzo (a) anthracene |
|
5 |
Benzo (a) pyrene |
|
6 |
Benzo (b) fluoranthene |
|
7 |
Benzo (ghi) perylene |
|
8 |
Benzo (k) fluoranthene |
|
9 |
Chrysene |
|
10 |
Dibenzo (a,h) anthracene |
|
11 |
Fluoranthene |
|
12 |
Fluorene |
|
13 |
Indeno (1,2,3-cd) pyrene |
|
14 |
Naphthalene |
|
15 |
Phenanthrene |
|
16 |
Pyrene |
Table 4. Assessment of diversity of benthic communities
|
Benthic diversity coefficient = 1 – 5 (Based on Shannon Weiner’s biodiversity index) |
|
|
Coef = 0 – 0.99 |
1 |
|
Coef = 1 – 1.99 |
2 |
|
Coef = 2 – 2.99 |
3 |
|
Coef = 3 – 3.99 |
4 |
|
Coef >4 |
5 |

 Thông tư 22/2015/TT-BTNMT quản lý chất thải quan trắc môi trường hoạt động dầu khí trên biển (Bản Pdf)
Thông tư 22/2015/TT-BTNMT quản lý chất thải quan trắc môi trường hoạt động dầu khí trên biển (Bản Pdf)
 Thông tư 22/2015/TT-BTNMT quản lý chất thải quan trắc môi trường hoạt động dầu khí trên biển (Bản Word)
Thông tư 22/2015/TT-BTNMT quản lý chất thải quan trắc môi trường hoạt động dầu khí trên biển (Bản Word)